MUI o Material-UI es una biblioteca de interfaz de usuario que proporciona componentes robustos y personalizables predefinidos para React para facilitar el desarrollo web. El diseño de MUI se basa en la parte superior de Material Design de Google.
En este artículo, discutiremos la API React MUI TabList . Las pestañas se utilizan para que la navegación sea más fácil y útil. Podemos cambiar fácilmente entre las vistas. TabList contiene la lista de pestañas. La API proporciona muchas funcionalidades y aprenderemos a implementarlas.
Importar API TabList:
import TabList from '@mui/lab/TabList';
// or
import { TabList } from '@mui/lab';
Lista de accesorios: aquí está la lista de diferentes accesorios utilizados con este componente. Podemos acceder a ellos y modificarlos según nuestras necesidades.
- children (Node): Es un componente similar a la fila de la tabla.
- clases (Objeto): reemplaza los estilos existentes o agrega nuevos estilos al componente.
- componente (elementType): Es el componente utilizado para el Node raíz. Puede ser una string HTML o un componente.
- sx (Array<func/objeto/bool>/func/objeto): La propiedad del sistema permite definir anulaciones del sistema, así como estilos CSS adicionales.
Sintaxis: Cree una TabList de la siguiente manera:
<TabListonChange={handleChange}>
<Tab label="Tutorial 1" value="1" />
</TabList>
Instalar y crear la aplicación React y agregar las dependencias de MUI:
Paso 1: Cree un proyecto de reacción usando el siguiente comando.
npx create-react-app gfg_tutorial
Paso 2: Entrar en el directorio del proyecto
cd gfg_tutorial
Paso 3: instale las dependencias de MUI de la siguiente manera:
npm install @mui/material @emotion/react @emotion/styled @mui/lab
Paso 4: Ejecute el proyecto de la siguiente manera:
npm start
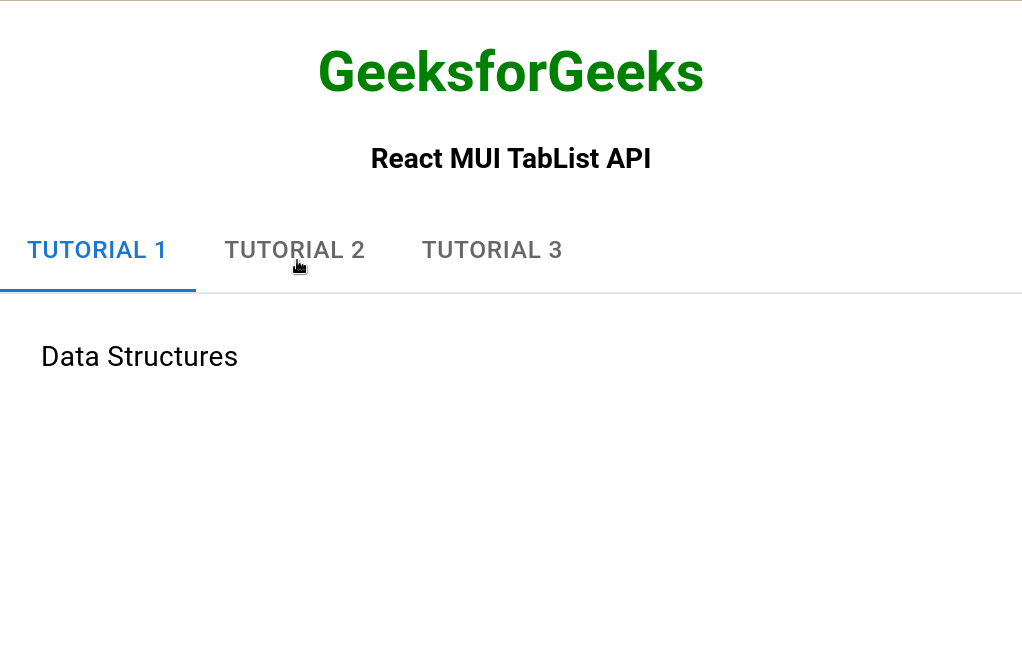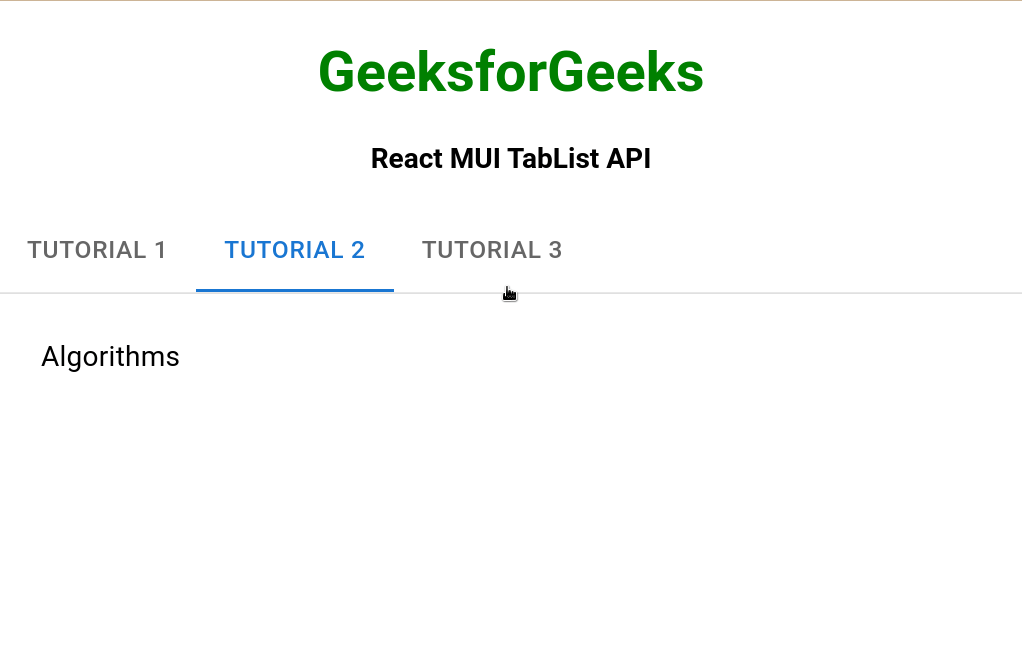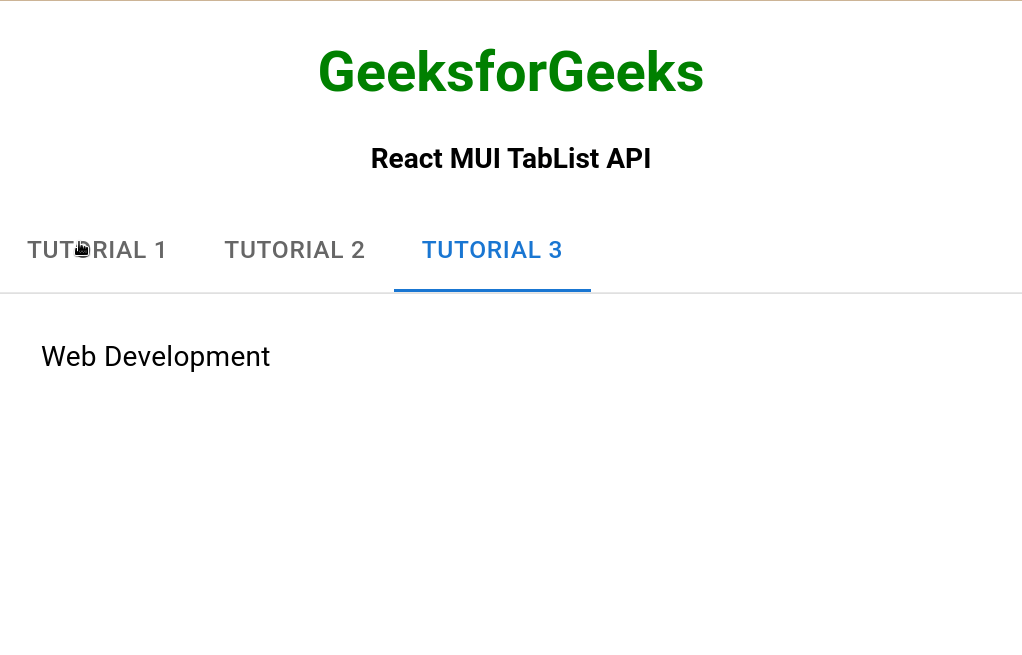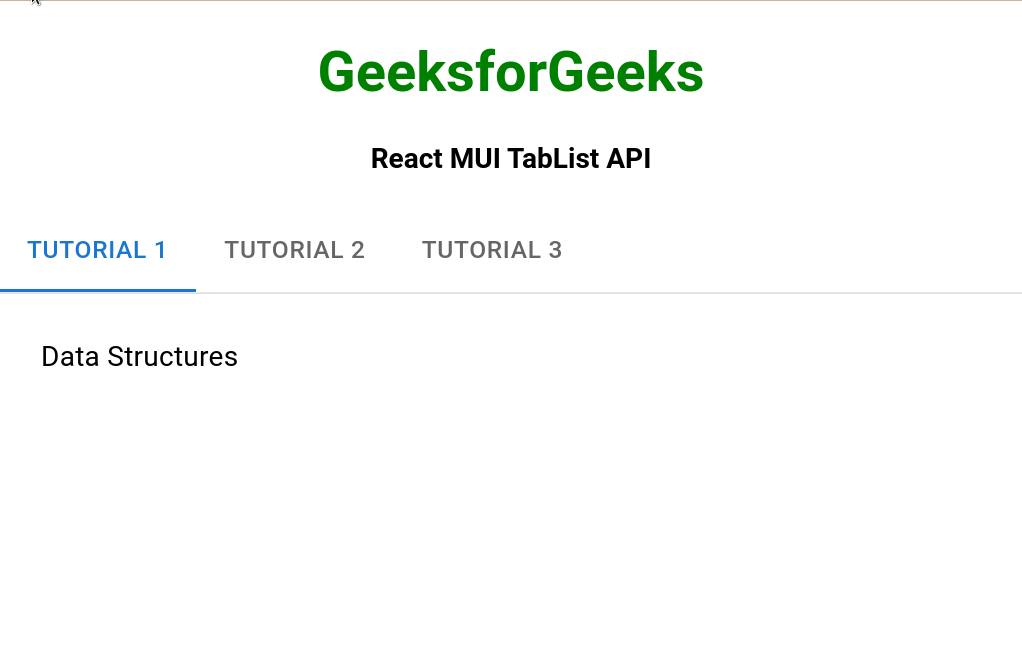
Ejemplo 1: En el siguiente ejemplo, tenemos una TabList que muestra diferentes pestañas.
App.js
import "./App.css";
import * as React from "react";
import Box from "@mui/material/Box";
import Tab from "@mui/material/Tab";
import TabContext from "@mui/lab/TabContext";
import TabList from "@mui/lab/TabList";
import TabPanel from "@mui/lab/TabPanel";
function App() {
const [value, setValue] = React.useState("1");
const handleChange = (event, newValue) => {
setValue(newValue);
};
return (
<div className="App">
<div
className="head"
style={{
width: "fit-content",
margin: "auto",
}}
>
<h1
style={{
color: "green",
}}
>
GeeksforGeeks
</h1>
</div>
<div
style={{
width: "fit-content",
margin: "auto",
}}
>
<strong>React MUI TabList API</strong>
</div>
<br />
<div
style={{
margin: "auto",
display: "flex",
justifyContent: "space-evenly",
}}
>
<Box sx={{ width: "100%", typography: "body1" }}>
<TabContext value={value}>
<Box sx={{ borderBottom: 1, borderColor: "divider" }}>
<TabList
onChange={handleChange}
>
<Tab label="Tutorial 1" value="1" />
<Tab label="Tutorial 2" value="2" />
<Tab label="Tutorial 3" value="3" />
</TabList>
</Box>
<TabPanel value="1">Data Structures</TabPanel>
<TabPanel value="2">Algorithms</TabPanel>
<TabPanel value="3">Web Development</TabPanel>
</TabContext>
</Box>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Producción:
Ejemplo 2: En el siguiente ejemplo, han cambiado el color de fondo de las pestañas.
App.js
import "./App.css";
import * as React from "react";
import Box from "@mui/material/Box";
import Tab from "@mui/material/Tab";
import TabContext from "@mui/lab/TabContext";
import TabList from "@mui/lab/TabList";
import TabPanel from "@mui/lab/TabPanel";
function App() {
const [value, setValue] = React.useState("1");
const handleChange = (event, newValue) => {
setValue(newValue);
};
return (
<div className="App">
<div
className="head"
style={{
width: "fit-content",
margin: "auto",
}}
>
<h1
style={{
color: "green",
}}
>
GeeksforGeeks
</h1>
</div>
<div
style={{
width: "fit-content",
margin: "auto",
}}
>
<strong>React MUI TabList API</strong>
</div>
<br />
<div
style={{
margin: "auto",
display: "flex",
justifyContent: "space-evenly",
}}
>
<Box sx={{ width: "100%", typography: "body1" }}>
<TabContext value={value}>
<Box sx={{ borderBottom: 1, borderColor: "divider" }}>
<TabList
sx={{
backgroundColor: "lightGreen",
}}
onChange={handleChange}
>
<Tab label="Tutorial 1" value="1" />
<Tab label="Tutorial 2" value="2" />
<Tab label="Tutorial 3" value="3" />
</TabList>
</Box>
<TabPanel value="1">Data Structures</TabPanel>
<TabPanel value="2">Algorithms</TabPanel>
<TabPanel value="3">Web Development</TabPanel>
</TabContext>
</Box>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Producción:

Referencia: https://mui.com/material-ui/api/tab-panel/
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por RajeevSarkar y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA