CRUD significa Crear, Leer/Recuperar, Actualizar y Eliminar y estas son las cuatro operaciones básicas que realizamos en el almacenamiento persistente. CRUD está orientado a datos y al uso estandarizado de métodos HTTP. HTTP tiene algunos métodos que funcionan como operaciones CRUD y tenga en cuenta que son muy vitales desde una perspectiva de punto de desarrollo en la programación que también nos ayuda a relacionarnos mejor con el desarrollo web y también nos ayuda cuando tratamos con bases de datos. Entonces, las operaciones CRUD estándar son las siguientes:
- POST : crea un nuevo recurso
- GET : lee/recupera un recurso
- PUT : Actualiza un recurso existente
- DELETE : Elimina un recurso
Para ilustrar las operaciones CRUD sobre el programa Student Management, consideremos que estamos creando un programa MENU DRIVER que tendrá una lista de estudiantes. La lista contendrá el objeto de estudiante que contiene los detalles del estudiante. Su menú debe tener 4 operaciones básicas como Agregar, Buscar, Eliminar y Mostrar detalles del estudiante.
Implementación:
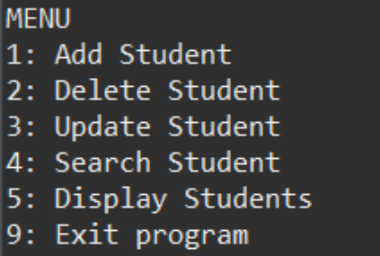
Menú
Las tareas a operar son las siguientes:
Cree un sistema de gestión de registros de estudiantes que pueda realizar las siguientes operaciones:
- Insertar registro de estudiante.
- Eliminar registro de estudiante
- Mostrar registro de estudiante
- Buscar registro de estudiante
El registro del estudiante debe contener los siguientes elementos
- Identificación del Estudiante
- Nombre de estudiante
- Número de contacto del estudiante
Vamos a crear los siguientes archivos como se enumeran a continuación:
- StudentRecordLinkedList: para crear el menú, solicite la función para realizar
- StudentRecordManagement: Contiene todas las funciones que hacen la operación.
- Registro: Para almacenar los datos.
A. Archivo: StudentRecordLinkedList.java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate StudentRecordLinkedList Class
package College;
// Importing required classes
import java.util.Scanner;
// Class
public class StudentRecordLinkedList {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating HumanResourceOffice Object.
StudentRecordManagement hr
= new StudentRecordManagement();
Record record = new Record();
.
// Initial Employee record
// Using mutators to had code the data
record.setIdNumber(6862);
record.setContactNumber(911);
record.setName("Ankit");
// Calling add() record method to
// add static data/(Hard CodedData) to linked List
hr.add(record);
// Creating Scanner Object to read input
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// Creating option integer variable
int option = 0;
// Do - While loop
do {
menu();
option = input.nextInt();
// Switch case
switch (option) {
// Case 1
case 1:
// Display message
System.out.print(
"What is the Student id Number ? ");
int idNumber = input.nextInt();
// Display message
System.out.print(
"What is the Student contact Number ? ");
int contactNumber = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
// Display message
System.out.print(
"What is the Student Name ? ");
String name = input.nextLine();
// Create record object and pass constructor
// parameters.
record = new Record(name, idNumber,
contactNumber);
// Call add() record
hr.add(record);
System.out.println(record.toString());
// Break statement used to terminate program
// from here only once it entered this case
break;
// Case 2
case 2:
// Display message
System.out.print(
"What is the Student id number ? ");
int rId = input.nextInt();
// Invoke remove/delete record
hr.delete(rId);
break;
// Case 3
case 3:
// Display message
System.out.print(
"What is the Student id number? ");
int rIdNo = input.nextInt();
hr.update(rIdNo, input);
break;
// Case 4
case 4:
// Display message
System.out.print(
"What is the Student id ? ");
int bookId = input.nextInt();
if (!hr.find(bookId)) {
System.out.println(
"Student id does not exist\n");
}
break;
// Case 5
case 5:
hr.display();
break;
// Case 6
case 9:
// Display message
System.out.println(
"\nThank you for using the program. Goodbye!\n");
System.exit(0);
break;
// Case 7: Default case
// If none above case executes
default:
// Print statement
System.out.println("\nInvalid input\n");
break;
}
}
// Checking condition
while (option != 9);
}
// Method 2
// Menu - Static menu for displaying options
public static void menu()
{
// Printing statements displaying menu on console
System.out.println("MENU");
System.out.println("1: Add Student");
System.out.println("2: Delete Student");
System.out.println("3: Update Student");
System.out.println("4: Search Student");
System.out.println("5: Display Students");
System.out.println("9: Exit program");
System.out.print("Enter your selection : ");
}
}
B. Archivo: StudentRecordManagement.java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate StudentRecordManagement Class
package College;
// Importing required classes
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
// Class
public class StudentRecordManagement {
// Creating an empty LinkedList
LinkedList<Record> list;
// Default Constructor
public StudentRecordManagement()
{
list = new LinkedList<>();
}
// Method 1
// Adding Record
// @param record
public void add(Record record)
{
// Checking if a record already exists or not,
// if not add it to Record list, Otherwise
// error display message
if (!find(record.getIdNumber())) {
list.add(record);
}
else {
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Record already exists in the Record list");
}
}
// Method 2
// Searching Record
// @param idNimber
// @return
public boolean find(int idNimber)
{
// Iterating record list
// using for eacj loop
for (Record l : list) {
// Checking record by id Number
if (l.getIdNumber() == idNimber) {
System.out.println(l);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Method 3
// Delete Record
// @param recIdNumber
public void delete(int recIdNumber)
{
Record recordDel = null;
// Iterating record list
for (Record ll : list) {
// Finding record to be deleted by id Number
if (ll.getIdNumber() == recIdNumber) {
recordDel = ll;
}
}
// If recordDel is null, then show error message,
// otherwise remove the record from Record list
if (recordDel == null) {
// Displaying no record found
System.out.println("Invalid record Id");
}
else {
list.remove(recordDel);
// Display message for successful deletion of
// record
System.out.println(
"Successfully removed record from the list");
}
}
// Method 4
// Finding Record
// @param idNumber
// @return
public Record findRecord(int idNumber)
{
// Iterate Record list
// using for each loop
for (Record l : list) {
// Checking record by id Number.
if (l.getIdNumber() == idNumber) {
return l;
}
}
return null;
}
// Method 5
// Update Record
// @param id
// @param input
public void update(int id, Scanner input)
{
if (find(id)) {
Record rec = findRecord(id);
// Display message only
System.out.print(
"What is the new Student id Number ? ");
int idNumber = input.nextInt();
// Display message only
System.out.print(
"What is the new Student contact Number ");
int contactNumber = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
// Display message only
System.out.print(
"What is the new Student Name ? ");
String name = input.nextLine();
rec.setIdNumber(idNumber);
rec.setName(name);
rec.setContactNumber(contactNumber);
System.out.println(
"Record Updated Successfully");
}
else {
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Record Not Found in the Student list");
}
}
// Method 6
// Display Records
public void display()
{
// If record list is empty then
// print the message below
if (list.isEmpty()) {
// Print statement
System.out.println("The list has no records\n");
}
// Iterating Record list
// using for each loop
for (Record record : list) {
// Printing the list
System.out.println(record.toString());
}
}
}
C. Archivo: Record.java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Record Class
package College;
// Class
public class Record {
// Instance variables
private String name;
private int idNumber;
private int contactNumber;
// Default Constructor
public Record() {}
// Parameterized Constructor
// @param name
// @param idNumber
// @param contactNumber
public Record(String name, int idNumber,
int contactNumber)
{
// this keyword refers to current instance itself
this.name = name;
this.idNumber = idNumber;
this.contactNumber = contactNumber;
}
// Getting the value of contactNumber
// @return the value of contactNumber
public int getContactNumber() { return contactNumber; }
// Set the value of contactNumber
// @param contactNumber new value of contactNumber
public void setContactNumber(int contactNumber)
{
this.contactNumber = contactNumber;
}
// Getting the value of idNumber
// @return the value of idNumber
public int getIdNumber() { return idNumber; }
// Setting the value of idNumber
// @param idNumber new value of idNumber
public void setIdNumber(int idNumber)
{
this.idNumber = idNumber;
}
// Getting the value of name
// @return the value of name
public String getName() { return name; }
// Setting the value of name
// @param name new value of name
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
// toString() Method
// @return
@Override public String toString()
{
// Returning the record
return "Records{"
+ "name=" + name + ", idNumber=" + idNumber
+ ", contactNumber=" + contactNumber + '}';
}
}
Producción:
Agregar

Actualizar

Búsqueda

Monitor

Borrar

Salida

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por dragonuncaged y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA