En este artículo, vamos a crear un contador de dedos usando Computer Vision, OpenCv en Python
Bibliotecas requeridas:
- OpenCV : OpenCV es una biblioteca muy utilizada para el procesamiento de imágenes.
- cvzone: es un paquete de visión por computadora que facilita la ejecución de funciones de procesamiento de imágenes e IA
Para instalar Cvzone, ejecute este comando en la terminal:
pip install cvzone
Implementación paso a paso:
Paso 1: importa las bibliotecas requeridas.
Python3
# import libraries and required classes import cv2 from cvzone.HandTrackingModule import HandDetector
Paso 2: Declare HandDetector y abra la cámara predeterminada para capturar la mano.
Python3
# declaring HandDetector with # some basic requirements detector = HandDetector(maxHands=1, detectionCon=0.8) # it detect only one hand from # video with 0.8 detection confidence video = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
Paso 3: cuenta el número de dedos
Capture los marcos continuamente y detecte la mano del marco, luego detecte cuántos dedos están levantados y cuéntelos. En el mostrador haga las condiciones apropiadas y coloque una imagen de los dedos.
Python3
while True:
# Capture frame-by-frame
_, img = video.read()
img = cv2.flip(img, 1)
# Find the hand with help of detector
hand = detector.findHands(img, draw=False)
# Here we take img by default if no hand found
fing = cv2.imread("Put image path with 0 fingures up")
if hand:
# Taking the landmarks of hand
lmlist = hand[0]
if lmlist:
# Find how many fingers are up
# This function return list
fingerup = detector.fingersUp(lmlist)
# Change image based on
# different-different conditions
if fingerup == [0, 1, 0, 0, 0]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image path of 1\
fingures up")
if fingerup == [0, 1, 1, 0, 0]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image path of 2\
fingures up")
if fingerup == [0, 1, 1, 1, 0]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image path of\
3 fingures up")
if fingerup == [0, 1, 1, 1, 1]:
fing = cv2.imread("sPut image path \
of 4 fingures up")
if fingerup == [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image path \
of 4 fingures and thumbs up")
# Resize the image
fing = cv2.resize(fing, (220, 280))
# Place the image in main frame
img[50:330, 20:240] = fing
# Display the resulting frame
cv2.imshow("Video", img)
Cómo en realidad el detector detecta los dedos hacia arriba o hacia abajo.
- Devuelve la lista de cinco elementos y cada elemento depende de la condición del dedo.
- El orden de la lista como [pulgar, dedo índice, dedo medio, dedo anular, meñique/meñique]
- Si alguno de los dedos está arriba, devuelve 1 para ese valor de índice en particular; de lo contrario, devuelve 0.
- Y después de hacer la lista volverá por la función.
Paso 4: terminar el ciclo
Python3
# Enter key 'q' to break the loop
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# When everything done, release
# the capture and destroy the windows
video.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
A continuación se muestra la implementación completa:
Python3
import cv2
from cvzone.HandTrackingModule import HandDetector
detector = HandDetector(maxHands=1, detectionCon=0.8)
video = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
while True:
_, img = video.read()
img = cv2.flip(img, 1)
hand = detector.findHands(img, draw=False)
fing = cv2.imread("Put image path with 0 fingures up")
if hand:
lmlist = hand[0]
if lmlist:
fingerup = detector.fingersUp(lmlist)
if fingerup == [0, 1, 0, 0, 0]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image \
path of 1 fingures up")
if fingerup == [0, 1, 1, 0, 0]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image \
path of 2 fingures up")
if fingerup == [0, 1, 1, 1, 0]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image \
path of 3 fingures up")
if fingerup == [0, 1, 1, 1, 1]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image \
path of 4 fingures up")
if fingerup == [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]:
fing = cv2.imread("Put image \
path of 4 fingures and thumbs up")
fing = cv2.resize(fing, (220, 280))
img[50:330, 20:240] = fing
cv2.imshow("Video", img)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
video.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Producción :
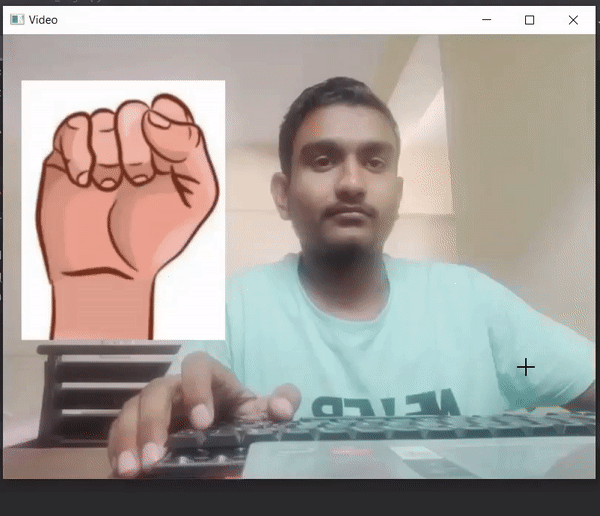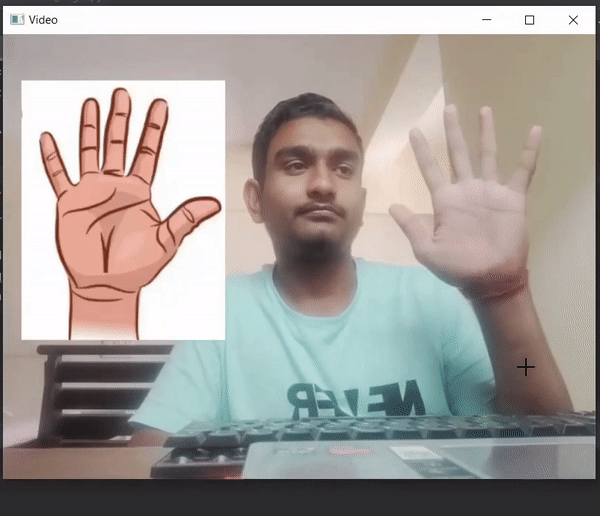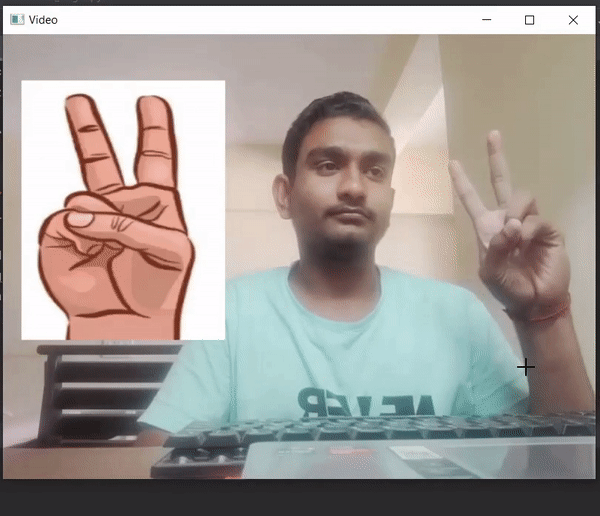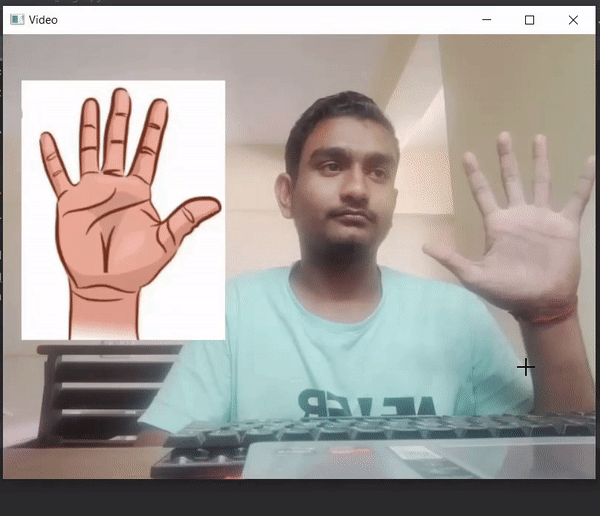
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por darshansol108 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA