Dada una lista enlazada individualmente que contiene n Nodes. El problema es ordenar la lista utilizando la técnica de ordenación por selección recursiva. El enfoque debe ser tal que implique intercambiar enlaces de Nodes en lugar de intercambiar datos de Nodes.
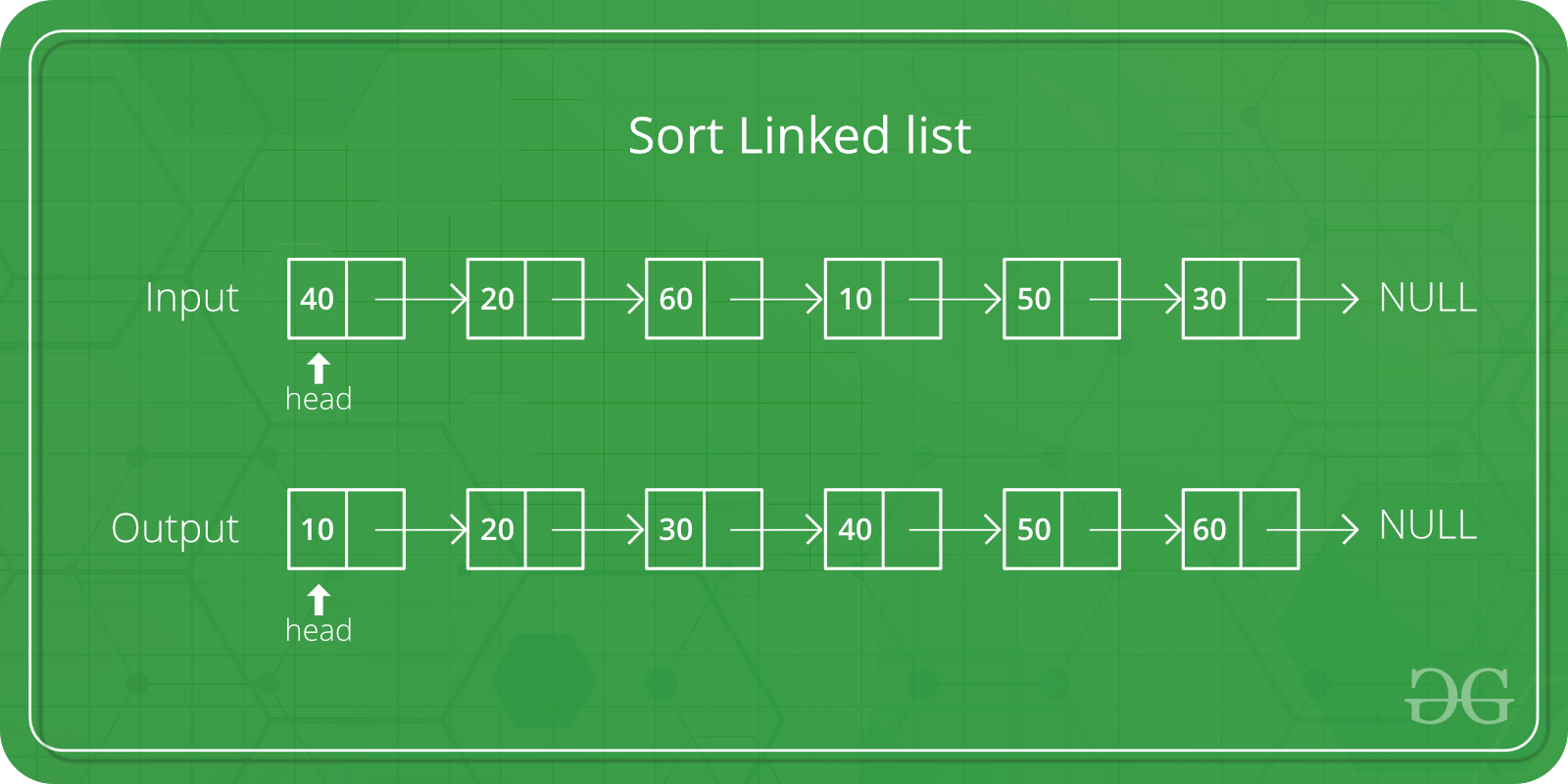
Ejemplos:
Input: 10 -> 12 -> 8 -> 4 -> 6 Output: 4 -> 6 -> 8 -> 10 -> 12
En la clasificación por selección, primero encontramos el elemento mínimo, lo intercambiamos con el Node inicial y recurrimos a la lista restante. A continuación se muestra la implementación recursiva de estos pasos para la lista enlazada.
recurSelectionSort(head)
if head->next == NULL
return head
Initialize min = head
Initialize beforeMin = NULL
Initialize ptr = head
while ptr->next != NULL
if min->data > ptr->next->data
min = ptr->next
beforeMin = ptr
ptr = ptr->next
if min != head
swapNodes(&head, head, min, beforeMin)
head->next = recurSelectionSort(head->next)
return head
swapNodes(head_ref, currX, currY, prevY)
head_ref = currY
prevY->next = currX
Initialize temp = currY->next
currY->next = currX->next
currX->next = temp
swapNodes (head_ref, currX, currY, prevY) se basa en el enfoque discutido aquí , pero se ha modificado en consecuencia para la implementación de esta publicación.
Java
// Java implementation of recursive
// selection sort for singly linked
// list | Swapping node links
class GFG{
// A Linked list node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
// Function to swap nodes 'currX'
// and 'currY' in a linked list
// without swapping data
static Node swapNodes(Node head_ref,
Node currX,
Node currY,
Node prevY)
{
// Make 'currY' as new head
head_ref = currY;
// Adjust links
prevY.next = currX;
// Swap next pointers
Node temp = currY.next;
currY.next = currX.next;
currX.next = temp;
return head_ref;
}
// function to sort the linked list using
// recursive selection sort technique
static Node recurSelectionSort(Node head)
{
// If there is only a single node
if (head.next == null)
return head;
// 'min' - pointer to store the node
// having minimum data value
Node min = head;
// 'beforeMin' - pointer to store
// node previous to 'min' node
Node beforeMin = null;
Node ptr;
// Traverse the list till the
// last node
for (ptr = head; ptr.next != null;
ptr = ptr.next)
{
// If true, then update 'min' and
// 'beforeMin'
if (ptr.next.data < min.data)
{
min = ptr.next;
beforeMin = ptr;
}
}
// If 'min' and 'head' are not same,
// swap the head node with the 'min' node
if (min != head)
head = swapNodes(head, head,
min, beforeMin);
// Recursively sort the remaining list
head.next =
recurSelectionSort(head.next);
return head;
}
// Function to sort the given linked list
static Node sort(Node head_ref)
{
// If list is empty
if ((head_ref) == null)
return null;
// Sort the list using recursive
// selection sort technique
head_ref = recurSelectionSort(head_ref);
return head_ref;
}
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the linked list
static Node push(Node head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list to the
// new node
new_node.next = (head_ref);
// Move the head to point to the
// new node
(head_ref) = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Function to print the linked list
static void printList( Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
// Create linked list 10.12.8.4.6
head = push(head, 6);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 8);
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 10);
System.out.println(
"Linked list before sorting:");
printList(head);
// sort the linked list
head = sort(head);
System.out.print(
"Linked list after sorting:");
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Producción:
Linked list before sorting: 10 12 8 4 6 Linked list after sorting: 4 6 8 10 12
Complejidad temporal: O(n 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n)
Consulte el artículo completo sobre la clasificación de selección recursiva para la lista de enlaces únicos | ¡Intercambio de enlaces de Nodes para obtener más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA