Dadas dos arrays, la tarea de multiplicarlas. Las arrays pueden ser cuadradas o rectangulares.
Ejemplos:
Input : mat1[][] = {{1, 2},
{3, 4}}
mat2[][] = {{1, 1},
{1, 1}}
Output : {{3, 3},
{7, 7}}
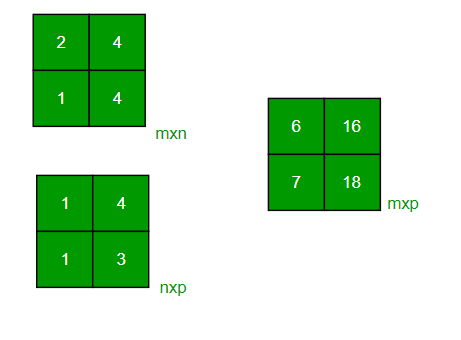
Input : mat1[][] = {{2, 4},
{3, 4}}
mat2[][] = {{1, 2},
{1, 3}}
Output : {{6, 16},
{7, 18}}
Multiplicación de Arrays Cuadradas:
El siguiente programa multiplica dos arrays cuadradas de tamaño 4*4, podemos cambiar N por diferentes dimensiones.
Python3
# 4x4 matrix multiplication using Python3
# Function definition
def matrix_multiplication(M, N):
# List to store matrix multiplication result
R = [[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]]
for i in range(0, 4):
for j in range(0, 4):
for k in range(0, 4):
R[i][j] += M[i][k] * N[k][j]
for i in range(0, 4):
for j in range(0, 4):
# if we use print(), by default cursor moves to next line each time,
# Now we can explicitly define ending character or sequence passing
# second parameter as end ="<character or string>"
# syntax: print(<variable or value to print>, end ="<ending with>")
# Here space (" ") is used to print a gap after printing
# each element of R
print(R[i][j], end =" ")
print("
", end ="")
# First matrix. M is a list
M = [[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 4]]
# Second matrix. N is a list
N = [[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 4]]
# Call matrix_multiplication function
matrix_multiplication(M, N)
# This code is contributed by Santanu
Result matrix is 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40
Complejidad temporal: O(n 3 ). Se puede optimizar utilizando la multiplicación de arrays de Strassen
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n 2 )
Multiplicación de Arrays Rectangulares:
Usamos punteros en C para multiplicar a arrays. Consulte la siguiente publicación como requisito previo del código.
¿Cómo pasar una array 2D como parámetro en C?
Python3
# Python3 program to multiply two # rectangular matrices # Multiplies two matrices mat1[][] # and mat2[][] and prints result. # (m1) x (m2) and (n1) x (n2) are # dimensions of given matrices. def multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2): res = [[0 for x in range(n2)] for y in range (m1)] for i in range(m1): for j in range(n2): res[i][j] = 0 for x in range(m2): res[i][j] += (mat1[ i][x] * mat2[ x][j]) for i in range(m1): for j in range(n2): print (res[i][j], end = " ") print () # Driver code if __name__ == "__main__": mat1 = [[2, 4], [3, 4]] mat2 = [[1, 2], [1, 3]] m1, m2, n1, n2 = 2, 2, 2, 2 # Function call multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2) # This code is contributed by Chitranayal
6 16 7 18
Complejidad temporal: O(n 3 ). Se puede optimizar utilizando la multiplicación de arrays de Strassen
Espacio Auxiliar: O(m1 * n2)
Consulte el artículo completo sobre Programa para multiplicar dos arrays para obtener más detalles.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA