Hemos introducido listas enlazadas en la publicación anterior . También creamos una lista enlazada simple con 3 Nodes y discutimos el recorrido de la lista enlazada.
Todos los programas discutidos en esta publicación consideran las siguientes representaciones de lista enlazada.
Python
# Node class class Node: # Function to initialize the # node object def __init__(self, data): # Assign data self.data = data # Initialize next as null self.next = None # Linked List class class LinkedList: # Function to initialize the # Linked List object def __init__(self): self.head = None
En esta publicación, se analizan los métodos para insertar un nuevo Node en la lista vinculada. Un Node se puede agregar de tres maneras
1) Al principio de la lista enlazada
2) Después de un Node dado.
3) Al final de la lista enlazada.
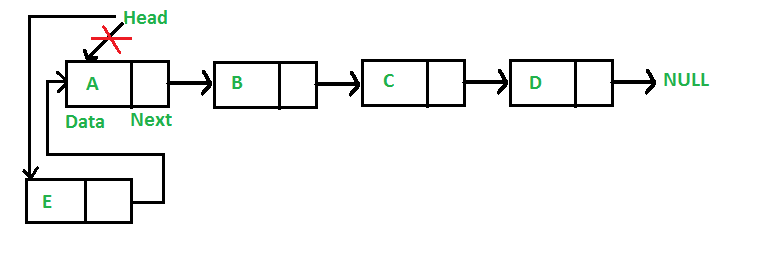
Agregar un Node al frente: (proceso de 4 pasos)
El nuevo Node siempre se agrega antes del encabezado de la lista enlazada dada. Y el Node recién agregado se convierte en el nuevo encabezado de la lista enlazada. Por ejemplo, si la lista enlazada dada es 10->15->20->25 y agregamos un elemento 5 al frente, entonces la lista enlazada se convierte en 5->10->15->20->25. Llamemos a la función que agrega al frente de la lista push(). Push() debe recibir un puntero al puntero principal, porque push debe cambiar el puntero principal para apuntar al nuevo Node (Ver esto )
Los siguientes son los 4 pasos para agregar un Node en la parte delantera.
Python
# This function is in LinkedList class # Function to insert a new node at # the beginning def push(self, new_data): # 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & # Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 3. Make next of new Node as head new_node.next = self.head # 4. Move the head to point to new Node self.head = new_node
La complejidad temporal de push() es O(1) ya que realiza una cantidad constante de trabajo.
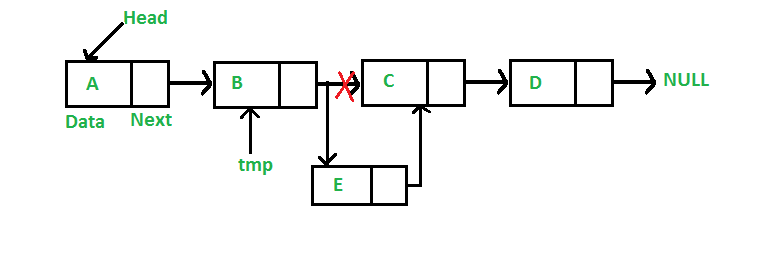
Agregar un Node después de un Node dado: (proceso de 5 pasos)
Se nos da un puntero a un Node y el nuevo Node se inserta después del Node dado.
Python
# This function is in LinkedList class. # Inserts a new node after the given # prev_node. This method is defined # inside LinkedList class shown above def insertAfter(self, prev_node, new_data): # 1. Check if the given prev_node exists if prev_node is None: print "The given previous node must in LinkedList." return # 2. Create new node & # 3. Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node new_node.next = prev_node.next # 5. make next of prev_node as new_node prev_node.next = new_node
La complejidad temporal de insertAfter() es O(1) ya que realiza una cantidad constante de trabajo.
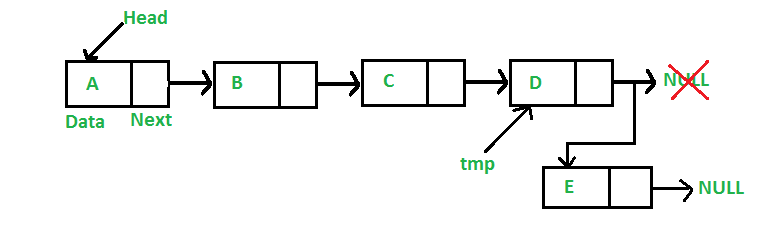
Agregar un Node al final: (proceso de 6 pasos)
El nuevo Node siempre se agrega después del último Node de la lista enlazada dada. Por ejemplo, si la lista enlazada dada es 5->10->15->20->25 y agregamos un elemento 30 al final, entonces la lista enlazada se convierte en 5->10->15->20->25- >30.
Dado que una lista enlazada suele estar representada por el encabezado de la misma, tenemos que recorrer la lista hasta el final y luego cambiar el penúltimo Node a un nuevo Node.
Los siguientes son los 6 pasos para agregar un Node al final.
Python
# This function is defined in Linked List # class appends a new node at the end. # This method is defined inside LinkedList # class shown above def append(self, new_data): # 1. Create a new node # 2. Put in the data # 3. Set next as None new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. If the Linked List is empty, then # make the new node as head if self.head is None: self.head = new_node return # 5. Else traverse till the last node last = self.head while (last.next): last = last.next # 6. Change the next of last node last.next = new_node
La complejidad temporal de agregar es O(n) donde n es el número de Nodes en la lista enlazada. Dado que hay un ciclo de principio a fin, la función funciona como O(n).
Este método también se puede optimizar para que funcione en O(1) manteniendo un puntero adicional al final de la lista enlazada/
El siguiente es un programa completo que utiliza todos los métodos anteriores para crear una lista enlazada.
Python
# A complete working Python program to demonstrate all # insertion methods of linked list # Node class class Node: # Function to initialize the # node object def __init__(self, data): # Assign data self.data = data # Initialize next as null self.next = None # Linked List class contains a # Node object class LinkedList: # Function to initialize head def __init__(self): self.head = None # Functio to insert a new node at # the beginning def push(self, new_data): # 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & # Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 3. Make next of new Node as head new_node.next = self.head # 4. Move the head to point to new Node self.head = new_node # This function is in LinkedList class. # Inserts a new node after the given # prev_node. This method is defined # inside LinkedList class shown above def insertAfter(self, prev_node, new_data): # 1. Check if the given prev_node exists if prev_node is None: print "The given previous node must inLinkedList." return # 2. Create new node & # Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. Make next of new Node as next # of prev_node new_node.next = prev_node.next # 5. make next of prev_node as new_node prev_node.next = new_node # This function is defined in Linked List class # Appends a new node at the end. This method is # defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ def append(self, new_data): # 1. Create a new node # 2. Put in the data # 3. Set next as None new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the # new node as head if self.head is None: self.head = new_node return # 5. Else traverse till the last node last = self.head while (last.next): last = last.next # 6. Change the next of last node last.next = new_node # Utility function to print the # linked list def printList(self): temp = self.head while (temp): print temp.data, temp = temp.next # Code execution starts here if __name__=='__main__': # Start with the empty list llist = LinkedList() # Insert 6. So linked list becomes 6->None llist.append(6) # Insert 7 at the beginning. So # linked list becomes 7->6->None llist.push(7); # Insert 1 at the beginning. So # linked list becomes 1->7->6->None llist.push(1); # Insert 4 at the end. So linked list # becomes 1->7->6->4->None llist.append(4) # Insert 8, after 7. So linked list # becomes 1 -> 7-> 8-> 6-> 4-> None llist.insertAfter(llist.head.next, 8) print 'Created linked list is:', llist.printList() # This code is contributed by Manikantan Narasimhan
Producción:
Created Linked list is: 1 7 8 6 4
Consulte el artículo completo en Lista vinculada | ¡ Establezca 2 (Inserción de un Node) para obtener más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA