Dada una lista enlazada de 0, 1 y 2, ordénela.
Ejemplos :
Input: 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0 -> 2 -> 0 -> 1 -> NULL Output: 0 -> 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 2 -> NULL Input: 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 0 -> NULL Output: 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> NULL
Fuente: Entrevista de Microsoft | Serie 1
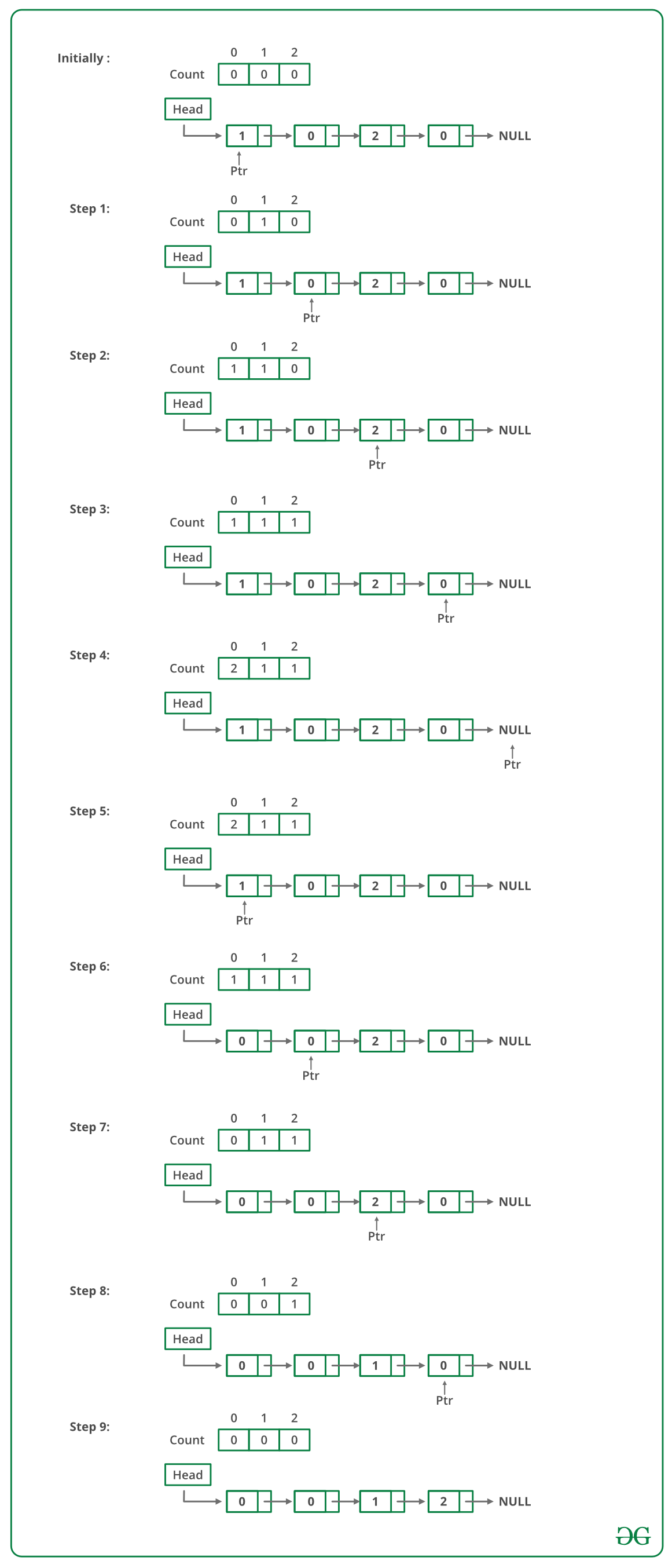
Los siguientes pasos se pueden utilizar para ordenar la lista vinculada dada.
- Recorra la lista y cuente el número de 0, 1 y 2. Sean los conteos n1, n2 y n3 respectivamente.
- Recorra la lista nuevamente, complete los primeros n1 Nodes con 0, luego n2 Nodes con 1 y finalmente n3 Nodes con 2.
La imagen de abajo es una ejecución en seco del enfoque anterior:
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to sort a
// linked list of 0, 1 and 2
// Head of list
var head;
// Linked list Node
class Node
{
constructor(val)
{
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
function sortList()
{
// Initialise count of 0 1
// and 2 as 0
var count = [ 0, 0, 0 ];
var ptr = head;
/* Count total number of '0', '1' and '2'
count[0] will store total number of
'0's count[1] will store total number
of '1's count[2] will store total
number of '2's */
while (ptr != null)
{
count[ptr.data]++;
ptr = ptr.next;
}
var i = 0;
ptr = head;
/* Let say count[0] = n1, count[1] = n2 and
count[2] = n3 now start traversing
list from head node, 1) fill the list
with 0, till n1 > 0 2) fill the list
with 1, till n2 > 0 3)
fill the list with 2, till n3 > 0 */
while (ptr != null)
{
if (count[i] == 0)
i++;
else
{
ptr.data = i;
--count[i];
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
}
// Utility functions
/* Inserts a new Node at front
of the list. */
function push(new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data */
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new Node as head
new_node.next = head;
// 4. Move the head to point to
// new Node
head = new_node;
}
// Function to print linked list
function printList()
{
var temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
document.write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
document.write("<br/>");
}
// Driver code
/* Constructed Linked List is
1->2->3->4->5->6->7-> 8->8->9->null */
push(0);
push(1);
push(0);
push(2);
push(1);
push(1);
push(2);
push(1);
push(2);
document.write(
"Linked List before sorting<br/>");
printList();
sortList();
document.write(
"Linked List after sorting<br/>");
printList();
// This code is contributed by todaysgaurav
</script>
Producción:
Linked List Before Sorting 2 1 2 1 1 2 0 1 0 Linked List After Sorting 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 2 2
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n) donde n es el número de Nodes en la lista enlazada.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Consulte el artículo completo sobre Ordenar una lista enlazada de 0, 1 y 2 para obtener más detalles.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA