Una array es un objeto de datos bidimensional formado por m filas y n columnas, por lo que tiene valores totales de mxn. Si la mayoría de los elementos de la array tienen valor 0 , entonces se llama array dispersa.
¿Por qué usar array dispersa en lugar de array simple?
- Almacenamiento: hay menos elementos distintos de cero que ceros y, por lo tanto, se puede usar menos memoria para almacenar solo esos elementos.
- Tiempo de cálculo: el tiempo de cálculo se puede ahorrar diseñando lógicamente una estructura de datos que atraviese solo elementos distintos de cero.
Ejemplo:
0 0 3 0 4 0 0 5 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 6 0 0
La representación de una array dispersa mediante una array 2D conduce al desperdicio de mucha memoria, ya que los ceros en la array no sirven en la mayoría de los casos. Entonces, en lugar de almacenar ceros con elementos distintos de cero, solo almacenamos elementos distintos de cero. Esto significa almacenar elementos distintos de cero con triples (fila, columna, valor).
Las representaciones de arrays dispersas se pueden hacer de muchas maneras, a continuación se muestran dos representaciones comunes:
- representación de array
- Representación de lista enlazada
Método 1: Uso de arrays:
La array 2D se usa para representar una array dispersa en la que hay tres filas nombradas como
- Fila: índice de la fila, donde se encuentra el elemento distinto de cero
- Columna: índice de la columna, donde se encuentra el elemento distinto de cero
- Valor: valor del elemento distinto de cero ubicado en el índice – (fila, columna)

Implementación:
C++
// C++ program for Sparse Matrix Representation
// using Array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Assume 4x5 sparse matrix
int sparseMatrix[4][5] =
{
{0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 },
{0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 },
{0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 }
};
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
size++;
// number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be
// equal to number of non - zero elements in
// sparseMatrix
int compactMatrix[3][size];
// Making of new matrix
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
compactMatrix[0][k] = i;
compactMatrix[1][k] = j;
compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j];
k++;
}
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<size; j++)
cout <<" "<< compactMatrix[i][j];
cout <<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
// this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C
// C++ program for Sparse Matrix Representation
// using Array
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Assume 4x5 sparse matrix
int sparseMatrix[4][5] =
{
{0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 },
{0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 },
{0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 }
};
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
size++;
// number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be
// equal to number of non - zero elements in
// sparseMatrix
int compactMatrix[3][size];
// Making of new matrix
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
compactMatrix[0][k] = i;
compactMatrix[1][k] = j;
compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j];
k++;
}
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<size; j++)
printf("%d ", compactMatrix[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for Sparse Matrix Representation
// using Array
class GFG
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int sparseMatrix[][]
= {
{0, 0, 3, 0, 4},
{0, 0, 5, 7, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 2, 6, 0, 0}
};
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
size++;
}
}
}
// number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be
// equal to number of non - zero elements in
// sparseMatrix
int compactMatrix[][] = new int[3][size];
// Making of new matrix
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
{
compactMatrix[0][k] = i;
compactMatrix[1][k] = j;
compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j];
k++;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
System.out.printf("%d ", compactMatrix[i][j]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Python3
# Python program for Sparse Matrix Representation # using arrays # assume a sparse matrix of order 4*5 # let assume another matrix compactMatrix # now store the value,row,column of arr1 in sparse matrix compactMatrix sparseMatrix = [[0,0,3,0,4],[0,0,5,7,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,2,6,0,0]] # initialize size as 0 size = 0 for i in range(4): for j in range(5): if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0): size += 1 # number of columns in compactMatrix(size) should # be equal to number of non-zero elements in sparseMatrix rows, cols = (3, size) compactMatrix = [[0 for i in range(cols)] for j in range(rows)] k = 0 for i in range(4): for j in range(5): if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0): compactMatrix[0][k] = i compactMatrix[1][k] = j compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j] k += 1 for i in compactMatrix: print(i) # This code is contributed by MRINALWALIA
C#
// C# program for Sparse Matrix Representation
// using Array
using System;
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Assume 4x5 sparse matrix
int[, ] sparseMatrix
= new int[4, 5] { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 },
{ 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } };
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0)
size++;
// number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be
// equal to number of non - zero elements in
// sparseMatrix
int[, ] compactMatrix = new int[3, size];
// Making of new matrix
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0) {
compactMatrix[0, k] = i;
compactMatrix[1, k] = j;
compactMatrix[2, k]
= sparseMatrix[i, j];
k++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
Console.Write(" " + compactMatrix[i, j]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Tapesh(tapeshdua420)
0 0 1 1 3 3 2 4 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 7 2 6
Método 2: uso de listas vinculadas
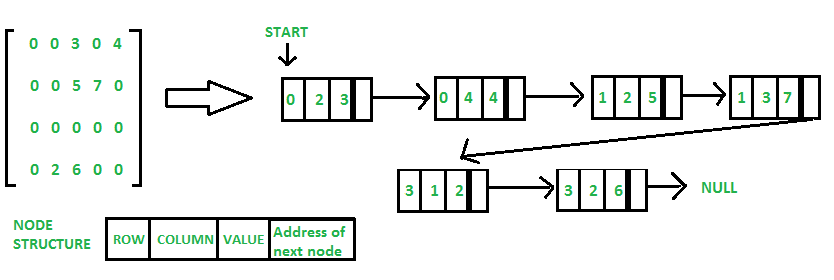
En la lista vinculada, cada Node tiene cuatro campos. Estos cuatro campos se definen como:
- Fila: índice de la fila, donde se encuentra el elemento distinto de cero
- Columna: índice de la columna, donde se encuentra el elemento distinto de cero
- Valor: valor del elemento distinto de cero ubicado en el índice – (fila, columna)
- Node siguiente: Dirección del Node siguiente
C++
// C++ program for sparse matrix representation.
// Using Link list
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Node class to represent link list
class Node
{
public:
int row;
int col;
int data;
Node *next;
};
// Function to create new node
void create_new_node(Node **p, int row_index,
int col_index, int x)
{
Node *temp = *p;
Node *r;
// If link list is empty then
// create first node and assign value.
if (temp == NULL)
{
temp = new Node();
temp->row = row_index;
temp->col = col_index;
temp->data = x;
temp->next = NULL;
*p = temp;
}
// If link list is already created
// then append newly created node
else
{
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
r = new Node();
r->row = row_index;
r->col = col_index;
r->data = x;
r->next = NULL;
temp->next = r;
}
}
// Function prints contents of linked list
// starting from start
void printList(Node *start)
{
Node *ptr = start;
cout << "row_position:";
while (ptr != NULL)
{
cout << ptr->row << " ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "column_position:";
ptr = start;
while (ptr != NULL)
{
cout << ptr->col << " ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Value:";
ptr = start;
while (ptr != NULL)
{
cout << ptr->data << " ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// 4x5 sparse matrix
int sparseMatrix[4][5] = { { 0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 },
{ 0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 } };
// Creating head/first node of list as NULL
Node *first = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
// Pass only those values which
// are non - zero
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0)
create_new_node(&first, i, j,
sparseMatrix[i][j]);
}
}
printList(first);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by ronaksuba
C
// C program for Sparse Matrix Representation
// using Linked Lists
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Node to represent sparse matrix
struct Node
{
int value;
int row_position;
int column_postion;
struct Node *next;
};
// Function to create new node
void create_new_node(struct Node** start, int non_zero_element,
int row_index, int column_index )
{
struct Node *temp, *r;
temp = *start;
if (temp == NULL)
{
// Create new node dynamically
temp = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
temp->value = non_zero_element;
temp->row_position = row_index;
temp->column_postion = column_index;
temp->next = NULL;
*start = temp;
}
else
{
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// Create new node dynamically
r = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
r->value = non_zero_element;
r->row_position = row_index;
r->column_postion = column_index;
r->next = NULL;
temp->next = r;
}
}
// This function prints contents of linked list
// starting from start
void PrintList(struct Node* start)
{
struct Node *temp, *r, *s;
temp = r = s = start;
printf("row_position: ");
while(temp != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", temp->row_position);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
printf("column_postion: ");
while(r != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", r->column_postion);
r = r->next;
}
printf("\n");
printf("Value: ");
while(s != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", s->value);
s = s->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver of the program
int main()
{
// Assume 4x5 sparse matrix
int sparseMatric[4][5] =
{
{0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 },
{0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 },
{0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 }
};
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* start = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
// Pass only those values which are non - zero
if (sparseMatric[i][j] != 0)
create_new_node(&start, sparseMatric[i][j], i, j);
PrintList(start);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for sparse matrix representation.
// Using Link list
import java.util.*;
public class SparseMatrix {
// Creating head/first node of list as NULL
static Node first = null;
// Node class to represent link list
public static class Node {
int row;
int col;
int data;
Node next;
};
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 4x5 sparse matrix
int[][] sparseMatrix = { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 },
{ 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
// Pass only those values which
// are non - zero
if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) {
create_new_node(i, j,
sparseMatrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
printList(first);
}
// Function to create new node
private static void
create_new_node(int row_index, int col_index, int x)
{
Node temp = first;
Node r;
// If link list is empty then
// create first node and assign value.
if (temp == null) {
temp = new Node();
temp.row = row_index;
temp.col = col_index;
temp.data = x;
temp.next = null;
first = temp;
}
// If link list is already created
// then append newly created node
else {
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
r = new Node();
r.row = row_index;
r.col = col_index;
r.data = x;
r.next = null;
temp.next = r;
}
}
// Function prints contents of linked list
// starting from start
public static void printList(Node start)
{
Node ptr = start;
System.out.print("row_position:");
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print(ptr.row + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.print("column_position:");
ptr = start;
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print(ptr.col + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.print("Value:");
ptr = start;
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print(ptr.data + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Tapesh (tapeshdua420)
Python3
# Python Program for Representation of
# Sparse Matrix into Linked List
# Node Class to represent Linked List Node
class Node:
# Making the slots for storing row,
# column, value, and address
__slots__ = "row", "col", "data", "next"
# Constructor to initialize the values
def __init__(self, row=0, col=0, data=0, next=None):
self.row = row
self.col = col
self.data = data
self.next = next
# Class to convert Sparse Matrix
# into Linked List
class Sparse:
# Initialize Class Variables
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.temp = None
self.size = 0
# Function which returns the size
# of the Linked List
def __len__(self):
return self.size
# Check the Linked List is
# Empty or not
def isempty(self):
return self.size == 0
# Responsible function to create
# Linked List from Sparse Matrix
def create_new_node(self, row, col, data):
# Creating New Node
newNode = Node(row, col, data, None)
# Check whether the List is
# empty or not
if self.isempty():
self.head = newNode
else:
self.temp.next = newNode
self.temp = newNode
# Incrementing the size
self.size += 1
# Function display the contents of
# Linked List
def PrintList(self):
temp = r = s = self.head
print("row_position:", end=" ")
while temp != None:
print(temp.row, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
print()
print("column_postion:", end=" ")
while r != None:
print(r.col, end=" ")
r = r.next
print()
print("Value:", end=" ")
while s != None:
print(s.data, end=" ")
s = s.next
print()
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Creating Object
s = Sparse()
# Assuming 4x5 Sparse Matrix
sparseMatric = [[0, 0, 3, 0, 4],
[0, 0, 5, 7, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 2, 6, 0, 0]]
for i in range(4):
for j in range(5):
# Creating Linked List by only those
# elements which are non-zero
if sparseMatric[i][j] != 0:
s.create_new_node(i, j, sparseMatric[i][j])
# Printing the Linked List Representation
# of the sparse matrix
s.PrintList()
# This code is contributed by Naveen Rathore
C#
// C# program for sparse matrix representation.
// Using Link list
using System;
class Program
{
// Creating head/first node of list as NULL
static Node first = null;
// Node class to represent link list
public class Node {
public int row;
public int col;
public int data;
public Node next;
};
// Driver Code
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 4x5 sparse matrix
int[, ] sparseMatrix = { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 },
{ 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
// Pass only those values which
// are non - zero
if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0) {
create_new_node(i, j,
sparseMatrix[i, j]);
}
}
}
printList(first);
}
// Function to create new node
private static void
create_new_node(int row_index, int col_index, int x)
{
Node temp = first;
Node r;
// If link list is empty then
// create first node and assign value.
if (temp == null) {
temp = new Node();
temp.row = row_index;
temp.col = col_index;
temp.data = x;
temp.next = null;
first = temp;
}
// If link list is already created
// then append newly created node
else
{
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
r = new Node();
r.row = row_index;
r.col = col_index;
r.data = x;
r.next = null;
temp.next = r;
}
}
// Function prints contents of linked list
// starting from start
public static void printList(Node start)
{
Node ptr = start;
Console.Write("row_position:");
while (ptr != null) {
Console.Write(ptr.row + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.Write("column_position:");
ptr = start;
while (ptr != null) {
Console.Write(ptr.col + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.Write("Value:");
ptr = start;
while (ptr != null) {
Console.Write(ptr.data + " ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Tapesh (tapeshdua420)
row_position:0 0 1 1 3 3 column_position:2 4 2 3 1 2 Value:3 4 5 7 2 6
Otras representaciones:
Como un diccionario donde los números de fila y columna se usan como claves y los valores son entradas de array. Este método ahorra espacio pero el acceso secuencial de elementos es costoso.
Como una lista de lista . La idea es hacer una lista de filas y cada elemento de la lista contiene valores. Podemos mantener los elementos de la lista ordenados por números de columna.
Sparse Matrix y sus representaciones | Conjunto 2 (usando la lista de listas y el diccionario de claves)
Este artículo es una contribución de Akash Gupta . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA