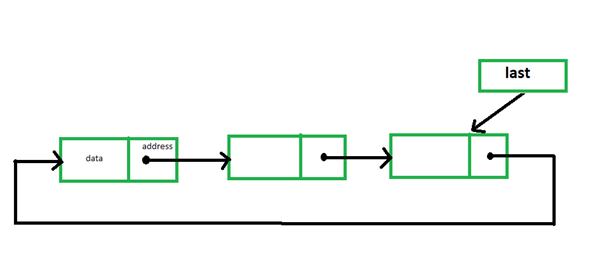
En una lista enlazada circular , cada elemento tiene un enlace a su siguiente elemento en la secuencia y el último elemento tiene un enlace al primer elemento. Una lista enlazada circular es similar a la lista enlazada simple excepto que el último Node apunta al primer Node. A continuación se muestra la imagen para ilustrar lo mismo:
Algunas operaciones comunes de una lista enlazada circular se implementan a continuación:
Inserción al principio : Insertar un nuevo Node como primer Node. El siguiente puntero del último apuntará a este Node y este nuevo Node apuntará al primer Node anterior.
C
// C program for the above operation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a linked list node
struct node {
int info;
struct node* next;
};
// Pointer to last node in the list
struct node* last = NULL;
// Function to insert a node in the
// starting of the list
void insertAtFront()
{
// Stores the number to be inserted
int data;
// Initialize a new node
struct node* temp;
temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Input data
printf("\nEnter data to be "
"inserted: \n");
scanf("%d", &data);
// If the new node is the only
// node in the list
if (last == NULL) {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
// Else last node contains the
// reference of the new node and
// new node contains the reference
// of the previous first node
else {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = last->next;
// last node now has reference
// of the new node temp
last->next = temp;
}
}
// Function to print the list
void viewList()
{
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty\n");
// Else print the list
else {
struct node* temp;
temp = last->next;
// While first node is not
// reached again, print,
// since the list is circular
do {
printf("\nData = %d", temp->info);
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != last->next);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Function Call
insertAtFront();
insertAtFront();
insertAtFront();
// Print list
viewList();
return 0;
}
Producción:

Inserción al final : Insertar un nuevo Node como último Node. El siguiente puntero del último apuntará a este Node y este nuevo Node apuntará al primer Node.
C
// C program for the above operation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a linked list node
struct node {
int info;
struct node* next;
};
// Pointer to last node in the list
struct node* last = NULL;
// Function to add a new node at the
// end of the list
void addatlast()
{
// Stores number to be inserted
int data;
// Initialize a new node
struct node* temp;
temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Input data
printf("\nEnter data to be "
"inserted : \n");
scanf("%d", &data);
// If the new node is the
// only node in the list
if (last == NULL) {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
// Else the new node will be the
// last node and will contain
// the reference of head node
else {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = last->next;
last->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
}
// Function to print the list
void viewList()
{
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty\n");
// Else print the list
else {
struct node* temp;
temp = last->next;
do {
printf("\nData = %d",
temp->info);
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != last->next);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Function Call
addatlast();
addatlast();
addatlast();
// Print list
viewList();
return 0;
}
Producción:

Inserción después de un elemento específico : A continuación se muestra el programa para insertar un Node después de un Node específico en la lista enlazada.
C
// C program for the above operation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a linked list node
struct node {
int info;
struct node* next;
};
// Pointer to last node in list
struct node* last = NULL;
// Function to add a new node
// at the end of the list
void addatlast()
{
// Stores number to be inserted
int data;
// Initialize a new node
struct node* temp;
temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Input data
printf("\nEnter data to be inserted : \n");
scanf("%d", &data);
// If the new node is the
// only node in the list
if (last == NULL) {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
// Else the new node will be the
// last node and will contain
// the reference of head node
else {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = last->next;
last->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
}
// Function to insert after any
// specified element
void insertafter()
{
// Stores data and element after
// which new node is to be inserted
int data, value;
// Initialize a new node
struct node *temp, *n;
// Input data
printf("\nEnter number after which"
" you want to enter number: \n");
scanf("%d", &value);
temp = last->next;
do {
// Element after which node is
// to be inserted is found
if (temp->info == value) {
n = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Input Data
printf("\nEnter data to be"
" inserted : \n");
scanf("%d", &data);
n->info = data;
n->next = temp->next;
temp->next = n;
// If temp is the last node
// so now n will become the
// last node
if (temp == last)
last = n;
break;
}
else
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != last->next);
}
// Function to print the list
void viewList()
{
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty\n");
// Else print the list
else {
struct node* temp;
temp = last->next;
do {
printf("\nData = %d",
temp->info);
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != last->next);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Initialize the list
addatlast();
addatlast();
addatlast();
// Function Call
insertafter();
// Print list
viewList();
return 0;
}
Producción:

Borrar primer elemento : Borrar el primer Node de la lista enlazada. Para ello, el siguiente puntero del último apuntará al segundo Node de la lista enlazada. A continuación se muestra el programa para el mismo:
C
// C program for the above operation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a linked list node
struct node {
int info;
struct node* next;
};
// Pointer to last node in list
struct node* last = NULL;
// Function to add a new node
// at the end of the list
void addatlast()
{
// Stores number to be inserted
int data;
// Initialize a new node
struct node* temp;
temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Input data
printf("\nEnter data to be"
" inserted: \n");
scanf("%d", &data);
// If the new node is the only
// node in the list
if (last == NULL) {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
// Else the new node will be the
// last node and will contain
// the reference of head node
else {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = last->next;
last->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
}
// Function to delete the first
// element of the list
void deletefirst()
{
struct node* temp;
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty.\n");
// Else last node now contains
// reference of the second node
// in the list because the
// list is circular
else {
temp = last->next;
last->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
}
// Function to print the list
void viewList()
{
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty\n");
// Else print the list
else {
struct node* temp;
temp = last->next;
do {
printf("\nData = %d",
temp->info);
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != last->next);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Initialize the list
addatlast();
addatlast();
addatlast();
// Function Call
deletefirst();
// Print list
viewList();
return 0;
}
Producción:

Eliminar el último elemento : Eliminar el último Node de la lista enlazada. Para ello, el penúltimo Node apuntará al primer Node de la lista. A continuación se muestra el programa para el mismo:
C
// C program for the above operation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a linked list node
struct node {
int info;
struct node* next;
};
// Pointer to last node in list
struct node* last = NULL;
// Function to add a new node
// at the end of the list
void addatlast()
{
// Stores number to be inserted
int data;
// Initialize a new node
struct node* temp;
temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Input data
printf("\nEnter data to be inserted : \n");
scanf("%d", &data);
// If the new node is the only
// node in the list
if (last == NULL) {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
// Else the new node will be
// last node and will contain
// the reference of head node
else {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = last->next;
last->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
}
// Function to delete the last node
// in the list
void deletelast()
{
struct node* temp;
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty.\n");
temp = last->next;
// Traverse the list till
// the second last node
while (temp->next != last)
temp = temp->next;
// Second last node now contains
// the reference of the first
// node in the list
temp->next = last->next;
last = temp;
}
// Function to print the list
void viewList()
{
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty\n");
// Else print the list
else {
struct node* temp;
temp = last->next;
do {
printf("\nData = %d",
temp->info);
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != last->next);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Initialize the list
addatlast();
addatlast();
addatlast();
// Function Call
deletelast();
// Print the list
viewList();
return 0;
}
Producción:

Eliminar en una posición dada : elimina un elemento de una posición específica en la lista vinculada. A continuación se muestra el programa para el mismo:
C
// C program for the above operation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a linked list node
struct node {
int info;
struct node* next;
};
// Pointer to last node in list
struct node* last = NULL;
// Function to add a new node
// at the end of the list
void addatlast()
{
// Stores number to be inserted
int data;
// Initialize a new node
struct node* temp;
temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Input data
printf("\nEnter data to be inserted : \n");
scanf("%d", &data);
// If the new node is the
// only node in the list
if (last == NULL) {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
// Else the new node will be
// last node and will contain
// the reference of head node
else {
temp->info = data;
temp->next = last->next;
last->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
}
// Function to delete an element
// at a specified index in the list
void deleteAtIndex()
{
// Stores the index at which
// the element is to be deleted
int pos, i = 1;
struct node *temp, *position;
temp = last->next;
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty.\n");
// Else
else {
// Input Data
printf("\nEnter index : ");
scanf("%d", &pos);
// Traverse till the node to
// be deleted is reached
while (i <= pos - 1) {
temp = temp->next;
i++;
}
// After the loop ends, temp
// points at a node just before
// the node to be deleted
// Reassigning links
position = temp->next;
temp->next = position->next;
free(position);
}
}
// Function to print the list
void viewList()
{
// If list is empty
if (last == NULL)
printf("\nList is empty\n");
// Else print the list
else {
struct node* temp;
temp = last->next;
do {
printf("\nData = %d", temp->info);
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != last->next);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Initialize the list
addatlast();
addatlast();
addatlast();
// Function Call
deleteAtIndex();
// Print the list
viewList();
return 0;
}
Producción:

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por imsushant12 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA