Dado un árbol con raíz y dos Nodes que están en el árbol, encuentre el ancestro común más bajo de ambos Nodes. El LCA para dos Nodes u y v se define como el Node más alejado de la raíz que es el ancestro de u y v.
Requisitos previos: LCA | SERIE 1
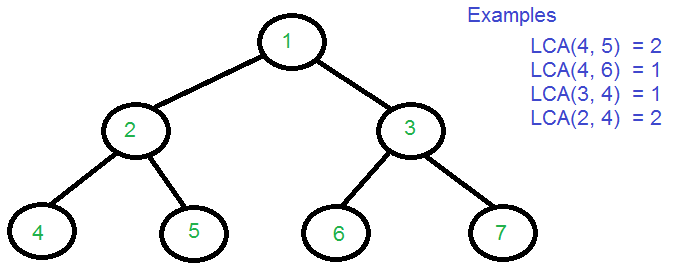
Ejemplo de la figura anterior:
Input : 4 5 Output : 2 Input : 4 7 Output : 1
Conversión de LCA a RMQ (consulta de rango mínimo):
tome una array denominada E[], que almacena el orden de recorrido de dfs, es decir, el orden en que se cubren los Nodes durante el recorrido de dfs. Por ejemplo,

El árbol dado arriba tiene dfs transversal en el orden: 1-2-4-2-5-2-1-3.
Tome otra array L[], en la que L[i] es el nivel del Node E[i].
Y la array H[], que almacena el índice de la primera aparición del i-ésimo Node en la array E[].
Entonces, para el árbol anterior,
E[] = {1, 2, 4, 2, 5, 2, 1, 3}
L[] = {1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2}
H [] = {0, 1, 7, 2, 4}
Tenga en cuenta que las arrays E y L tienen una indexación basada en uno, pero la array H tiene una indexación basada en cero.
Ahora, para encontrar el LCA(4, 3), primero, use la array H y encuentre los índices en los que 4 y 3 se encuentran en E, es decir, H[4] y H[3]. Entonces, los índices resultan ser 2 y 7. Ahora, mire el subarreglo L[2 : 7], y encuentre el mínimo en este subarreglo que es 1 (en el sexto índice), y el elemento correspondiente en el arreglo E es decir, E[6] es el LCA(4, 3).
Para entender por qué esto funciona, tome LCA (4, 3) nuevamente. El camino por el cual se puede llegar al Node 3 desde el Node 4 es el subarreglo E[2 : 7]. Y, si hay un Node con el nivel más bajo en esta ruta, simplemente se puede afirmar que es el LCA (4, 3).
Ahora, el problema es encontrar el mínimo en el subarreglo E[H[u]….H[v]] (suponiendo que H[u] >= H[v]). Y eso podría hacerse usando un árbol de segmentos o una tabla dispersa. A continuación se muestra el código que utiliza el árbol de segmentos.
C++
// CPP code to find LCA of given
// two nodes in a tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define sz(x) x.size()
#define pb push_back
#define left 2 * i + 1
#define right 2 * i + 2
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100005;
// the graph
vector<vector<int>> g(maxn);
// level of each node
int level[maxn];
vector<int> e;
vector<int> l;
int h[maxn];
// the segment tree
int st[5 * maxn];
// adding edges to the graph(tree)
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
g[u].pb(v);
g[v].pb(u);
}
// assigning level to nodes
void leveling(int src) {
for (int i = 0; i < sz(g[src]); i++) {
int des = g[src][i];
if (!level[des]) {
level[des] = level[src] + 1;
leveling(des);
}
}
}
bool visited[maxn];
// storing the dfs traversal
// in the array e
void dfs(int src) {
e.pb(src);
visited[src] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < sz(g[src]); i++) {
int des = g[src][i];
if (!visited[des]) {
dfs(des);
e.pb(src);
}
}
}
// making the array l
void setting_l(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < sz(e); i++)
l.pb(level[e[i]]);
}
// making the array h
void setting_h(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
h[i] = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < sz(e); i++) {
// if is already stored
if (h[e[i]] == -1)
h[e[i]] = i;
}
}
// Range minimum query to return the index
// of minimum in the subarray L[qs:qe]
int RMQ(int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int i) {
if (ss > se)
return -1;
// out of range
if (se < qs || qe < ss)
return -1;
// in the range
if (qs <= ss && se <= qe)
return st[i];
int mid = (ss + se) >> 1;
int st = RMQ(ss, mid, qs, qe, left);
int en = RMQ(mid + 1, se, qs, qe, right);
if (st != -1 && en != -1) {
if (l[st] < l[en])
return st;
return en;
} else if (st != -1)
return st;
else if (en != -1)
return en;
}
// constructs the segment tree
void SegmentTreeConstruction(int ss, int se, int i) {
if (ss > se)
return;
if (ss == se) // leaf
{
st[i] = ss;
return;
}
int mid = (ss + se) >> 1;
SegmentTreeConstruction(ss, mid, left);
SegmentTreeConstruction(mid + 1, se, right);
if (l[st[left]] < l[st[right]])
st[i] = st[left];
else
st[i] = st[right];
}
// Function to get LCA
int LCA(int x, int y) {
if (h[x] > h[y])
swap(x, y);
return e[RMQ(0, sz(l) - 1, h[x], h[y], 0)];
}
// Driver code
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// n=number of nodes in the tree
// q=number of queries to answer
int n = 15, q = 5;
// making the tree
/*
1
/ | \
2 3 4
| \
5 6
/ | \
8 7 9 (right of 5)
/ | \ | \
10 11 12 13 14
|
15
*/
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(1, 3);
add_edge(1, 4);
add_edge(3, 5);
add_edge(4, 6);
add_edge(5, 7);
add_edge(5, 8);
add_edge(5, 9);
add_edge(7, 10);
add_edge(7, 11);
add_edge(7, 12);
add_edge(9, 13);
add_edge(9, 14);
add_edge(12, 15);
level[1] = 1;
leveling(1);
dfs(1);
setting_l(n);
setting_h(n);
SegmentTreeConstruction(0, sz(l) - 1, 0);
cout << LCA(10, 15) << endl;
cout << LCA(11, 14) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// JAVA code to find LCA of given
// two nodes in a tree
import java.util.*;
public class GFG
{
static int maxn = 100005;
static int left(int i)
{
return (2 * i + 1);
}
static int right(int i) { return 2 * i + 2;}
// the graph
static Vector<Integer> []g = new Vector[maxn];
// level of each node
static int []level = new int[maxn];
static Vector<Integer> e = new Vector<>();
static Vector<Integer> l= new Vector<>();
static int []h = new int[maxn];
// the segment tree
static int []st = new int[5 * maxn];
// adding edges to the graph(tree)
static void add_edge(int u, int v)
{
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
}
// assigning level to nodes
static void levelling(int src)
{
for (int i = 0; i < (g[src].size()); i++)
{
int des = g[src].get(i);
if (level[des] != 0)
{
level[des] = level[src] + 1;
leveling(des);
}
}
}
static boolean []visited = new boolean[maxn];
// storing the dfs traversal
// in the array e
static void dfs(int src)
{
e.add(src);
visited[src] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < (g[src]).size(); i++)
{
int des = g[src].get(i);
if (!visited[des])
{
dfs(des);
e.add(src);
}
}
}
// making the array l
static void setting_l(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < e.size(); i++)
l.add(level[e.get(i)]);
}
// making the array h
static void setting_h(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
h[i] = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < e.size(); i++)
{
// if is already stored
if (h[e.get(i)] == -1)
h[e.get(i)] = i;
}
}
// Range minimum query to return the index
// of minimum in the subarray L[qs:qe]
static int RMQ(int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int i)
{
if (ss > se)
return -1;
// out of range
if (se < qs || qe < ss)
return -1;
// in the range
if (qs <= ss && se <= qe)
return st[i];
int mid = (ss + se)/2 ;
int st = RMQ(ss, mid, qs, qe, left(i));
int en = RMQ(mid + 1, se, qs, qe, right(i));
if (st != -1 && en != -1)
{
if (l.get(st) < l.get(en))
return st;
return en;
} else if (st != -1)
return st-2;
else if (en != -1)
return en-1;
return 0;
}
// constructs the segment tree
static void SegmentTreeConstruction(int ss,
int se, int i)
{
if (ss > se)
return;
if (ss == se) // leaf
{
st[i] = ss;
return;
}
int mid = (ss + se) /2;
SegmentTreeConstruction(ss, mid, left(i));
SegmentTreeConstruction(mid + 1, se, right(i));
if (l.get(st[left(i)]) < l.get(st[right(i)]))
st[i] = st[left(i)];
else
st[i] = st[right(i)];
}
// Function to get LCA
static int LCA(int x, int y)
{
if (h[x] > h[y])
{
int t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
return e.get(RMQ(0, l.size() - 1, h[x], h[y], 0));
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// n=number of nodes in the tree
// q=number of queries to answer
int n = 15, q = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < g.length; i++)
g[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
// making the tree
/*
1
/ | \
2 3 4
| \
5 6
/ | \
8 7 9 (right of 5)
/ | \ | \
10 11 12 13 14
|
15
*/
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(1, 3);
add_edge(1, 4);
add_edge(3, 5);
add_edge(4, 6);
add_edge(5, 7);
add_edge(5, 8);
add_edge(5, 9);
add_edge(7, 10);
add_edge(7, 11);
add_edge(7, 12);
add_edge(9, 13);
add_edge(9, 14);
add_edge(12, 15);
level[1] = 1;
leveling(1);
dfs(1);
setting_l(n);
setting_h(n);
SegmentTreeConstruction(0, l.size() - 1, 0);
System.out.print(LCA(10, 15) +"\n");
System.out.print(LCA(11, 14) +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python code to find LCA of given # two nodes in a tree maxn = 100005 # the graph g = [[] for i in range(maxn)] # level of each node level = [0] * maxn e = [] l = [] h = [0] * maxn # the segment tree st = [0] * (5 * maxn) # adding edges to the graph(tree) def add_edge(u: int, v: int): g[u].append(v) g[v].append(u) # assigning level to nodes def levelling(src: int): for i in range(len(g[src])): des = g[src][i] if not level[des]: level[des] = level[src] + 1 leveling(des) visited = [False] * maxn # storing the dfs traversal # in the array e def dfs(src: int): e.append(src) visited[src] = True for i in range(len(g[src])): des = g[src][i] if not visited[des]: dfs(des) e.append(src) # making the array l def setting_l(n: int): for i in range(len(e)): l.append(level[e[i]]) # making the array h def setting_h(n: int): for i in range(n + 1): h[i] = -1 for i in range(len(e)): # if is already stored if h[e[i]] == -1: h[e[i]] = i # Range minimum query to return the index # of minimum in the subarray L[qs:qe] def RMQ(ss: int, se: int, qs: int, qe: int, i: int) -> int: global st if ss > se: return -1 # out of range if se < qs or qe < ss: return -1 # in the range if qs <= ss and se <= qe: return st[i] mid = (se + ss) >> 1 stt = RMQ(ss, mid, qs, qe, 2 * i + 1) en = RMQ(mid + 1, se, qs, qe, 2 * i + 2) if stt != -1 and en != -1: if l[stt] < l[en]: return stt return en elif stt != -1: return stt elif en != -1: return en # constructs the segment tree def segmentTreeConstruction(ss: int, se: int, i: int): if ss > se: return if ss == se: # leaf st[i] = ss return mid = (ss + se) >> 1 segmentTreeConstruction(ss, mid, 2 * i + 1) segmentTreeConstruction(mid + 1, se, 2 * i + 2) if l[st[2 * i + 1]] < l[st[2 * i + 2]]: st[i] = st[2 * i + 1] else: st[i] = st[2 * i + 2] # Function to get LCA def LCA(x: int, y: int) -> int: if h[x] > h[y]: x, y = y, x return e[RMQ(0, len(l) - 1, h[x], h[y], 0)] # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": # n=number of nodes in the tree # q=number of queries to answer n = 15 q = 5 # making the tree # /* # 1 # / | \ # 2 3 4 # | \ # 5 6 # / | \ # 8 7 9 (right of 5) # / | \ | \ # 10 11 12 13 14 # | # 15 # */ add_edge(1, 2) add_edge(1, 3) add_edge(1, 4) add_edge(3, 5) add_edge(4, 6) add_edge(5, 7) add_edge(5, 8) add_edge(5, 9) add_edge(7, 10) add_edge(7, 11) add_edge(7, 12) add_edge(9, 13) add_edge(9, 14) add_edge(12, 15) level[1] = 1 leveling(1) dfs(1) setting_l(n) setting_h(n) segmentTreeConstruction(0, len(l) - 1, 0) print(LCA(10, 15)) print(LCA(11, 14)) # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552
C#
// C# code to find LCA of given
// two nodes in a tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static int maxn = 100005;
static int left(int i)
{
return (2 * i + 1);
}
static int right(int i) { return 2 * i + 2;}
// the graph
static List<int> []g = new List<int>[maxn];
// level of each node
static int []level = new int[maxn];
static List<int> e = new List<int>();
static List<int> l= new List<int>();
static int []h = new int[maxn];
// the segment tree
static int []st;
// adding edges to the graph(tree)
static void add_edge(int u, int v)
{
g[u].Add(v);
g[v].Add(u);
}
// assigning level to nodes
static void leveling(int src)
{
for (int i = 0; i < (g[src].Count); i++)
{
int des = g[src][i];
if (level[des] != 0)
{
level[des] = level[src] + 1;
leveling(des);
}
}
}
static bool []visited = new bool[maxn];
// storing the dfs traversal
// in the array e
static void dfs(int src)
{
e.Add(src);
visited[src] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < (g[src]).Count; i++)
{
int des = g[src][i];
if (!visited[des])
{
dfs(des);
e.Add(src);
}
}
}
// making the array l
static void setting_l(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < e.Count; i++)
l.Add(level[e[i]]);
}
// making the array h
static void setting_h(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
h[i] = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < e.Count; i++)
{
// if is already stored
if (h[e[i]] == -1)
h[e[i]] = i;
}
}
// Range minimum query to return the index
// of minimum in the subarray L[qs:qe]
static int RMQ(int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int i)
{
if (ss > se)
return -1;
// out of range
if (se < qs || qe < ss)
return -1;
// in the range
if (qs <= ss && se <= qe)
return st[i];
int mid = (ss + se)/2 ;
int sti = RMQ(ss, mid, qs, qe, left(i));
int en = RMQ(mid + 1, se, qs, qe, right(i));
if (sti != -1 && en != -1)
{
if (l[sti] < l[en])
return sti;
return en;
} else if (sti != -1)
return sti-2;
else if (en != -1)
return en-1;
return 0;
}
// constructs the segment tree
static void SegmentTreeConstruction(int ss,
int se, int i)
{
if (ss > se)
return;
if (ss == se) // leaf
{
st[i] = ss;
return;
}
int mid = (ss + se) /2;
SegmentTreeConstruction(ss, mid, left(i));
SegmentTreeConstruction(mid + 1, se, right(i));
if (l[st[left(i)]] < l[st[right(i)]])
st[i] = st[left(i)];
else
st[i] = st[right(i)];
}
// Function to get LCA
static int LCA(int x, int y)
{
if (h[x] > h[y])
{
int t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
return e[RMQ(0, l.Count - 1, h[x], h[y], 0)];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
st = new int[5 * maxn];
// n=number of nodes in the tree
// q=number of queries to answer
int n = 15;
for (int i = 0; i < g.Length; i++)
g[i] = new List<int>();
// making the tree
/*
1
/ | \
2 3 4
| \
5 6
/ | \
8 7 9 (right of 5)
/ | \ | \
10 11 12 13 14
|
15
*/
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(1, 3);
add_edge(1, 4);
add_edge(3, 5);
add_edge(4, 6);
add_edge(5, 7);
add_edge(5, 8);
add_edge(5, 9);
add_edge(7, 10);
add_edge(7, 11);
add_edge(7, 12);
add_edge(9, 13);
add_edge(9, 14);
add_edge(12, 15);
level[1] = 1;
leveling(1);
dfs(1);
setting_l(n);
setting_h(n);
SegmentTreeConstruction(0, l.Count - 1, 0);
Console.Write(LCA(10, 15) +"\n");
Console.Write(LCA(11, 14) +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code to find LCA of given
// two nodes in a tree
let maxn = 100005;
function left(i)
{
return (2 * i + 1);
}
function right(i) { return 2 * i + 2;}
// the graph
let g = new Array(maxn);
// level of each node
let level = new Array(maxn);
level.fill(0);
let e = [];
let l= [];
let h = new Array(maxn);
h.fill(0);
// the segment tree
let st = new Array(5 * maxn);
st.fill(0);
// adding edges to the graph(tree)
function add_edge(u, v)
{
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
// assigning level to nodes
function levelling(src)
{
for (let i = 0; i < (g[src].length); i++)
{
let des = g[src][i];
if (level[des] != 0)
{
level[des] = level[src] + 1;
levelling(des);
}
}
}
let visited = new Array(maxn);
visited.fill(false);
// storing the dfs traversal
// in the array e
function dfs(src)
{
e.push(src);
visited[src] = true;
for (let i = 0; i < (g[src]).length; i++)
{
let des = g[src][i];
if (!visited[des])
{
dfs(des);
e.push(src);
}
}
}
// making the array l
function setting_l(n)
{
for (let i = 0; i < e.length; i++)
l.push(level[e[i]]);
}
// making the array h
function setting_h(n)
{
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++)
h[i] = -1;
for (let i = 0; i < e.length; i++)
{
// if is already stored
if (h[e[i]] == -1)
h[e[i]] = i;
}
}
// Range minimum query to return the index
// of minimum in the subarray L[qs:qe]
function RMQ(ss, se, qs, qe, i)
{
if (ss > se)
return -1;
// out of range
if (se < qs || qe < ss)
return -1;
// in the range
if (qs <= ss && se <= qe)
return st[i];
let mid = parseInt((ss + se)/2 , 10);
let St = RMQ(ss, mid, qs, qe, left(i));
let en = RMQ(mid + 1, se, qs, qe, right(i));
if (St != -1 && en != -1)
{
if (l[St] < l[en])
return St;
return en;
} else if (St != -1)
return St-2;
else if (en != -1)
return en-1;
return 0;
}
// constructs the segment tree
function SegmentTreeConstruction(ss, se, i)
{
if (ss > se)
return;
if (ss == se) // leaf
{
st[i] = ss;
return;
}
let mid = parseInt((ss + se) /2, 10);
SegmentTreeConstruction(ss, mid, left(i));
SegmentTreeConstruction(mid + 1, se, right(i));
if (l[st[left(i)]] < l[st[right(i)]])
st[i] = st[left(i)];
else
st[i] = st[right(i)];
}
// Function to get LCA
function LCA(x, y)
{
if (h[x] > h[y])
{
let t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
return e[RMQ(0, l.length - 1, h[x], h[y], 0)];
}
// n=number of nodes in the tree
// q=number of queries to answer
let n = 15, q = 5;
for (let i = 0; i < g.length; i++)
g[i] = [];
// making the tree
/*
1
/ | \
2 3 4
| \
5 6
/ | \
8 7 9 (right of 5)
/ | \ | \
10 11 12 13 14
|
15
*/
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(1, 3);
add_edge(1, 4);
add_edge(3, 5);
add_edge(4, 6);
add_edge(5, 7);
add_edge(5, 8);
add_edge(5, 9);
add_edge(7, 10);
add_edge(7, 11);
add_edge(7, 12);
add_edge(9, 13);
add_edge(9, 14);
add_edge(12, 15);
level[1] = 1;
levelling(1);
dfs(1);
setting_l(n);
setting_h(n);
SegmentTreeConstruction(0, l.length - 1, 0);
document.write(LCA(10, 15) +"</br>");
document.write(LCA(11, 14) +"</br>");
</script>
7 5
Complejidad de tiempo:
las arrays definidas se almacenan en O (n). La construcción del árbol de segmentos también requiere tiempo O(n). La función LCA llama a la función RMQ que toma O (logn) por consulta (ya que usa el árbol de segmentos). Entonces, la complejidad del tiempo general es O(n + q * logn) .
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Amritya Vagmi y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA