Dado un gráfico dirigido, la tarea es contar el grado de entrada y salida de cada vértice del gráfico.
Ejemplos:
Input:
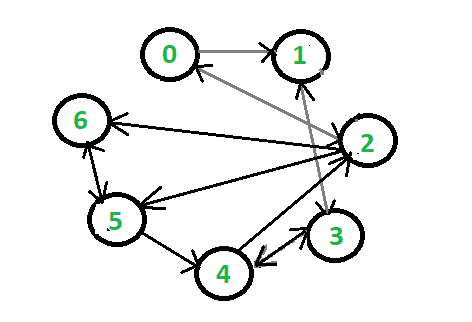
Output: Vertex In Out 0 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 3 3 2 2 4 2 2 5 2 2 6 2 1
Enfoque: Lista de adyacencia transversal para cada vértice, si el tamaño de la lista de adyacencia del vértice i es x , entonces el grado de salida para i = x e incrementa el grado de entrada de cada vértice que tiene un borde entrante desde i . Repita los pasos para cada vértice e imprima los grados de entrada y salida para todos los vértices al final.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to find the in and out degrees
// of the vertices of the given graph
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to print the in and out degrees
// of all the vertices of the given graph
void findInOutDegree(vector<vector<int>> adjlist,
int n)
{
vector<int> iN(n,0);
vector<int> ouT(n,0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
// Out degree for ith vertex will be the count
// of direct paths from i to other vertices
ouT[i] = adjlist[i].size();
// Every vertex that has an incoming
// edge from i
for(int j=0;j<adjlist[i].size();j++)
iN[adjlist[i][j]]++;
}
cout << "Vertex\t\tIn\t\tOut" << endl;
for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
cout << k << "\t\t"
<< iN[k] << "\t\t"
<< ouT[k] << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Adjacency list representation of the graph
vector<vector<int>> adjlist;
// Vertices 1 and 2 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 0
vector<int> tmp;
tmp.push_back(1);
tmp.push_back(2);
adjlist.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
// Vertex 3 has an incoming edge
// from vertex 1
tmp.push_back(3);
adjlist.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
// Vertices 0, 5 and 6 have an incoming
// edge from vertex 2
tmp.push_back(0);
tmp.push_back(5);
tmp.push_back(6);
adjlist.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
// Vertices 1 and 4 have an incoming
// edge from vertex 3
tmp.push_back(1);
tmp.push_back(4);
adjlist.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
// Vertices 2 and 3 have an incoming
// edge from vertex 4
tmp.push_back(2);
tmp.push_back(3);
adjlist.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
// Vertices 4 and 6 have an incoming
// edge from vertex 5
tmp.push_back(4);
tmp.push_back(6);
adjlist.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
// Vertex 5 has an incoming
// edge from vertex 6
tmp.push_back(5);
adjlist.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
int n = adjlist.size();
findInOutDegree(adjlist, n);
}
// This code is contributed by saurabhgpta248
Java
// Java program to find the in and out degrees
// of the vertices of the given graph
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Function to print the in and out degrees
// of all the vertices of the given graph
static void findInOutDegree(List<List<Integer> > adjList, int n)
{
int in[] = new int[n];
int out[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < adjList.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> list = adjList.get(i);
// Out degree for ith vertex will be the count
// of direct paths from i to other vertices
out[i] = list.size();
for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++)
// Every vertex that has an incoming
// edge from i
in[list.get(j)]++;
}
System.out.println("Vertex\tIn\tOut");
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
System.out.println(k + "\t" + in[k] + "\t" + out[k]);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Adjacency list representation of the graph
List<List<Integer> > adjList = new ArrayList<>();
// Vertices 1 and 2 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 0
List<Integer> tmp =
new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1, 2));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertex 3 has an incoming edge from vertex 1
tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(3));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertices 0, 5 and 6 have an incoming
// edge from vertex 2
tmp =
new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 5, 6));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertices 1 and 4 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 3
tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1, 4));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertices 2 and 3 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 4
tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(2, 3));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertices 4 and 6 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 5
tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(4, 6));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertex 5 has an incoming edge from vertex 6
tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(5));
adjList.add(tmp);
int n = adjList.size();
findInOutDegree(adjList, n);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to find the in and out
# degrees of the vertices of the given graph
# Function to print the in and out degrees
# of all the vertices of the given graph
def findInOutDegree(adjList, n):
_in = [0] * n
out = [0] * n
for i in range(0, len(adjList)):
List = adjList[i]
# Out degree for ith vertex will be the count
# of direct paths from i to other vertices
out[i] = len(List)
for j in range(0, len(List)):
# Every vertex that has
# an incoming edge from i
_in[List[j]] += 1
print("Vertex\tIn\tOut")
for k in range(0, n):
print(str(k) + "\t" + str(_in[k]) +
"\t" + str(out[k]))
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Adjacency list representation of the graph
adjList = []
# Vertices 1 and 2 have an incoming edge
# from vertex 0
adjList.append([1, 2])
# Vertex 3 has an incoming edge from vertex 1
adjList.append([3])
# Vertices 0, 5 and 6 have an
# incoming edge from vertex 2
adjList.append([0, 5, 6])
# Vertices 1 and 4 have an
# incoming edge from vertex 3
adjList.append([1, 4])
# Vertices 2 and 3 have an
# incoming edge from vertex 4
adjList.append([2, 3])
# Vertices 4 and 6 have an
# incoming edge from vertex 5
adjList.append([4, 6])
# Vertex 5 has an incoming edge from vertex 6
adjList.append([5])
n = len(adjList)
findInOutDegree(adjList, n)
# This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain
C#
// C# program to find the in and out degrees
// of the vertices of the given graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Function to print the in and out degrees
// of all the vertices of the given graph
static void findInOutDegree(List<List<int>> adjList, int n)
{
int []iN = new int[n];
int []ouT = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < adjList.Count; i++)
{
List<int> list = adjList[i];
// Out degree for ith vertex will be the count
// of direct paths from i to other vertices
ouT[i] = list.Count;
for (int j = 0; j < list.Count; j++)
// Every vertex that has an incoming
// edge from i
iN[list[j]]++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Vertex\t\tIn\t\tOut");
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
Console.WriteLine(k + "\t\t" +
iN[k] + "\t\t" + ouT[k]);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Adjacency list representation of the graph
List<List<int> > adjList = new List<List<int>>();
// Vertices 1 and 2 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 0
List<int> tmp =
new List<int>{1, 2};
adjList.Add(tmp);
// Vertex 3 has an incoming edge from vertex 1
tmp = new List<int>{3};
adjList.Add(tmp);
// Vertices 0, 5 and 6 have an incoming
// edge from vertex 2
tmp =
new List<int>{0, 5, 6};
adjList.Add(tmp);
// Vertices 1 and 4 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 3
tmp = new List<int>{1, 4};
adjList.Add(tmp);
// Vertices 2 and 3 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 4
tmp = new List<int>{2, 3};
adjList.Add(tmp);
// Vertices 4 and 6 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 5
tmp = new List<int>{4, 6};
adjList.Add(tmp);
// Vertex 5 has an incoming edge from vertex 6
tmp = new List<int>{5};
adjList.Add(tmp);
int n = adjList.Count;
findInOutDegree(adjList, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Vertex In Out 0 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 3 3 2 2 4 2 2 5 2 2 6 2 1
Complejidad temporal : O(V + E) donde V y E son los números de vértices y aristas en el gráfico respectivamente.
Espacio Auxiliar : O(V + E).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por janice_shah y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA