Dadas las siguientes entradas:
- Una ecuación diferencial ordinaria que define el valor de dy/dx en la forma x e y .
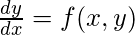
- Valor inicial de y, es decir, y(0) .
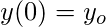
La tarea es encontrar el valor de la función desconocida y en un punto dado x, es decir, y(x) .
Ejemplo:
Entrada: x 0 = 0, y 0 = 1, x = 2, h = 0,2
Salida: y(x) = 0,645590
Entrada: x 0 = 2, y 0 = 1, x = 4, h = 0,4;
Salida: y(x) = 4.122991
Enfoque:
El método de Runge-Kutta encuentra un valor aproximado de y para una x dada. Solo las ecuaciones diferenciales ordinarias de primer orden se pueden resolver utilizando el método de segundo orden de Runge Kutta.
A continuación se muestra la fórmula utilizada para calcular el siguiente valor y n+1 a partir del valor anterior y n .
Por lo tanto:
yn+1 = value of y at (x = n + 1) yn = value of y at (x = n) where 0 ≤ n ≤ (x - x0)/h h is step height xn+1 = x0 + h
La fórmula esencial para calcular el valor de y(n+1): ![]()
![]()
![]()
La fórmula básicamente calcula el siguiente valor y n+1 utilizando y n actual más el promedio ponderado de dos incrementos:
- K 1 es el incremento basado en la pendiente al comienzo del intervalo, usando y.
- K 2 es el incremento basado en la pendiente en el punto medio del intervalo, usando (y + h*K 1/2 ) .
El método es de segundo orden, lo que significa que el error de truncamiento local es del orden de O(h 3 ), mientras que el error total acumulado es del orden de O(h 4 ).
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to implement Runge
// Kutta method
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A sample differential equation
// "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
float dydx(float x, float y)
{
return (x + y - 2);
}
// Finds value of y for a given x
// using step size h
// and initial value y0 at x0.
float rungeKutta(float x0, float y0,
float x, float h)
{
// Count number of iterations
// using step size or
// step height h
int n = (int)((x - x0) / h);
float k1, k2;
// Iterate for number of iterations
float y = y0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Apply Runge Kutta Formulas
// to find next value of y
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1);
// Update next value of y
y = y + (1.0 / 6.0) * (k1 + 2 * k2);
// Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
}
return y;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
float x0 = 0, y = 1,
x = 2, h = 0.2;
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << "y(x) = " << rungeKutta(x0, y, x, h);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivani
C
// C program to implement Runge
// Kutta method
#include <stdio.h>
// A sample differential equation
// "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
float dydx(float x, float y)
{
return (x + y - 2);
}
// Finds value of y for a given x
// using step size h
// and initial value y0 at x0.
float rungeKutta(float x0, float y0,
float x, float h)
{
// Count number of iterations
// using step size or
// step height h
int n = (int)((x - x0) / h);
float k1, k2;
// Iterate for number of iterations
float y = y0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Apply Runge Kutta Formulas
// to find next value of y
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1);
// Update next value of y
y = y + (1.0 / 6.0) * (k1 + 2 * k2);
// Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
}
return y;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
float x0 = 0, y = 1,
x = 2, h = 0.2;
printf("y(x) = %f",
rungeKutta(x0, y, x, h));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to implement Runge
// Kutta method
class GFG {
// A sample differential equation
// "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
static double dydx(double x, double y)
{
return (x + y - 2);
}
// Finds value of y for a given x
// using step size h
// and initial value y0 at x0.
static double rungeKutta(double x0, double y0,
double x, double h)
{
// Count number of iterations
// using step size or
// step height h
int n = (int)((x - x0) / h);
double k1, k2;
// Iterate for number of iterations
double y = y0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Apply Runge Kutta Formulas
// to find next value of y
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1);
// Update next value of y
y = y + (1.0 / 6.0) * (k1 + 2 * k2);
// Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
}
return y;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
double x0 = 0, y = 1,
x = 2, h = 0.2;
System.out.println(rungeKutta(x0, y, x, h));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Yash_R
Python3
# Python3 program to implement Runge
# Kutta method
# A sample differential equation
# "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
def dydx(x, y) :
return (x + y - 2);
# Finds value of y for a given x
# using step size h
# and initial value y0 at x0.
def rungeKutta(x0, y0, x, h) :
# Count number of iterations
# using step size or
# step height h
n = round((x - x0) / h);
# Iterate for number of iterations
y = y0;
for i in range(1, n + 1) :
# Apply Runge Kutta Formulas
# to find next value of y
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h, y + 0.5 * k1);
# Update next value of y
y = y + (1.0 / 6.0) * (k1 + 2 * k2);
# Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
return y;
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
x0 = 0; y = 1;
x = 2; h = 0.2;
print("y(x) =",rungeKutta(x0, y, x, h));
# This code is contributed by Yash_R
C#
// C# program to implement Runge
// Kutta method
using System;
class GFG {
// A sample differential equation
// "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
static double dydx(double x, double y)
{
return (x + y - 2);
}
// Finds value of y for a given x
// using step size h
// and initial value y0 at x0.
static double rungeKutta(double x0, double y0,
double x, double h)
{
// Count number of iterations
// using step size or
// step height h
int n = (int)((x - x0) / h);
double k1, k2;
// Iterate for number of iterations
double y = y0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Apply Runge Kutta Formulas
// to find next value of y
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1);
// Update next value of y
y = y + (1.0 / 6.0) * (k1 + 2 * k2);
// Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
}
return y;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main (string[] args)
{
double x0 = 0, y = 1,
x = 2, h = 0.2;
Console.WriteLine(rungeKutta(x0, y, x, h));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Yash_R
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to implement Runge
// Kutta method
// A sample differential equation
// "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
function dydx(x, y)
{
return (x + y - 2);
}
// Finds value of y for a given x
// using step size h
// and initial value y0 at x0.
function rungeKutta(x0, y0, x, h)
{
// Count number of iterations
// using step size or
// step height h
let n = ((x - x0) / h);
let k1, k2;
// Iterate for number of iterations
let y = y0;
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Apply Runge Kutta Formulas
// to find next value of y
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1);
// Update next value of y
y = y + (1.0 / 6.0) * (k1 + 2 * k2);
// Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
}
return y;
}
// Driver Code
let x0 = 0, y = 1,
x = 2, h = 0.2;
document.write(rungeKutta(x0, y, x, h).toFixed(6));
</script>
y(x) = 0.645590
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Referencia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Runge%E2%80%93Kutta_methods
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por kondalalith1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA