Prerrequisito: Introducción a las Redes Sociales
En las redes sociales, la red es de 2 tipos: red sin firmar y red firmada. En la red sin firmar, no hay señales entre ningún Node, y en la red firmada, siempre hay una señal entre 2 Nodes, ya sea + o -. El signo ‘+’ indica amistad entre 2 Nodes y el signo ‘-‘ indica enemistad entre 2 Nodes.
Nuestra tarea es crear una red firmada en N Nodes utilizando el lenguaje python.
Acercarse:
- Cree un gráfico y agréguele Nodes.
- Agregue todos los bordes posibles y asígnele un signo.
- Obtenga una lista de todos los triángulos posibles en una red.
- Almacene los detalles del signo de todos los triángulos en la red.
- Cuente el número total del triángulo inestable en la red
- Ahora toma un triángulo inestable de la lista y hazlo estable.
- Nuevamente cuente un número de triángulos inestables.
- Repita los pasos 6 y 7 hasta que no haya un triángulo inestable.
- Ahora forme una coalición (Nodes amigos en la coalición 1 con color rojo y Nodes enemigos en otra coalición con color azul) y muestre el gráfico.
A continuación se muestra la implementación.
Python3
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import itertools
def get_signs_of_graph(g, tris_list):
# eg-['A-B','B-C','C-A']
all_signs = []
for i in range(len(tris_list)):
t = []
t.append(g[tris_list[i][0]][tris_list[i][1]]['sign'])
t.append(g[tris_list[i][1]][tris_list[i][2]]['sign'])
t.append(g[tris_list[i][2]][tris_list[i][0]]['sign'])
all_signs.append(t)
return all_signs
def unstablecount(all_signs):
stable = 0
unstable = 0
for i in range(len(all_signs)):
if (((all_signs[i]).count('+')) == 1 or ((all_signs[i]).count('+')) == 3):
stable += 1
unstable = len(all_signs) - stable
return unstable
def move_graph_to_stable(g, tris_list, all_signs):
found_unstable = False
ran = 0
while (found_unstable == False):
ran = random.randint(0, len(tris_list) - 1)
if (all_signs[ran].count('+') % 2 == 0):
found_unstable = True
else:
continue
r = random.randint(1, 3)
if (all_signs[ran].count('+') == 2):
if (r == 1):
if (g[tris_list[ran][0]][tris_list[ran][1]]['sign'] == '+'):
g[tris_list[ran][0]][tris_list[ran][1]]['sign'] = '-'
else:
g[tris_list[ran][0]][tris_list[ran][1]]['sign'] = '+'
elif (r == 2):
if (g[tris_list[ran][1]][tris_list[ran][2]]['sign'] == '+'):
g[tris_list[ran][1]][tris_list[ran][2]]['sign'] = '-'
else:
g[tris_list[ran][1]][tris_list[ran][2]]['sign'] = '+'
else:
if (g[tris_list[ran][0]][tris_list[ran][2]]['sign'] == '+'):
g[tris_list[ran][0]][tris_list[ran][2]]['sign'] = '-'
else:
g[tris_list[ran][0]][tris_list[ran][2]]['sign'] = '+'
else:
if (r == 1):
g[tris_list[ran][0]][tris_list[ran][1]]['sign'] = '+'
elif (r == 2):
g[tris_list[ran][1]][tris_list[ran][2]]['sign'] = '+'
else:
g[tris_list[ran][0]][tris_list[ran][2]]['sign'] = '+'
return g
def Coalition(g):
f = []
s = []
nodes = g.nodes()
r = random.choice(list(nodes))
f.append(r)
processed_nodes = []
to_be_processed = [r]
for each in to_be_processed:
if each not in processed_nodes:
neigh = list(g.neighbors(each))
for i in range(len(neigh)):
if (g[each][neigh[i]]['sign'] == '+'):
if (neigh[i] not in f):
f.append(neigh[i])
if (neigh[i] not in to_be_processed):
to_be_processed.append(neigh[i])
elif (g[each][neigh[i]]['sign'] == '-'):
if (neigh[i] not in s):
s.append(neigh[i])
processed_nodes.append(neigh[i])
processed_nodes.append(each)
return f, s
# 1.Create graph
g = nx.Graph()
n = 8
g.add_nodes_from(range(1, n + 1))
map = {1: "A", 2: "B", 3: "C", 4: "D", 5: "E",
6: "F", 7: "G", 8: "H", 9: "I", 10: "J"}
signs = ['+', '-']
g = nx.relabel_nodes(g, map)
# 2.Add every possible edge and assign sign
for i in g.nodes():
for j in g.nodes():
if (i != j):
g.add_edge(i, j, sign=random.choice(signs))
# 3.Display graph
edge_attributes = nx.get_edge_attributes(g, 'sign')
pos = nx.circular_layout(g)
nx.draw(g, pos, node_size=3000, with_labels=1)
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(
g, pos, edge_labels=edge_attributes, font_size=20, font_color='blue')
plt.show()
# 4.1.Get list of all the triangles in network
nodes = g.nodes()
tris_list = [list(x) for x in itertools.combinations(nodes, 3)]
# 4.2.Store the sign details of all the triangles
all_signs = get_signs_of_graph(g, tris_list)
# 4.3.Count total number of unstable triangle
# in the network
unstable = unstablecount(all_signs)
# 5 chose the triangle in the graph that is unstable
# and make the triangle stable
unstable_track = [unstable]
while (unstable != 0):
g = move_graph_to_stable(g, tris_list, all_signs)
all_signs = get_signs_of_graph(g, tris_list)
unstable = unstablecount(all_signs)
unstable_track.append(unstable)
# 6 Form the coalition
first, second = Coalition(g)
print(first)
print(second)
edge_labels = nx.get_edge_attributes(g, 'sign')
pos = nx.circular_layout(g)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(g, pos, nodelist=first,
node_color='red', node_size=4000)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(g, pos, nodelist=second,
node_color='blue', node_size=4000)
nx.draw_networkx_labels(g, pos)
nx.draw_networkx_edges(g, pos)
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(g, pos, edge_labels=edge_labels, font_color="red")
plt.show()
Producción:
['G', 'B', 'C', 'H'] ['A', 'D', 'E', 'F']
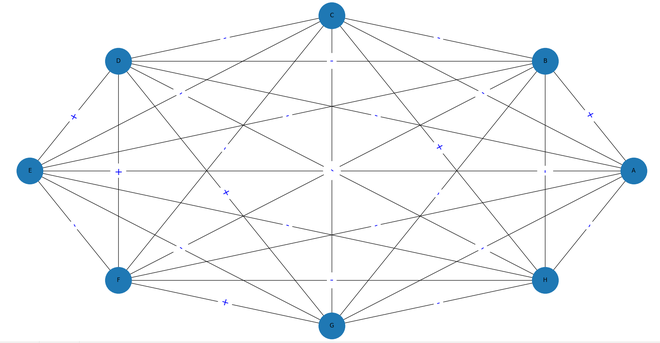
Red firmada inicial sin coalición
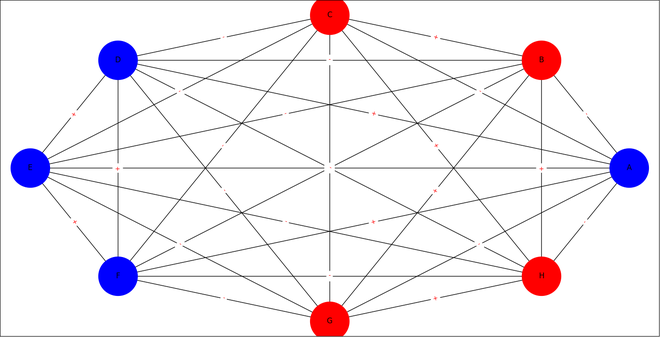
Red firmada final con coalición
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sankalpsharma424 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA