Al diseñar una aplicación GUI (interfaz gráfica de usuario), tendemos a hacer muchas etiquetas, pero a veces algunas etiquetas se superponen entre sí y solo se ve la etiqueta que está en la parte superior, por eso se necesita una etiqueta semitransparente.
Etiqueta normal vs Etiqueta semitransparente –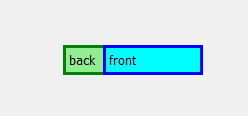

Para crear etiquetas semitransparentes setStyleSheet()se utiliza el método.
Sintaxis: label.setStyleSheet(“background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 10);”)
Aquí estamos configurando el color usando,RGBApor ejemplo, el factor de transparencia, 255 es completamente opaco y un alfa de 0 es completamente transparente.Argumento: Toma una string como argumento.
Acción realizada: Hace transparente el color de la etiqueta.
Código:
# importing the required libraries
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
import sys
class Window(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# set the title
self.setWindowTitle("Label")
# setting the geometry of window
self.setGeometry(0, 0, 400, 300)
# creating a label widget
# by default label will display at top left corner
self.label_1 = QLabel('back', self)
# moving position
self.label_1.move(100, 100)
# setting up border and background color
self.label_1.setStyleSheet("background-color: lightgreen;
border: 3px solid green")
# creating a label widget
# by default label will display at top left corner
self.label_2 = QLabel('front', self)
# moving position
self.label_2.move(140, 100)
# setting up border and background
# color with transparency factor
self.label_2.setStyleSheet("border: 3px solid blue;
background-color: rgba(0, 255, 255, 90);")
# show all the widgets
self.show()
# create pyqt5 app
App = QApplication(sys.argv)
# create the instance of our Window
window = Window()
# start the app
sys.exit(App.exec())
Producción :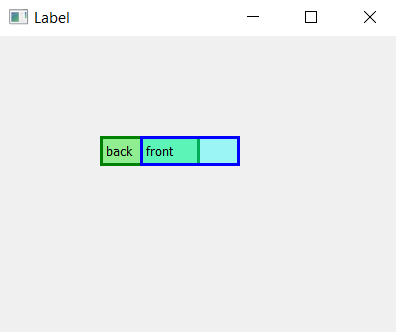
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por rakshitarora y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA