Matplotlib es una increíble biblioteca de visualización en Python para gráficos 2D de arrays. Matplotlib es una biblioteca de visualización de datos multiplataforma basada en arrays NumPy y diseñada para funcionar con la pila SciPy más amplia.
matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom
La matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom clase es una clase auxiliar a la que se puede llamar para trabajar con Annotation.
Sintaxis: class matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom(artist, ref_coord, unit=’points’)
Parámetro:
- artista: este objeto se utiliza para calcular el desplazamiento. Generalmente es un Artista, un BboxBase o Transform.
- ref_coord: Es una secuencia de longitud 2. Este valor es la ubicación del origen del desplazamiento en fracciones del cuadro delimitador del artista si es un Artista o BboxBase, mientras que el origen del desplazamiento es la transformación aplicada a este valor si el artista es una Transformación.
- unidad : Se utiliza para gestionar las unidades de pantalla a utilizar (píxeles o puntos) para la entrada de compensación.
Métodos de la clase:
- get_unit(self) : Es la unidad de entrada a la transformación utilizada por __call__.
- set_unit(self, unit): Es la unidad de entrada a la transformación utilizada por __call__ donde, el argumento de la unidad está en ‘puntos’ o ‘píxeles’.
Ejemplo 1:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.text
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([5,1], label="Label 1")
ax.plot([3,0], label="Label 2")
legend = ax.legend(loc="upper right")
# Create offset from lower right
# corner of legend box, (1.0,0) is
# the coordinates of the offset point
# in the legend coordinate system
offset = matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom(legend, (1.0, 0.0))
# Create annotation. Top right corner
# located -20 pixels below the offset
# point (lower right corner of legend).
ax.annotate("info_string",
xy = (0,0),
size = 14,
xycoords = 'figure fraction',
xytext = (0,-20),
textcoords = offset,
horizontalalignment = 'right',
verticalalignment = 'top')
# Draw the canvas for offset to take effect
fig.canvas.draw()
plt.show()
Producción: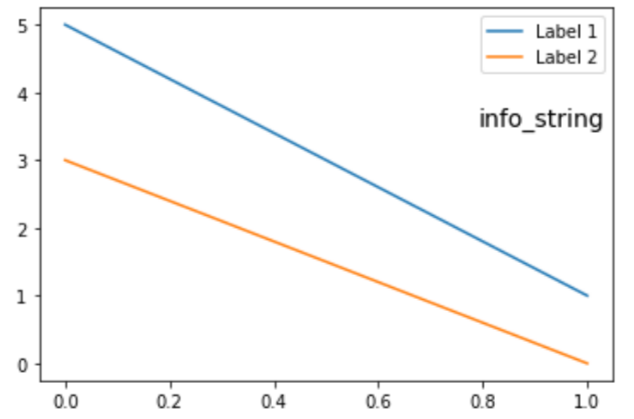
Ejemplo 2:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.text import OffsetFrom
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
bbox_args = dict(boxstyle ="round", fc ="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle ="->")
# Here we'll demonstrate the extents of the coordinate system and how
# we place annotating text.
ax1.annotate('figure fraction : 0, 0',
xy =(0, 0),
xycoords ='figure fraction',
xytext =(20, 20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "left",
va = "bottom",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax1.annotate('figure fraction : 1, 1',
xy =(1, 1),
xycoords ='figure fraction',
xytext = (-20, -20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "right",
va = "top",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax1.annotate('axes fraction : 0, 0',
xy = (0, 0),
xycoords ='axes fraction',
xytext = (20, 20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "left",
va = "bottom",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax1.annotate('axes fraction : 1, 1',
xy =(1, 1),
xycoords ='axes fraction',
xytext = (-20, -20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "right",
va = "top",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
# It is also possible to generate
# draggable annotations
an1 = ax1.annotate('Drag me 1', xy =(.5, .7),
xycoords ='data',
ha ="center", va ="center",
bbox = bbox_args,
)
an2 = ax1.annotate('Drag me 2', xy =(.5, .5),
xycoords = an1,
xytext =(.5, .3),
textcoords = 'axes fraction',
ha = "center",
va = "center",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = dict(patchB = an1.get_bbox_patch(),
connectionstyle = "arc3, rad = 0.2",
**arrow_args))
an1.draggable()
an2.draggable()
an3 = ax1.annotate('', xy =(.5, .5), xycoords = an2,
xytext =(.5, .5), textcoords = an1,
ha ="center", va ="center",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = dict(patchA = an1.get_bbox_patch(),
patchB = an2.get_bbox_patch(),
connectionstyle ="arc3, rad = 0.2",
**arrow_args))
# Finally we'll show off some more
# complex annotation and placement
text = ax2.annotate('xy =(0, 1)\nxycoords = ("data", "axes fraction")',
xy =(0, 1),
xycoords = ("data", 'axes fraction'),
xytext = (0, -20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "center",
va = "top",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax2.annotate('xy =(0.5, 0)\nxycoords = artist',
xy =(0.5, 0.),
xycoords = text,
xytext = (0, -20),
textcoords = 'offset points',
ha = "center",
va = "top",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax2.annotate('xy =(0.8, 0.5)\nxycoords = ax1.transData',
xy =(0.8, 0.5),
xycoords = ax1.transData,
xytext = (10, 10),
textcoords = OffsetFrom(ax2.bbox, (0, 0), "points"),
ha = "left",
va = "bottom",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax2.set(xlim =[-2, 2], ylim =[-2, 2])
plt.show()
Producción: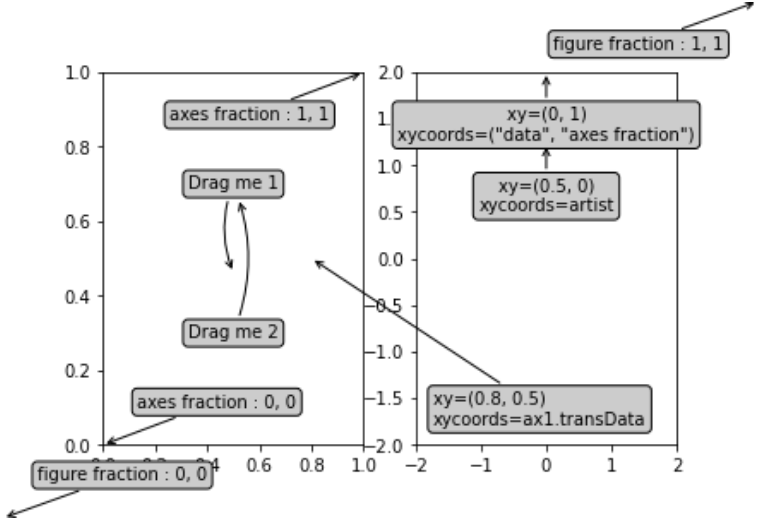
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por RajuKumar19 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA