El método setFrame() de p5.Image en la biblioteca p5.js se usa para establecer el índice del marco actualmente visible de la animación GIF.
Sintaxis:
setFrame( index )
Parámetros: Esta función acepta un solo parámetro como se mencionó anteriormente y se describe a continuación.
- índice: Es un número que denota el índice del cuadro que se va a mostrar.
Las siguientes bibliotecas se incluyen en la sección «head» de la página HTML al implementar los siguientes ejemplos.
<script src=”p5.Image.js”></script>
<script src=”p5.min.js”></script>
Ejemplo 1: Los siguientes ejemplos ilustran el método setFrame() en la biblioteca p5.js.
Javascript
function preload() {
example_gif =
loadImage("sample-gif.gif");
}
function setup() {
createCanvas(500, 300);
textSize(18);
example_gif.pause();
decFrameBtn =
createButton("Skip Backward 10 Frames");
decFrameBtn.position(30, 240);
decFrameBtn.mousePressed(skipBackward);
incFrameBtn =
createButton("Skip Forward 10 Frames");
incFrameBtn.position(220, 240);
incFrameBtn.mousePressed(skipForward);
}
function draw() {
clear();
text("Skip frames forward or backward " +
"by pressing the buttons", 20, 20);
// Draw the GIF on screen
image(example_gif, 20, 40, 260, 140);
// Get the current frame
let currFrame =
example_gif.getCurrentFrame();
text("The current frame is: " +
currFrame, 20, 200);
}
function skipForward() {
// Get the current playing frame of the GIF
let currFrame =
example_gif.getCurrentFrame();
// Move forward only if possible
if (currFrame <
example_gif.numFrames() - 10) {
// Add 10 to skip forward
let newFrame = currFrame + 10;
example_gif.setFrame(newFrame);
}
}
function skipBackward() {
// Get the current playing frame of the GIF
let currFrame =
example_gif.getCurrentFrame();
// Move forward only if possible
if (currFrame > 10) {
// Subtract 10 to skip forward
let newFrame = currFrame - 10;
example_gif.setFrame(newFrame);
}
}
Producción:
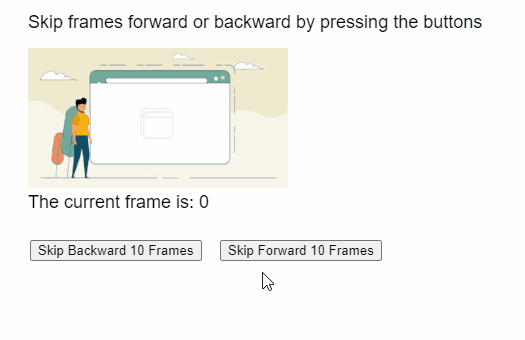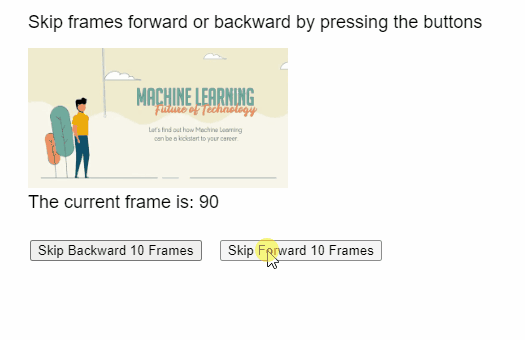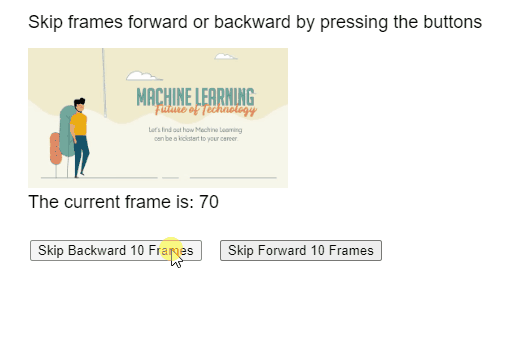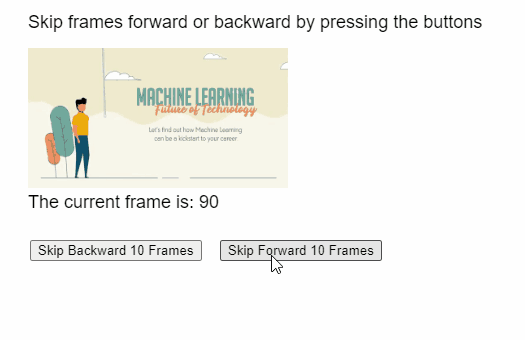
Ejemplo 2:
Javascript
function preload() {
example_gif =
loadImage("sample-gif.gif");
}
function setup() {
createCanvas(500, 300);
textSize(18);
example_gif.pause();
let totalFrames =
example_gif.numFrames() - 1;
frameSlider =
createSlider(0, totalFrames, 0, 1);
frameSlider.position(30, 240);
frameSlider.size(250);
}
function draw() {
clear();
text("Move the slider to set the " +
"current frame of the GIF", 20, 20);
// Draw the GIF on screen
image(example_gif, 20, 40, 260, 140);
// Set the current frame according to the
// value of the slider
example_gif.setFrame(frameSlider.value());
// Get the current frame
let currFrame =
example_gif.getCurrentFrame();
text("The current frame is: " +
currFrame, 20, 220);
}
Producción:

Editor en línea: https://editor.p5js.org/
Configuración del entorno: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/p5-js-soundfile-object-installation-and-methods/
Referencia: https://p5js.org/ referencia/#/p5.Imagen/setFrame
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sayantanm19 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA