La función zoom.scaleBy() en D3.js se usa para escalar la transformación de zoom actual de los elementos seleccionados por k. pags
Sintaxis:
zoom.scaleBy(selection, k[, p])
Parámetros: esta función acepta tres parámetros, como se mencionó anteriormente y se describe a continuación:
- selección: Este parámetro puede ser de selección o de transición.
- k: este parámetro es un factor de escala, especificado como números o como funciones
- p: el valor de p no se especifica, su valor predeterminado es el centro de la extensión de la ventana gráfica.
Valor devuelto: esta función devuelve el comportamiento del zoom.
Los siguientes programas ilustran la función zoom.scaleBy() en D3.js
Ejemplo 1:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src=
"https://d3js.org/d3.v4.min.js">
</script>
<style>
circle {
opacity: 0.7;
}
g.zoom-controls {
cursor: pointer;
pointer-events: all;
}
g.zoom-controls rect {
fill: white;
stroke: #596877;
stroke-width: 1;
}
g.zoom-controls line {
stroke: #596877;
stroke-width: 2;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h1 style="color: green;">
Geeksforgeeks
</h1>
<h3>
D3.js | zoom.scaleBy() Function
</h3>
<svg>
<g class="zoom-controls" transform="translate(10, 10)">
<g id="zoom-in" transform="translate(0, 0)">
<rect width="30" height="30"></rect>
<line x1="5" y1="15" x2="25" y2="15"></line>
<line x1="15" y1="5" x2="15" y2="25"></line>
</g>
<g id="zoom-out" transform="translate(30, 0)">
<rect width="30" height="30"></rect>
<line x1="5" y1="15" x2="25" y2="15"></line>
</g>
</g>
</svg>
<script>
var radius = 10;
var svg = d3.select('svg');
var dimension = document.body.getBoundingClientRect();
var data = d3.range(0, 25).map(function() {
return {
x: getRandom(radius, dimension.width - radius),
y: getRandom(radius, dimension.height - radius)
}
});
var zoom = d3.zoom()
.on('zoom', function() {
canvas.attr('transform', d3.event.transform);
});
var canvas = svg
.attr('width', dimension.width)
.attr('height', dimension.height)
.call(zoom)
.insert('g', ':first-child');
canvas.selectAll('circle')
.data(data)
.enter()
.append('circle')
.attr('r', radius)
.attr('cx', function(d) {
return d.x;
}).attr('cy', function(d) {
return d.y;
}).style('fill', function() {
return d3.schemeCategory10[getRandom(0, 9)]
});
d3.select('#zoom-in').on('click', function() {
// Smooth zooming
zoom.scaleBy(svg.transition().duration(750), 1.3);
});
d3.select('#zoom-out').on('click', function() {
// Ordinal zooming
zoom.scaleBy(svg, 1 / 1.3);
});
function getRandom(min, max) {
min = Math.ceil(min);
max = Math.floor(max);
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}
</script>
</center>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
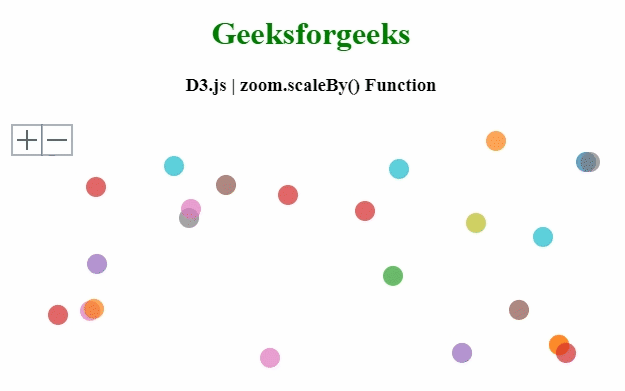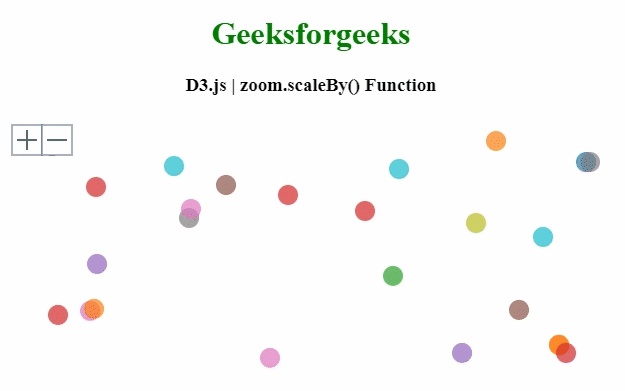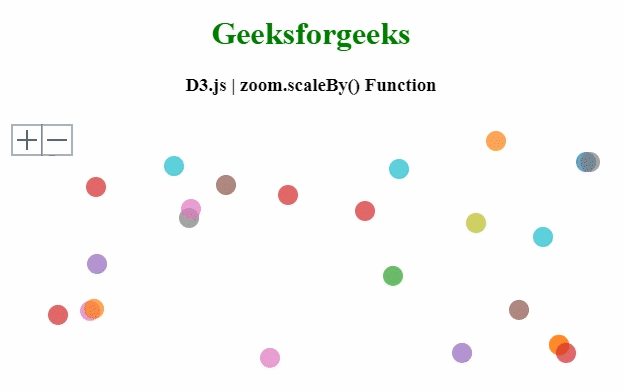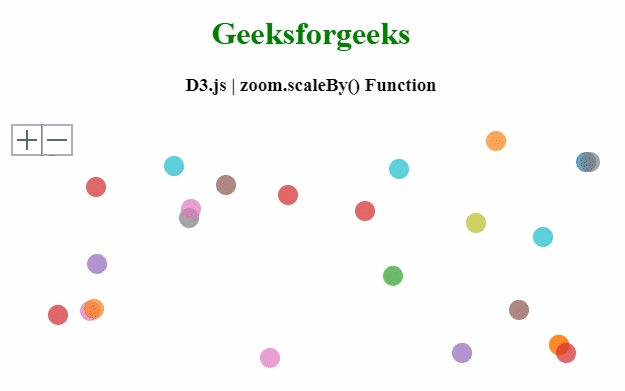
Ejemplo 2:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src=
"https://d3js.org/d3.v5.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h1 style="color: green;">
Geeksforgeeks
</h1>
<h3>D3.js | zoom.scaleBy() Function</h3>
<svg height="100px" width="100px"></svg>
<script>
const zoom_action = () => g.attr("transform", d3.event.transform);
// Create the zoom handler
const zoom = d3.zoom()
.on("zoom", zoom_action);
// Get SVG element and apply zoom behaviour
var svg = d3
.select("svg")
.call(zoom);
// Create Group that will be zoomed
var g = svg.append("g");
// Create circle
g.append("circle")
.attr("cx",0)
.attr("cy",0)
.attr("r", 5)
.style("fill","green");
// Use of zoom.scaleBy Function
zoom.scaleBy(svg, 5);
zoom.translateBy(svg, 50, 50);
</script>
</center>
</body>
</html>
Producción:

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por SHUBHAMSINGH10 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA