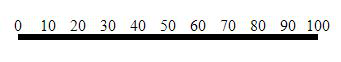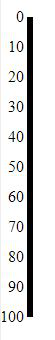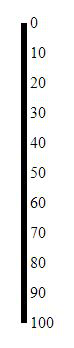La función d3.axis.orient() en D3.js se usa para establecer la orientación y devuelve el eje. Si no se especifica la orientación, devuelve la orientación actual que por defecto es «abajo».
Sintaxis:
axis.orient([orientation])
Parámetros: esta función acepta un solo parámetro como se mencionó anteriormente y se describe a continuación:
- orientación: Este parámetro es el tamaño para establecer la orientación del eje. Se admiten cuatro orientaciones: «superior», «inferior». «izquierda y derecha».
Valor devuelto: esta función devuelve el eje.
Los siguientes programas ilustran la función d3.axis.orient() en D3.js:
Ejemplo 1:
HTML
<html>
<head>
<title>
D3.js | d3.axis.orient() Function
</title>
<script src = "//d3js.org/d3.v3.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var svg = d3.select("body").append("svg")
.attr("width", 400)
.attr("height", 400);
// Create the Scale we will use for the Axis
var axisScale = d3.scale.linear()
.domain([0, 100])
.range([0, 300]);
// Create the Axis
var xAxis = d3.svg.axis()
.scale(axisScale)
.orient("top");
// Create an SVG group Element for the Axis
// elements and call the xAxis function
svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(50,50)")
.call(xAxis);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
Ejemplo 2:
HTML
<html>
<head>
<title>
D3.js | d3.axis.orient() Function
</title>
<script src = "//d3js.org/d3.v3.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var svg = d3.select("body").append("svg")
.attr("width", 400)
.attr("height", 400);
// Create the Scale we will use for the Axis
var axisScale = d3.scale.linear()
.domain([0, 100])
.range([0, 300]);
// Create the Axis
var xAxis = d3.svg.axis()
.scale(axisScale)
.orient("left");
// Create an SVG group Element for the Axis
// elements and call the xAxis function
svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(50,50)")
.call(xAxis);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
Ejemplo 3:
HTML
<html>
<head>
<title>
D3.js | d3.axis.orient() Function
</title>
<script src = "//d3js.org/d3.v3.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var svg = d3.select("body").append("svg")
.attr("width", 400)
.attr("height", 400);
// Create the Scale we will use for the Axis
var axisScale = d3.scale.linear()
.domain([0, 100])
.range([0, 300]);
// Create the Axis
var xAxis = d3.svg.axis()
.scale(axisScale)
.orient("right");
// Create an SVG group Element for the Axis
// elements and call the xAxis function
svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(50,50)")
.call(xAxis);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por SHUBHAMSINGH10 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA