¿Qué es la cola?
Una cola es una estructura lineal que sigue un orden particular en el que se realizan las operaciones. El orden es Primero en entrar, primero en salir (FIFO). Un buen ejemplo de una cola es cualquier cola de consumidores de un recurso donde se atiende primero al consumidor que llegó primero. Se necesita un tiempo constante para agregar o eliminar un elemento en una cola.
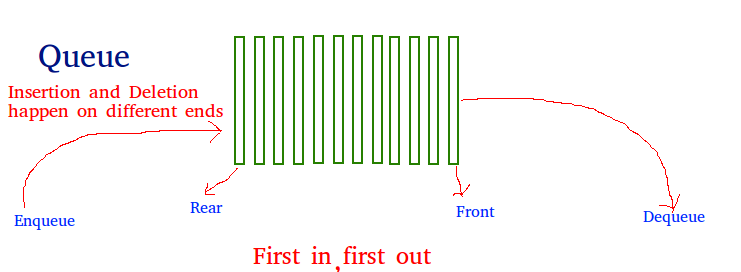
Las colas deben usarse sobre arreglos cuando necesitamos trabajar con datos en el formulario FIFO .
Limitación de cola: solo se puede acceder a un elemento a la vez.

En JavaScript, las arrays tienen métodos como pop y shift que definen la clase Queue: operaciones Enqueue y Dequeue. Con esto, una cola se puede implementar fácilmente.
Estructura básica de la cola: el siguiente ejemplo se ejecuta con el comando “$node skeleton.js” para obtener la estructura básica de la cola.
javascript
// Define Queue function
function Queue(array) {
this.array = [];
if (array) this.array = array;
}
// Add Get Buffer property to object
// constructor which slices the array
Queue.prototype.getBuffer = function() {
return this.array.slice();
}
// Add isEmpty properties to object constructor
// which returns the length of the array
Queue.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.array.length == 0;
}
// Instance of the Queue class
var queue1 = new Queue(); //Queue { array: [] }
console.log(queue1);
Ejemplo:
javascript
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Enqueue Operation</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src=
"https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/p5.js/0.8.0/p5.min.js"
type="text/javascript"></script>
<style>
body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
canvas {
vertical-align: top;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Define Queue function
function Queue(array) {
this.array = [];
if (array) this.array = array;
}
// Add Get Buffer property to object
// constructor which slices the array
Queue.prototype.getBuffer = function() {
return this.array.slice();
}
// Add isEmpty properties to object constructor
// which returns the length of the array
Queue.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.array.length == 0;
}
// Instance of the Queue class
var queue1 = new Queue(); // Queue { array: [] }
console.log(queue1);
// Add Push property to object constructor
// which push elements to the array
Queue.prototype.enqueue = function(value) {
this.array.push(value);
}
function setup() {
// Create Canvas of size display width * 300
createCanvas(displayWidth, 300);
}
function draw() {
// Set background color
background("grey");
// Set stroke weight
strokeWeight(3);
textAlign(CENTER);
textSize(24);
text("Queue Implementation Using P5.js",
windowWidth/2, 20);
textAlign(LEFT);
textSize(14);
// Set stroke color
stroke('green');
line(10, 45, 90, 45);
rect(10, 30, 60, 30);
noStroke();
text("FRONT", 20, 50);
// Display queue
for(var i = 0; i <= queue1['array'].length-1; i++) {
var p = 10;
translate(70, 0);
strokeWeight(3);
stroke('green');
line(10+p, 45, p+80, 45);
rect(10+p, 30, 40+p, 30);
noStroke();
text(queue1['array'][i], 40, 50);
p += 10;
}
// Set stroke color
stroke('green');
translate(70, 0);
rect(10, 30, 60, 30);
noStroke();
text("REAR", 20, 50);
}
// Peek Function
Queue.prototype.peek = function() {
return this.array[this.array.length-1];
}
// Driver Code
// Call to Enqueue operation
queue1.enqueue(1);
queue1.enqueue(2);
queue1.enqueue(3);
queue1.enqueue(19);
queue1.enqueue(11);
queue1.enqueue(15);
queue1.enqueue(14);
queue1.enqueue(18);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:

Después de poner en cola ’25’ llamando a queue1.enqueue(25) la función de cambios posteriores a 25.

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sarthak_ishu11 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA