El método defaultReadObject() de la clase ObjectInputStream en Java se usa para leer los campos no estáticos y no transitorios de la clase actual de esta secuencia.
Sintaxis:
public void defaultReadObject()
Parámetros: Este método no acepta ningún parámetro.
Valor devuelto: este método devuelve el valor que se ha leído.
Errores y excepciones: la función arroja tres excepciones que se describen a continuación:
- ClassNotFoundException: la excepción se lanza si no se pudo encontrar la clase de un objeto serializado.
- IOException: la excepción se lanza si se produce un error de E/S.
- NotActiveException: la excepción se lanza si la secuencia no está leyendo objetos actualmente.
El siguiente programa ilustra el método anterior:
Programa 1:
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// the above method
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
// create a new file
// with an ObjectOutputStream
FileOutputStream out
= new FileOutputStream("Shubham.txt");
ObjectOutputStream out1
= new ObjectOutputStream(out);
// write
out1.writeObject(new solve());
// Flushes the stream
out1.flush();
// create an ObjectInputStream
// for the file
ObjectInputStream example
= new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("Shubham.txt"));
// Read from the stream
solve ans = (solve)example.readObject();
System.out.println(ans.str);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class solve implements Serializable {
String str = "Geeksforgeeks";
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream res)
throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException
{
// By using defaultReadObject() method is
// to read non-static fields of the present
// class from the ObjectInputStream
res.defaultReadObject();
}
}
}
Producción:
Programa 2:
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// the above method
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
// create a new file
// with an ObjectOutputStream
FileOutputStream out
= new FileOutputStream("Shubham.txt");
ObjectOutputStream out1
= new ObjectOutputStream(out);
// write
out1.writeObject(new solve());
// Flushes the stream
out1.flush();
// create an ObjectInputStream
// for the file
ObjectInputStream example
= new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("Shubham.txt"));
// Read from the stream
solve ans = (solve)example.readObject();
// System.out.println(ans.str);
System.out.println(ans.in);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class solve implements Serializable {
// String str = "Geeksforgeeks";
Integer in = new Integer(112414);
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream res)
throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException
{
// By using defaultReadObject() method is
// to read non-static fields of the present
// class from the ObjectInputStream
res.defaultReadObject();
}
}
}
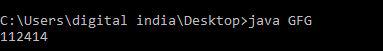
Producción:
Referencia:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/10/docs/api/java/io/ObjectInputStream.html#defaultReadObject()
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por SHUBHAMSINGH10 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA