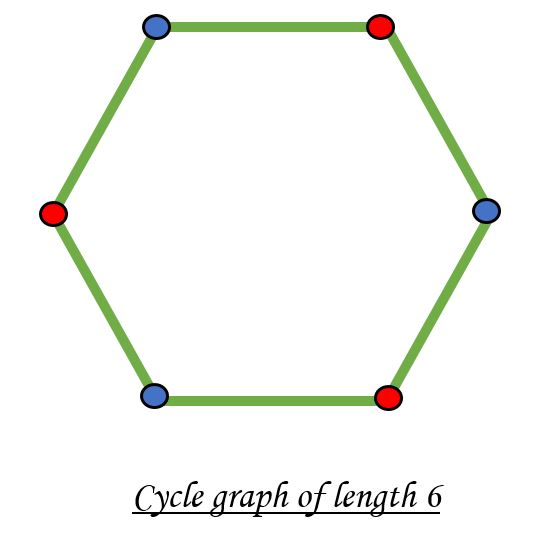
Dado un grafo conexo, comprueba si el grafo es bipartito o no. Un gráfico bipartito es posible si la coloración del gráfico es posible utilizando dos colores, de modo que los vértices de un conjunto estén coloreados con el mismo color. Tenga en cuenta que es posible colorear un gráfico de ciclo con un ciclo par usando dos colores. Por ejemplo, vea el siguiente gráfico.
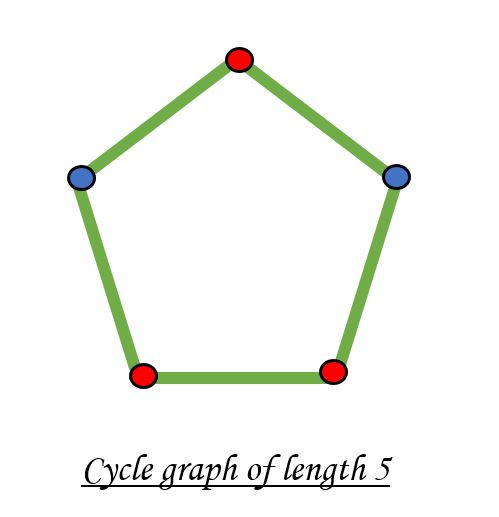
No es posible colorear un gráfico de ciclo con un ciclo impar utilizando dos colores.
En la publicación anterior, se discutió un enfoque que usa BFS . En esta publicación, se ha implementado un enfoque que utiliza DFS .
A continuación se muestra el algoritmo para verificar la bipartición de un gráfico.
- Use una array color[] que almacena 0 o 1 para cada Node que denota colores opuestos.
- Llame a la función DFS desde cualquier Node.
- Si el Node u no ha sido visitado anteriormente, entonces asigne !color[v] a color[u] y vuelva a llamar a DFS para visitar los Nodes conectados a u.
- Si en algún punto color[u] es igual a color[v], entonces el Node no es bipartito.
- Modifique la función DFS para que devuelva un valor booleano al final.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to check if a connected
// graph is bipartite or not using DFS
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to store the connected nodes
void addEdge(vector<int> adj[], int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
// function to check whether a graph is bipartite or not
bool isBipartite(vector<int> adj[], int v,
vector<bool>& visited, vector<int>& color)
{
for (int u : adj[v]) {
// if vertex u is not explored before
if (visited[u] == false) {
// mark present vertices as visited
visited[u] = true;
// mark its color opposite to its parent
color[u] = !color[v];
// if the subtree rooted at vertex v is not bipartite
if (!isBipartite(adj, u, visited, color))
return false;
}
// if two adjacent are colored with same color then
// the graph is not bipartite
else if (color[u] == color[v])
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// no of nodes
int N = 6;
// to maintain the adjacency list of graph
vector<int> adj[N + 1];
// to keep a check on whether
// a node is discovered or not
vector<bool> visited(N + 1);
// to color the vertices
// of graph with 2 color
vector<int> color(N + 1);
// adding edges to the graph
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
addEdge(adj, 5, 6);
addEdge(adj, 6, 1);
// marking the source node as visited
visited[1] = true;
// marking the source node with a color
color[1] = 0;
// Function to check if the graph
// is Bipartite or not
if (isBipartite(adj, 1, visited, color)) {
cout << "Graph is Bipartite";
}
else {
cout << "Graph is not Bipartite";
}
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to check if a connected
// graph is bipartite or not using DFS
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to store the connected nodes
static void addEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj,
int u, int v)
{
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
// Function to check whether a
// graph is bipartite or not
static boolean isBipartite(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj,
int v, boolean visited[],
int color[])
{
for(int u : adj.get(v))
{
// If vertex u is not explored before
if (visited[u] == false)
{
// Mark present vertices as visited
visited[u] = true;
// Mark its color opposite to its parent
color[u] = 1 - color[v];
// If the subtree rooted at vertex
// v is not bipartite
if (!isBipartite(adj, u, visited, color))
return false;
}
// If two adjacent are colored with
// same color then the graph is
// not bipartite
else if (color[u] == color[v])
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No of nodes
int N = 6;
// To maintain the adjacency list of graph
ArrayList<
ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<
ArrayList<Integer>>(N + 1);
// Initialize all the vertex
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
{
adj.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// To keep a check on whether
// a node is discovered or not
boolean visited[] = new boolean[N + 1];
// To color the vertices
// of graph with 2 color
int color[] = new int[N + 1];
// The value '-1' of colorArr[i] is
// used to indicate that no color is
// assigned to vertex 'i'. The value
// 1 is used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
Arrays.fill(color, -1);
// Adding edges to the graph
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
addEdge(adj, 5, 6);
addEdge(adj, 6, 1);
// Marking the source node as visited
visited[1] = true;
// Marking the source node with a color
color[1] = 0;
// Function to check if the graph
// is Bipartite or not
if (isBipartite(adj, 1, visited, color))
{
System.out.println("Graph is Bipartite");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Graph is not Bipartite");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by adityapande88
Python3
# Python3 program to check if a connected
# graph is bipartite or not using DFS
# Function to store the connected nodes
def addEdge(adj, u, v):
adj[u].append(v)
adj[v].append(u)
# Function to check whether a graph is
# bipartite or not
def isBipartite(adj, v, visited, color):
for u in adj[v]:
# If vertex u is not explored before
if (visited[u] == False):
# Mark present vertices as visited
visited[u] = True
# Mark its color opposite to its parent
color[u] = not color[v]
# If the subtree rooted at vertex v
# is not bipartite
if (not isBipartite(adj, u,
visited, color)):
return False
# If two adjacent are colored with
# same color then the graph is not
# bipartite
elif (color[u] == color[v]):
return False
return True
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
# No of nodes
N = 6
# To maintain the adjacency list of graph
adj = [[] for i in range(N + 1)]
# To keep a check on whether
# a node is discovered or not
visited = [0 for i in range(N + 1)]
# To color the vertices
# of graph with 2 color
color = [0 for i in range(N + 1)]
# Adding edges to the graph
addEdge(adj, 1, 2)
addEdge(adj, 2, 3)
addEdge(adj, 3, 4)
addEdge(adj, 4, 5)
addEdge(adj, 5, 6)
addEdge(adj, 6, 1)
# Marking the source node as visited
visited[1] = True
# Marking the source node with a color
color[1] = 0
# Function to check if the graph
# is Bipartite or not
if (isBipartite(adj, 1, visited, color)):
print("Graph is Bipartite")
else:
print("Graph is not Bipartite")
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# program to check if a connected
// graph is bipartite or not using DFS
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to store the connected nodes
static void addEdge(List<List<int>> adj,
int u, int v)
{
adj[u].Add(v);
adj[v].Add(u);
}
// Function to check whether a
// graph is bipartite or not
static bool isBipartite(List<List<int>> adj,
int v, bool []visited,
int []color)
{
foreach(int u in adj[v])
{
// If vertex u is not explored before
if (visited[u] == false)
{
// Mark present vertic as visited
visited[u] = true;
// Mark its color opposite to its parent
color[u] = 1 - color[v];
// If the subtree rooted at vertex
// v is not bipartite
if (!isBipartite(adj, u, visited, color))
return false;
}
// If two adjacent are colored with
// same color then the graph is
// not bipartite
else if (color[u] == color[v])
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// No of nodes
int N = 6;
// To maintain the adjacency list of graph
List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>(N + 1);
// Initialize all the vertex
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
{
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
// To keep a check on whether
// a node is discovered or not
bool []visited = new bool[N + 1];
// To color the vertices
// of graph with 2 color
int []color = new int[N + 1];
// The value '-1' of colorArr[i] is
// used to indicate that no color is
// assigned to vertex 'i'. The value
// 1 is used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
color[i] = -1;
// Adding edges to the graph
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
addEdge(adj, 5, 6);
addEdge(adj, 6, 1);
// Marking the source node as visited
visited[1] = true;
// Marking the source node with a color
color[1] = 0;
// Function to check if the graph
// is Bipartite or not
if (isBipartite(adj, 1, visited, color))
{
Console.WriteLine("Graph is Bipartite");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Graph is not Bipartite");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to check if a connected
// graph is bipartite or not using DFS
// function to store the connected nodes
function addEdge(adj, u, v)
{
adj[u].push(v);
adj[v].push(u);
}
// function to check whether a graph is bipartite or not
function isBipartite(adj, v, visited, color)
{
adj[v].forEach(u => {
// if vertex u is not explored before
if (visited[u] == false) {
// mark present vertices as visited
visited[u] = true;
// mark its color opposite to its parent
color[u] = !color[v];
// if the subtree rooted at vertex v is not bipartite
if (!isBipartite(adj, u, visited, color))
return false;
}
// if two adjacent are colored with same color then
// the graph is not bipartite
else if (color[u] == color[v])
return false;
});
return true;
}
// Driver Code
// no of nodes
var N = 6;
// to maintain the adjacency list of graph
var adj = Array.from(Array(N+1), ()=>Array());
// to keep a check on whether
// a node is discovered or not
var visited = Array(N+1);;
// to color the vertices
// of graph with 2 color
var color = Array(N+1);
// adding edges to the graph
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
addEdge(adj, 5, 6);
addEdge(adj, 6, 1);
// marking the source node as visited
visited[1] = true;
// marking the source node with a color
color[1] = 0;
// Function to check if the graph
// is Bipartite or not
if (isBipartite(adj, 1, visited, color)) {
document.write( "Graph is Bipartite");
}
else {
document.write( "Graph is not Bipartite");
}
</script>
Graph is Bipartite
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Shashank_Pathak y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA