Requisito previo: introducción al hash , implementación de nuestra propia tabla hash con enstringmiento separado en Java
En el direccionamiento abierto, todos los elementos se almacenan en la propia tabla hash. Entonces, en cualquier momento, el tamaño de la tabla debe ser mayor o igual que el número total de claves (tenga en cuenta que podemos aumentar el tamaño de la tabla copiando datos antiguos si es necesario).
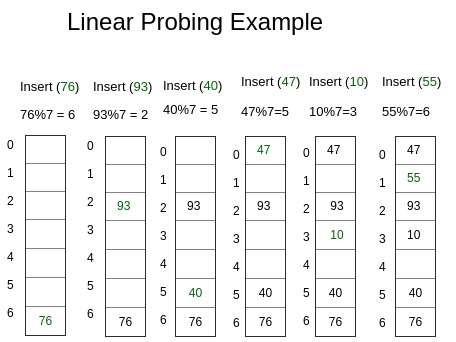
- Insertar (k): siga sondeando hasta encontrar una ranura vacía. Una vez que encuentre una ranura vacía, inserte k.
- Buscar (k): siga sondeando hasta que la clave de la ranura no sea igual a k o se alcance una ranura vacía.
- Eliminar (k): la operación de eliminación es interesante. Si simplemente eliminamos una clave, la búsqueda puede fallar. Por lo tanto, las ranuras de claves eliminadas se marcan especialmente como «eliminadas».
Aquí, para marcar un Node eliminado, hemos utilizado un Node ficticio con clave y valor -1.
Insertar puede insertar un elemento en un espacio eliminado, pero la búsqueda no se detiene en un espacio eliminado.
Todo el proceso asegura que para cualquier clave obtengamos una posición entera dentro del tamaño de la Tabla Hash para insertar el valor correspondiente.
Entonces, el proceso es simple, el usuario proporciona un conjunto de pares (clave, valor) como entrada y, en función del valor generado por la función hash, se genera un índice donde se almacena el valor correspondiente a la clave en particular. Entonces, siempre que necesitemos obtener un valor correspondiente a una clave que es solo O (1).
Código –
CPP
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// template for generic type
template <typename K, typename V>
// Hashnode class
class HashNode {
public:
V value;
K key;
// Constructor of hashnode
HashNode(K key, V value)
{
this->value = value;
this->key = key;
}
};
// template for generic type
template <typename K, typename V>
// Our own Hashmap class
class HashMap {
// hash element array
HashNode<K, V>** arr;
int capacity;
// current size
int size;
// dummy node
HashNode<K, V>* dummy;
public:
HashMap()
{
// Initial capacity of hash array
capacity = 20;
size = 0;
arr = new HashNode<K, V>*[capacity];
// Initialise all elements of array as NULL
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++)
arr[i] = NULL;
// dummy node with value and key -1
dummy = new HashNode<K, V>(-1, -1);
}
// This implements hash function to find index
// for a key
int hashCode(K key)
{
return key % capacity;
}
// Function to add key value pair
void insertNode(K key, V value)
{
HashNode<K, V>* temp = new HashNode<K, V>(key, value);
// Apply hash function to find index for given key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// find next free space
while (arr[hashIndex] != NULL
&& arr[hashIndex]->key != key
&& arr[hashIndex]->key != -1) {
hashIndex++;
hashIndex %= capacity;
}
// if new node to be inserted
// increase the current size
if (arr[hashIndex] == NULL
|| arr[hashIndex]->key == -1)
size++;
arr[hashIndex] = temp;
}
// Function to delete a key value pair
V deleteNode(int key)
{
// Apply hash function
// to find index for given key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// finding the node with given key
while (arr[hashIndex] != NULL) {
// if node found
if (arr[hashIndex]->key == key) {
HashNode<K, V>* temp = arr[hashIndex];
// Insert dummy node here for further use
arr[hashIndex] = dummy;
// Reduce size
size--;
return temp->value;
}
hashIndex++;
hashIndex %= capacity;
}
// If not found return null
return NULL;
}
// Function to search the value for a given key
V get(int key)
{
// Apply hash function to find index for given key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
int counter = 0;
// finding the node with given key
while (arr[hashIndex] != NULL) { // int counter =0; // BUG!
if (counter++ > capacity) // to avoid infinite loop
return NULL;
// if node found return its value
if (arr[hashIndex]->key == key)
return arr[hashIndex]->value;
hashIndex++;
hashIndex %= capacity;
}
// If not found return null
return NULL;
}
// Return current size
int sizeofMap()
{
return size;
}
// Return true if size is 0
bool isEmpty()
{
return size == 0;
}
// Function to display the stored key value pairs
void display()
{
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
if (arr[i] != NULL && arr[i]->key != -1)
cout << "key = " << arr[i]->key
<< " value = "
<< arr[i]->value << endl;
}
}
};
// Driver method to test map class
int main()
{
HashMap<int, int>* h = new HashMap<int, int>;
h->insertNode(1, 1);
h->insertNode(2, 2);
h->insertNode(2, 3);
h->display();
cout << h->sizeofMap() << endl;
cout << h->deleteNode(2) << endl;
cout << h->sizeofMap() << endl;
cout << h->isEmpty() << endl;
cout << h->get(2);
return 0;
}
Producción –
key = 1 value = 1 key = 2 value = 3 2 3 1 0 0
Este artículo es una contribución de Chhavi . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA