Dado un gráfico no dirigido acíclico que tiene N Nodes y N-1 aristas en forma de una array 2D arr[][] en la que cada fila consta de dos números L y R que denotan la arista entre L y R . Para cada Node X en el árbol, sea dis(X) el número de aristas desde X hasta el Node más lejano. La tarea es encontrar el valor mínimo de dis(x) para el gráfico dado.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 6, arr[][] = { {1, 4}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6} }
Salida: 2
Explicación:
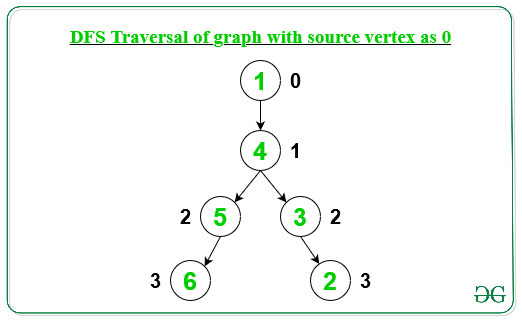
A continuación se muestra el gráfico de la información anterior:
Como podemos ver en el gráfico anterior, el Node más alejado del vértice 0 está a la distancia 3. Al repetir el recorrido DFS para todos los Nodes del gráfico, tenemos la distancia máxima[] desde el Node de origen hasta el Node más lejano como:
distancia[] = {3, 4, 3, 2, 3, 4} y el mínimo de las distancias es el resultado requerido.Entrada: N = 6, arr[][] = { {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {1, 4}, {2, 5}, {2, 6} }
Salida: 2
Explicación:
La distancia [] desde cada Node hasta el Node más lejano para el gráfico anterior es:
distancia[] = {3, 4, 3, 2, 3, 4} y el mínimo de las distancias es 1.
Enfoque:
la idea es utilizar DFS transversal para resolver este problema. A continuación se muestran los pasos:
- Para cualquier Node (por ejemplo , a ), recorra el gráfico utilizando DFS Traversal con la distancia del Node consigo mismo como 0.
- Para cada llamada recursiva al Node a , siga actualizando la distancia del Node recursivo con el Node a en una array (digamos distancia[] ).
- Al tomar el máximo de la distancia con cada llamada recursiva para el Node a, proporcione el número de aristas entre los Nodes a y su Node más lejano .
- Repita los pasos anteriores para todos los Nodes en el gráfico y siga actualizando la distancia del Node más lejano de cada Node en la array de distancia ( distance[] ).
- El valor mínimo de la array distancia[] es el resultado deseado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Distance vector to find the distance of
// a node to it's farthest node
vector<int> dist;
// To keep the track of visited array
// while DFS Traversal
vector<int> vis;
// Function for DFS traversal to update
// the distance vector
void dfs(int u, vector<int> Adj[], int s)
{
// Mark the visited array for vertex u
vis[u] = true;
// Traverse the adjacency list for u
for (auto& it : Adj[u]) {
// If the any node is not visited,
// then recursively call for next
// vertex with distance increment
// by 1
if (vis[it] == false) {
dfs(it, Adj, s + 1);
}
}
// Update the maximum distance for the
// farthest vertex from node u
dist[u] = max(dist[u], s);
}
// Function to find the minimum of the
// farthest vertex for every vertex in
// the graph
void minFarthestDistance(int arr[][2], int n)
{
// Resize distance vector
dist.resize(n + 1, 0);
// To create adjacency list for graph
vector<int> Adj[n + 1];
// Create Adjacency list for every
// edge given in arr[][]
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
Adj[arr[i][0]].push_back(arr[i][1]);
Adj[arr[i][1]].push_back(arr[i][0]);
}
// DFS Traversal for every node in the
// graph to update the distance vector
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Clear and resize vis[] before
// DFS traversal for every vertex
vis.clear();
vis.resize(n + 1, false);
// DFS Traversal for vertex i
dfs(i, Adj, 0);
}
cout << *min_element(dist.begin() + 1,
dist.end());
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of Nodes
int N = 6;
int arr[][2] = { { 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 },
{ 4, 5 }, { 5, 6 } };
minFarthestDistance(arr, N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Distance vector to find the distance
// of a node to it's farthest node
static int[] dist;
// To keep the track of visited array
// while DFS Traversal
static boolean[] vis;
// Function for DFS traversal to update
// the distance vector
static void dfs(int u, Vector<Integer>[] Adj, int s)
{
// Mark the visited array for vertex u
vis[u] = true;
// Traverse the adjacency list for u
for (int it : Adj[u])
{
// If the any node is not visited,
// then recursively call for next
// vertex with distance increment
// by 1
if (vis[it] == false)
{
dfs(it, Adj, s + 1);
}
}
// Update the maximum distance for
// the farthest vertex from node u
dist[u] = Math.max(dist[u], s);
}
// Function to find the minimum of the
// farthest vertex for every vertex in
// the graph
static void minFarthestDistance(int[][] arr, int n)
{
// Resize distance vector
dist = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dist, 0);
// To create adjacency list for graph
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector<Integer>[] Adj = new Vector[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
Adj[i] = new Vector<>();
}
// Create Adjacency list for every
// edge given in arr[][]
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
Adj[arr[i][0]].add(arr[i][1]);
Adj[arr[i][1]].add(arr[i][0]);
}
// DFS Traversal for every node in the
// graph to update the distance vector
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Clear and resize vis[] before
// DFS traversal for every vertex
vis = new boolean[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(vis, false);
// DFS Traversal for vertex i
dfs(i, Adj, 0);
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 1; i < dist.length; i++)
{
if (dist[i] < min)
min = dist[i];
}
System.out.println(min);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of Nodes
int N = 6;
int[][] arr = { { 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 4, 5 },
{ 5, 6 } };
minFarthestDistance(arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function for DFS traversal to update # the distance vector def dfs(u, s): global vis, Adj, dist # Mark the visited array for vertex u vis[u] = True # Traverse the adjacency list for u for it in Adj[u]: # If the any node is not visited, # then recursively call for next # vertex with distance increment # by 1 if (vis[it] == False): dfs(it, s + 1) # Update the maximum distance for the # farthest vertex from node u dist[u] = max(dist[u], s) # Function to find the minimum of the # farthest vertex for every vertex in # the graph def minFarthestDistance(arr, n): global dist, vis, Adj # Create Adjacency list for every # edge given in arr[][] for i in range(n - 1): Adj[arr[i][0]].append(arr[i][1]) Adj[arr[i][1]].append(arr[i][0]) # DFS Traversal for every node in the # graph to update the distance vector for i in range(1, n + 1): # Clear and resize vis[] before # DFS traversal for every vertex # vis.clear() for j in range(n + 1): vis[j] = False # vis.resize(n + 1, false) # DFS Traversal for vertex i dfs(i, 0) print(min(dist[i] for i in range(1, n + 1))) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': dist = [0 for i in range(1001)] vis = [False for i in range(1001)] Adj = [[] for i in range(1001)] # Number of Nodes N = 6 arr = [ [ 1, 4 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 3, 4 ], [ 4, 5 ], [ 5, 6 ] ] minFarthestDistance(arr, N) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Distance vector to find the distance
// of a node to it's farthest node
static int[] dist;
// To keep the track of visited array
// while DFS Traversal
static bool[] vis;
// Function for DFS traversal to update
// the distance vector
static void dfs(int u, List<List<int>> Adj, int s)
{
// Mark the visited array for vertex u
vis[u] = true;
// Traverse the adjacency list for u
foreach(int it in Adj[u])
{
// If the any node is not visited,
// then recursively call for next
// vertex with distance increment
// by 1
if (vis[it] == false)
{
dfs(it, Adj, s + 1);
}
}
// Update the maximum distance for
// the farthest vertex from node u
dist[u] = Math.Max(dist[u], s);
}
// Function to find the minimum of the
// farthest vertex for every vertex in
// the graph
static void minFarthestDistance(int[,] arr, int n)
{
// Resize distance vector
dist = new int[n + 1];
Array.Fill(dist, 0);
// To create adjacency list for graph
List<List<int>> Adj = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
Adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
// Create Adjacency list for every
// edge given in arr[][]
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
Adj[arr[i, 0]].Add(arr[i, 1]);
Adj[arr[i, 1]].Add(arr[i, 0]);
}
// DFS Traversal for every node in the
// graph to update the distance vector
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Clear and resize vis[] before
// DFS traversal for every vertex
vis = new bool[n + 1];
Array.Fill(vis, false);
// DFS Traversal for vertex i
dfs(i, Adj, 0);
}
int min = Int32.MaxValue;
for(int i = 1; i < dist.Length; i++)
{
if (dist[i] < min)
{
min = dist[i];
}
}
Console.WriteLine(min);
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main ()
{
// Number of Nodes
int N = 6;
int[,] arr = { { 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 },{ 3, 4 },
{ 4, 5 }, { 5, 6 } };
minFarthestDistance(arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Distance vector to find the distance
// of a node to it's farthest node
let dist=[];
// To keep the track of visited array
// while DFS Traversal
let vis=[];
// Function for DFS traversal to update
// the distance vector
function dfs(u,Adj,s)
{
// Mark the visited array for vertex u
vis[u] = true;
// Traverse the adjacency list for u
for (let it=0;it<Adj[u].length;it++)
{
// If the any node is not visited,
// then recursively call for next
// vertex with distance increment
// by 1
if (vis[Adj[u][it]] == false)
{
dfs(Adj[u][it], Adj, s + 1);
}
}
// Update the maximum distance for
// the farthest vertex from node u
dist[u] = Math.max(dist[u], s);
}
// Function to find the minimum of the
// farthest vertex for every vertex in
// the graph
function minFarthestDistance(arr,n)
{
// Resize distance vector
dist = new Array(n + 1);
for(let i=0;i<(n+1);i++)
{
dist[i]=0;
}
// To create adjacency list for graph
let Adj = new Array(n + 1);
for(let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
Adj[i] = [];
}
// Create Adjacency list for every
// edge given in arr[][]
for(let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
Adj[arr[i][0]].push(arr[i][1]);
Adj[arr[i][1]].push(arr[i][0]);
}
// DFS Traversal for every node in the
// graph to update the distance vector
for(let i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Clear and resize vis[] before
// DFS traversal for every vertex
vis = new Array(n + 1);
for(let i=0;i<(n+1);i++)
{
vis[i]=false;
}
// DFS Traversal for vertex i
dfs(i, Adj, 0);
}
let min = Number.MAX_VALUE;
for(let i = 1; i < dist.length; i++)
{
if (dist[i] < min)
min = dist[i];
}
document.write(min);
}
// Driver Code
// Number of Nodes
let N = 6;
let arr=[[ 1, 4 ], [ 2, 3 ],
[ 3, 4 ], [ 4, 5 ],
[ 5, 6 ]];
minFarthestDistance(arr, N);
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
2
Complejidad temporal: O(V*(V+E)), donde V es el número de vértices y E es el número de aristas.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(V + E)