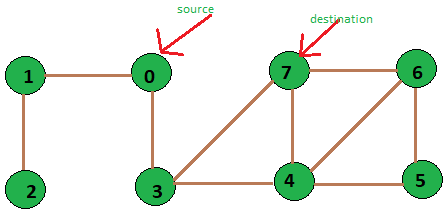
Dado un gráfico no ponderado, un origen y un destino, necesitamos encontrar el camino más corto desde el origen hasta el destino en el gráfico de la manera más óptima.
Input: source vertex = 0 and destination vertex is = 7.
Output: Shortest path length is:2
Path is::
0 3 7
Input: source vertex is = 2 and destination vertex is = 6.
Output: Shortest path length is:5
Path is::
2 1 0 3 4 6
Una solución es resolver en tiempo O(VE) usando Bellman-Ford . Si no hay ciclos de peso negativos, entonces podemos resolver en tiempo O(E + VLogV) usando el algoritmo de Dijkstra .
Como la gráfica no está ponderada, podemos resolver este problema en tiempo O(V + E). La idea es utilizar una versión modificada de la búsqueda en anchura en la que seguimos almacenando el predecesor de un vértice dado mientras realizamos la búsqueda en anchura.
Primero inicializamos una array dist[0, 1, …., v-1] tal que dist[i] almacena la distancia del vértice i desde el vértice de origen y la array pred[0, 1, ….., v-1] tal que pred[i] representa el predecesor inmediato del vértice i en la búsqueda en anchura a partir de la fuente.
Ahora obtenemos la longitud de la ruta desde el origen hasta cualquier otro vértice en el tiempo O(1) del arreglo d, y para imprimir el camino desde el origen hasta cualquier vértice podemos usar el arreglo p y eso tomará el tiempo O(V) en el peor de los casos. caso, ya que V es el tamaño de la array P. Por lo tanto, la mayor parte del tiempo del algoritmo se dedica a realizar la búsqueda primero en amplitud desde una fuente determinada que sabemos que toma tiempo O (V + E). Por tanto, la complejidad temporal de nuestro algoritmo es O(V+E).
Tome el siguiente gráfico no ponderado como ejemplo:
A continuación se muestra el algoritmo completo para encontrar el camino más corto:
C++
// CPP code for printing shortest path between
// two vertices of unweighted graph
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// utility function to form edge between two vertices
// source and dest
void add_edge(vector<int> adj[], int src, int dest)
{
adj[src].push_back(dest);
adj[dest].push_back(src);
}
// a modified version of BFS that stores predecessor
// of each vertex in array p
// and its distance from source in array d
bool BFS(vector<int> adj[], int src, int dest, int v,
int pred[], int dist[])
{
// a queue to maintain queue of vertices whose
// adjacency list is to be scanned as per normal
// DFS algorithm
list<int> queue;
// boolean array visited[] which stores the
// information whether ith vertex is reached
// at least once in the Breadth first search
bool visited[v];
// initially all vertices are unvisited
// so v[i] for all i is false
// and as no path is yet constructed
// dist[i] for all i set to infinity
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
pred[i] = -1;
}
// now source is first to be visited and
// distance from source to itself should be 0
visited[src] = true;
dist[src] = 0;
queue.push_back(src);
// standard BFS algorithm
while (!queue.empty()) {
int u = queue.front();
queue.pop_front();
for (int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++) {
if (visited[adj[u][i]] == false) {
visited[adj[u][i]] = true;
dist[adj[u][i]] = dist[u] + 1;
pred[adj[u][i]] = u;
queue.push_back(adj[u][i]);
// We stop BFS when we find
// destination.
if (adj[u][i] == dest)
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// utility function to print the shortest distance
// between source vertex and destination vertex
void printShortestDistance(vector<int> adj[], int s,
int dest, int v)
{
// predecessor[i] array stores predecessor of
// i and distance array stores distance of i
// from s
int pred[v], dist[v];
if (BFS(adj, s, dest, v, pred, dist) == false) {
cout << "Given source and destination"
<< " are not connected";
return;
}
// vector path stores the shortest path
vector<int> path;
int crawl = dest;
path.push_back(crawl);
while (pred[crawl] != -1) {
path.push_back(pred[crawl]);
crawl = pred[crawl];
}
// distance from source is in distance array
cout << "Shortest path length is : "
<< dist[dest];
// printing path from source to destination
cout << "\nPath is::\n";
for (int i = path.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
cout << path[i] << " ";
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// no. of vertices
int v = 8;
// array of vectors is used to store the graph
// in the form of an adjacency list
vector<int> adj[v];
// Creating graph given in the above diagram.
// add_edge function takes adjacency list, source
// and destination vertex as argument and forms
// an edge between them.
add_edge(adj, 0, 1);
add_edge(adj, 0, 3);
add_edge(adj, 1, 2);
add_edge(adj, 3, 4);
add_edge(adj, 3, 7);
add_edge(adj, 4, 5);
add_edge(adj, 4, 6);
add_edge(adj, 4, 7);
add_edge(adj, 5, 6);
add_edge(adj, 6, 7);
int source = 0, dest = 7;
printShortestDistance(adj, source, dest, v);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find shortest path in an undirected
// graph
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class pathUnweighted {
// Driver Program
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No of vertices
int v = 8;
// Adjacency list for storing which vertices are connected
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj =
new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(v);
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// Creating graph given in the above diagram.
// add_edge function takes adjacency list, source
// and destination vertex as argument and forms
// an edge between them.
addEdge(adj, 0, 1);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
addEdge(adj, 3, 7);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
addEdge(adj, 4, 6);
addEdge(adj, 4, 7);
addEdge(adj, 5, 6);
addEdge(adj, 6, 7);
int source = 0, dest = 7;
printShortestDistance(adj, source, dest, v);
}
// function to form edge between two vertices
// source and dest
private static void addEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int i, int j)
{
adj.get(i).add(j);
adj.get(j).add(i);
}
// function to print the shortest distance and path
// between source vertex and destination vertex
private static void printShortestDistance(
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj,
int s, int dest, int v)
{
// predecessor[i] array stores predecessor of
// i and distance array stores distance of i
// from s
int pred[] = new int[v];
int dist[] = new int[v];
if (BFS(adj, s, dest, v, pred, dist) == false) {
System.out.println("Given source and destination" +
"are not connected");
return;
}
// LinkedList to store path
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int crawl = dest;
path.add(crawl);
while (pred[crawl] != -1) {
path.add(pred[crawl]);
crawl = pred[crawl];
}
// Print distance
System.out.println("Shortest path length is: " + dist[dest]);
// Print path
System.out.println("Path is ::");
for (int i = path.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print(path.get(i) + " ");
}
}
// a modified version of BFS that stores predecessor
// of each vertex in array pred
// and its distance from source in array dist
private static boolean BFS(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int src,
int dest, int v, int pred[], int dist[])
{
// a queue to maintain queue of vertices whose
// adjacency list is to be scanned as per normal
// BFS algorithm using LinkedList of Integer type
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
// boolean array visited[] which stores the
// information whether ith vertex is reached
// at least once in the Breadth first search
boolean visited[] = new boolean[v];
// initially all vertices are unvisited
// so v[i] for all i is false
// and as no path is yet constructed
// dist[i] for all i set to infinity
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
pred[i] = -1;
}
// now source is first to be visited and
// distance from source to itself should be 0
visited[src] = true;
dist[src] = 0;
queue.add(src);
// bfs Algorithm
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.remove();
for (int i = 0; i < adj.get(u).size(); i++) {
if (visited[adj.get(u).get(i)] == false) {
visited[adj.get(u).get(i)] = true;
dist[adj.get(u).get(i)] = dist[u] + 1;
pred[adj.get(u).get(i)] = u;
queue.add(adj.get(u).get(i));
// stopping condition (when we find
// our destination)
if (adj.get(u).get(i) == dest)
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sahil Vaid
Python3
# Python3 code for printing shortest path between
# two vertices of unweighted graph
# utility function to form edge between two vertices
# source and dest
def add_edge(adj, src, dest):
adj[src].append(dest);
adj[dest].append(src);
# a modified version of BFS that stores predecessor
# of each vertex in array p
# and its distance from source in array d
def BFS(adj, src, dest, v, pred, dist):
# a queue to maintain queue of vertices whose
# adjacency list is to be scanned as per normal
# DFS algorithm
queue = []
# boolean array visited[] which stores the
# information whether ith vertex is reached
# at least once in the Breadth first search
visited = [False for i in range(v)];
# initially all vertices are unvisited
# so v[i] for all i is false
# and as no path is yet constructed
# dist[i] for all i set to infinity
for i in range(v):
dist[i] = 1000000
pred[i] = -1;
# now source is first to be visited and
# distance from source to itself should be 0
visited[src] = True;
dist[src] = 0;
queue.append(src);
# standard BFS algorithm
while (len(queue) != 0):
u = queue[0];
queue.pop(0);
for i in range(len(adj[u])):
if (visited[adj[u][i]] == False):
visited[adj[u][i]] = True;
dist[adj[u][i]] = dist[u] + 1;
pred[adj[u][i]] = u;
queue.append(adj[u][i]);
# We stop BFS when we find
# destination.
if (adj[u][i] == dest):
return True;
return False;
# utility function to print the shortest distance
# between source vertex and destination vertex
def printShortestDistance(adj, s, dest, v):
# predecessor[i] array stores predecessor of
# i and distance array stores distance of i
# from s
pred=[0 for i in range(v)]
dist=[0 for i in range(v)];
if (BFS(adj, s, dest, v, pred, dist) == False):
print("Given source and destination are not connected")
# vector path stores the shortest path
path = []
crawl = dest;
crawl = dest;
path.append(crawl);
while (pred[crawl] != -1):
path.append(pred[crawl]);
crawl = pred[crawl];
# distance from source is in distance array
print("Shortest path length is : " + str(dist[dest]), end = '')
# printing path from source to destination
print("\nPath is : : ")
for i in range(len(path)-1, -1, -1):
print(path[i], end=' ')
# Driver program to test above functions
if __name__=='__main__':
# no. of vertices
v = 8;
# array of vectors is used to store the graph
# in the form of an adjacency list
adj = [[] for i in range(v)];
# Creating graph given in the above diagram.
# add_edge function takes adjacency list, source
# and destination vertex as argument and forms
# an edge between them.
add_edge(adj, 0, 1);
add_edge(adj, 0, 3);
add_edge(adj, 1, 2);
add_edge(adj, 3, 4);
add_edge(adj, 3, 7);
add_edge(adj, 4, 5);
add_edge(adj, 4, 6);
add_edge(adj, 4, 7);
add_edge(adj, 5, 6);
add_edge(adj, 6, 7);
source = 0
dest = 7;
printShortestDistance(adj, source, dest, v);
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# program to find shortest
// path in an undirected graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class pathUnweighted{
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// No of vertices
int v = 8;
// Adjacency list for storing
// which vertices are connected
List<List<int>> adj =
new List<List<int>>(v);
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++)
{
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
// Creating graph given in the
// above diagram. add_edge
// function takes adjacency list,
// source and destination vertex
// as argument and forms an edge
// between them.
addEdge(adj, 0, 1);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
addEdge(adj, 3, 7);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5);
addEdge(adj, 4, 6);
addEdge(adj, 4, 7);
addEdge(adj, 5, 6);
addEdge(adj, 6, 7);
int source = 0, dest = 7;
printShortestDistance(adj, source,
dest, v);
}
// function to form edge between
// two vertices source and dest
private static void addEdge(List<List<int>> adj,
int i, int j)
{
adj[i].Add(j);
adj[j].Add(i);
}
// function to print the shortest
// distance and path between source
// vertex and destination vertex
private static void printShortestDistance(List<List<int>> adj,
int s, int dest, int v)
{
// predecessor[i] array stores
// predecessor of i and distance
// array stores distance of i
// from s
int []pred = new int[v];
int []dist = new int[v];
if (BFS(adj, s, dest,
v, pred, dist) == false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Given source and destination" +
"are not connected");
return;
}
// List to store path
List<int> path = new List<int>();
int crawl = dest;
path.Add(crawl);
while (pred[crawl] != -1)
{
path.Add(pred[crawl]);
crawl = pred[crawl];
}
// Print distance
Console.WriteLine("Shortest path length is: " +
dist[dest]);
// Print path
Console.WriteLine("Path is ::");
for (int i = path.Count - 1;
i >= 0; i--)
{
Console.Write(path[i] + " ");
}
}
// a modified version of BFS that
// stores predecessor of each vertex
// in array pred and its distance
// from source in array dist
private static bool BFS(List<List<int>> adj,
int src, int dest,
int v, int []pred,
int []dist)
{
// a queue to maintain queue of
// vertices whose adjacency list
// is to be scanned as per normal
// BFS algorithm using List of int type
List<int> queue = new List<int>();
// bool array visited[] which
// stores the information whether
// ith vertex is reached at least
// once in the Breadth first search
bool []visited = new bool[v];
// initially all vertices are
// unvisited so v[i] for all i
// is false and as no path is
// yet constructed dist[i] for
// all i set to infinity
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
dist[i] = int.MaxValue;
pred[i] = -1;
}
// now source is first to be
// visited and distance from
// source to itself should be 0
visited[src] = true;
dist[src] = 0;
queue.Add(src);
// bfs Algorithm
while (queue.Count != 0)
{
int u = queue[0];
queue.RemoveAt(0);
for (int i = 0;
i < adj[u].Count; i++)
{
if (visited[adj[u][i]] == false)
{
visited[adj[u][i]] = true;
dist[adj[u][i]] = dist[u] + 1;
pred[adj[u][i]] = u;
queue.Add(adj[u][i]);
// stopping condition (when we
// find our destination)
if (adj[u][i] == dest)
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Shortest path length is : 2 Path is:: 0 3 7
Complejidad temporal: O(V + E)
Espacio auxiliar: O(V)