Dado un árbol binario y una clave, escriba una función que devuelva el nivel de la clave.
Por ejemplo, considere el siguiente árbol. Si la clave de entrada es 3, entonces su función debería devolver 1. Si la clave de entrada es 4, entonces su función debería devolver 3. Y para la clave que no está presente en key, entonces su función debería devolver 0.
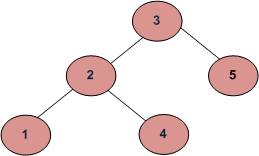
El enfoque recursivo de este problema se analiza aquí
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/get-level-of-a-node-in-a-binary-tree/
El enfoque iterativo se analiza a continuación:
El enfoque iterativo es una versión modificada de Level Order Tree Traversal
Algoritmo
create a empty queue q
push root and then NULL to q
loop till q is not empty
get the front node into temp node
if it is NULL, it means all nodes of
one level are traversed, so increment
level
else
check if temp data is equal to data
to be searched
if yes then return level
if temp->left is not NULL,
enqueue temp->left
if temp->right is not NULL,
enqueue temp->right
if value not found, then return 0
Implementación:
C++
// CPP program to print level of given node
// in binary tree iterative approach
/* Example binary tree
root is at level 1
20
/ \
10 30
/ \ / \
5 15 25 40
/
12 */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// node of binary tree
struct node {
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
// utility function to create
// a new node
node* getnode(int data)
{
node* newnode = new node();
newnode->data = data;
newnode->left = NULL;
newnode->right = NULL;
}
// utility function to return level of given node
int getlevel(node* root, int data)
{
queue<node*> q;
int level = 1;
q.push(root);
// extra NULL is pushed to keep track
// of all the nodes to be pushed before
// level is incremented by 1
q.push(NULL);
while (!q.empty()) {
node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (temp == NULL) {
if (q.front() != NULL) {
q.push(NULL);
}
level += 1;
} else {
if (temp->data == data) {
return level;
}
if (temp->left) {
q.push(temp->left);
}
if (temp->right) {
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
// create a binary tree
node* root = getnode(20);
root->left = getnode(10);
root->right = getnode(30);
root->left->left = getnode(5);
root->left->right = getnode(15);
root->left->right->left = getnode(12);
root->right->left = getnode(25);
root->right->right = getnode(40);
// return level of node
int level = getlevel(root, 30);
(level != 0) ? (cout << "level of node 30 is " << level << endl) :
(cout << "node 30 not found" << endl);
level = getlevel(root, 12);
(level != 0) ? (cout << "level of node 12 is " << level << endl) :
(cout << "node 12 not found" << endl);
level = getlevel(root, 25);
(level != 0) ? (cout << "level of node 25 is " << level << endl) :
(cout << "node 25 not found" << endl);
level = getlevel(root, 27);
(level != 0) ? (cout << "level of node 27 is " << level << endl) :
(cout << "node 27 not found" << endl);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to print level of given node
// in binary tree iterative approach
/* Example binary tree
root is at level 1
20
/ \
10 30
/ \ / \
5 15 25 40
/
12 */
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// node of binary tree
static class node
{
int data;
node left, right;
node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// utility function to return level of given node
static int getLevel(node root, int data)
{
Queue<node> q = new LinkedList<>();
int level = 1;
q.add(root);
// extra NULL is pushed to keep track
// of all the nodes to be pushed before
// level is incremented by 1
q.add(null);
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
node temp = q.poll();
if (temp == null)
{
if (q.peek() != null)
{
q.add(null);
}
level += 1;
}
else
{
if (temp.data == data)
{
return level;
}
if (temp.left != null)
{
q.add(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null)
{
q.add(temp.right);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create a binary tree
node root = new node(20);
root.left = new node(10);
root.right = new node(30);
root.left.left = new node(5);
root.left.right = new node(15);
root.left.right.left = new node(12);
root.right.left = new node(25);
root.right.right = new node(40);
// return level of node
int level = getLevel(root, 30);
if (level != 0)
System.out.println("level of node 30 is " + level);
else
System.out.println("node 30 not found");
level = getLevel(root, 12);
if (level != 0)
System.out.println("level of node 12 is " + level);
else
System.out.println("node 12 not found");
level = getLevel(root, 25);
if (level != 0)
System.out.println("level of node 25 is " + level);
else
System.out.println("node 25 not found");
level = getLevel(root, 27);
if (level != 0)
System.out.println("level of node 27 is " + level);
else
System.out.println("node 27 not found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552
Python3
# Python3 program to find closest
# value in Binary search Tree
_MIN = -2147483648
_MAX = 2147483648
# Helper function that allocates a new
# node with the given data and None
# left and right pointers.
class getnode:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# utility function to return level
# of given node
def getlevel(root, data):
q = []
level = 1
q.append(root)
# extra None is appended to keep track
# of all the nodes to be appended
# before level is incremented by 1
q.append(None)
while (len(q)):
temp = q[0]
q.pop(0)
if (temp == None) :
if len(q) == 0:
return 0
if (q[0] != None):
q.append(None)
level += 1
else :
if (temp.data == data) :
return level
if (temp.left):
q.append(temp.left)
if (temp.right) :
q.append(temp.right)
return 0
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# create a binary tree
root = getnode(20)
root.left = getnode(10)
root.right = getnode(30)
root.left.left = getnode(5)
root.left.right = getnode(15)
root.left.right.left = getnode(12)
root.right.left = getnode(25)
root.right.right = getnode(40)
# return level of node
level = getlevel(root, 30)
if level != 0:
print("level of node 30 is", level)
else:
print("node 30 not found")
level = getlevel(root, 12)
if level != 0:
print("level of node 12 is", level)
else:
print("node 12 not found")
level = getlevel(root, 25)
if level != 0:
print("level of node 25 is", level)
else:
print("node 25 not found")
level = getlevel(root, 27)
if level != 0:
print("level of node 27 is", level)
else:
print("node 27 not found")
# This code is contributed by
# Shubham Singh(SHUBHAMSINGH10)
C#
// C# program to print level of given node
// in binary tree iterative approach
/* Example binary tree
root is at level 1
20
/ \
10 30
/ \ / \
5 15 25 40
/
12 */
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// node of binary tree
public class node
{
public int data;
public node left, right;
public node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// utility function to return level of given node
static int getLevel(node root, int data)
{
Queue<node> q = new Queue<node>();
int level = 1;
q.Enqueue(root);
// extra NULL is pushed to keep track
// of all the nodes to be pushed before
// level is incremented by 1
q.Enqueue(null);
while (q.Count > 0)
{
node temp = q.Dequeue();
if (temp == null)
{
if (q.Count > 0)
{
q.Enqueue(null);
}
level += 1;
}
else
{
if (temp.data == data)
{
return level;
}
if (temp.left != null)
{
q.Enqueue(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null)
{
q.Enqueue(temp.right);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// create a binary tree
node root = new node(20);
root.left = new node(10);
root.right = new node(30);
root.left.left = new node(5);
root.left.right = new node(15);
root.left.right.left = new node(12);
root.right.left = new node(25);
root.right.right = new node(40);
// return level of node
int level = getLevel(root, 30);
if (level != 0)
Console.WriteLine("level of node 30 is " + level);
else
Console.WriteLine("node 30 not found");
level = getLevel(root, 12);
if (level != 0)
Console.WriteLine("level of node 12 is " + level);
else
Console.WriteLine("node 12 not found");
level = getLevel(root, 25);
if (level != 0)
Console.WriteLine("level of node 25 is " + level);
else
Console.WriteLine("node 25 not found");
level = getLevel(root, 27);
if (level != 0)
Console.WriteLine("level of node 27 is " + level);
else
Console.WriteLine("node 27 not found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to print level of given node
// in binary tree iterative approach
/* Example binary tree
root is at level 1
20
/ \
10 30
/ \ / \
5 15 25 40
/
12 */
class node
{
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
}
}
// utility function to return level of given node
function getLevel(root, data)
{
let q = [];
let level = 1;
q.push(root);
// extra NULL is pushed to keep track
// of all the nodes to be pushed before
// level is incremented by 1
q.push(null);
while (q.length > 0)
{
let temp = q[0];
q.shift()
if (temp == null)
{
if (q[0] != null)
{
q.push(null);
}
level += 1;
}
else
{
if (temp.data == data)
{
return level;
}
if (temp.left != null)
{
q.push(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null)
{
q.push(temp.right);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// create a binary tree
let root = new node(20);
root.left = new node(10);
root.right = new node(30);
root.left.left = new node(5);
root.left.right = new node(15);
root.left.right.left = new node(12);
root.right.left = new node(25);
root.right.right = new node(40);
// return level of node
let level = getLevel(root, 30);
if (level != 0)
document.write("level of node 30 is " + level + "</br>");
else
document.write("node 30 not found" + "</br>");
level = getLevel(root, 12);
if (level != 0)
document.write("level of node 12 is " + level + "</br>");
else
document.write("node 12 not found" + "</br>");
level = getLevel(root, 25);
if (level != 0)
document.write("level of node 25 is " + level + "</br>");
else
document.write("node 25 not found" + "</br>");
level = getLevel(root, 27);
if (level != 0)
document.write("level of node 27 is " + level + "</br>");
else
document.write("node 27 not found" + "</br>");
// This code is contributed by suresh07.
</script>
level of node 30 is 2 level of node 12 is 4 level of node 25 is 3 node 27 not found
Este artículo es una contribución de Mandeep Singh . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA