Dados dos montones máximos binarios como arrays, combine los montones dados.
Ejemplos:
Input : a = {10, 5, 6, 2},
b = {12, 7, 9}
Output : {12, 10, 9, 2, 5, 7, 6}
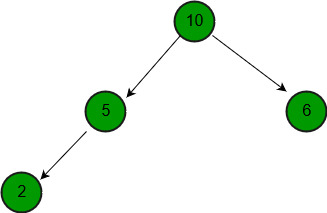
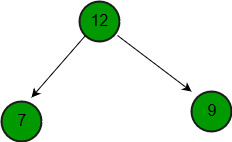
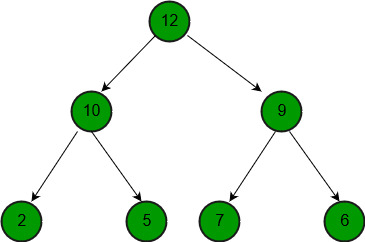
La idea es sencilla. Creamos una array para almacenar el resultado. Copiamos ambas arrays dadas una por una para dar como resultado. Una vez que hemos copiado todos los elementos, llamamos al montón de compilación estándar para construir un montón máximo combinado completo.
Implementación:
C++
// C++ program to merge two max heaps.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Standard heapify function to heapify a
// subtree rooted under idx. It assumes
// that subtrees of node are already heapified.
void maxHeapify(int arr[], int n, int idx)
{
// Find largest of node and its children
if (idx >= n)
return;
int l = 2 * idx + 1;
int r = 2 * idx + 2;
int max;
if (l < n && arr[l] > arr[idx])
max = l;
else
max = idx;
if (r < n && arr[r] > arr[max])
max = r;
// Put maximum value at root and
// recur for the child with the
// maximum value
if (max != idx) {
swap(arr[max], arr[idx]);
maxHeapify(arr, n, max);
}
}
// Builds a max heap of given arr[0..n-1]
void buildMaxHeap(int arr[], int n)
{
// building the heap from first non-leaf
// node by calling max heapify function
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
maxHeapify(arr, n, i);
}
// Merges max heaps a[] and b[] into merged[]
void mergeHeaps(int merged[], int a[], int b[],
int n, int m)
{
// Copy elements of a[] and b[] one by one
// to merged[]
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
merged[i] = a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
merged[n + i] = b[i];
// build heap for the modified array of
// size n+m
buildMaxHeap(merged, n + m);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int a[] = { 10, 5, 6, 2 };
int b[] = { 12, 7, 9 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
int m = sizeof(b) / sizeof(b[0]);
int merged[m + n];
mergeHeaps(merged, a, b, n, m);
for (int i = 0; i < n + m; i++)
cout << merged[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to merge two max heaps.
class GfG {
// Standard heapify function to heapify a
// subtree rooted under idx. It assumes
// that subtrees of node are already heapified.
public static void maxHeapify(int[] arr, int n,
int i)
{
// Find largest of node and its children
if (i >= n) {
return;
}
int l = i * 2 + 1;
int r = i * 2 + 2;
int max;
if (l < n && arr[l] > arr[i]) {
max = l;
}
else
max = i;
if (r < n && arr[r] > arr[max]) {
max = r;
}
// Put maximum value at root and
// recur for the child with the
// maximum value
if (max != i) {
int temp = arr[max];
arr[max] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
maxHeapify(arr, n, max);
}
}
// Merges max heaps a[] and b[] into merged[]
public static void mergeHeaps(int[] arr, int[] a,
int[] b, int n, int m)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
arr[n + i] = b[i];
}
n = n + m;
// Builds a max heap of given arr[0..n-1]
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
maxHeapify(arr, n, i);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = {10, 5, 6, 2};
int[] b = {12, 7, 9};
int n = a.length;
int m = b.length;
int[] merged = new int[m + n];
mergeHeaps(merged, a, b, n, m);
for (int i = 0; i < m + n; i++)
System.out.print(merged[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to merge two Max heaps. # Standard heapify function to heapify a # subtree rooted under idx. It assumes that # subtrees of node are already heapified. def MaxHeapify(arr, n, idx): # Find largest of node and # its children if idx >= n: return l = 2 * idx + 1 r = 2 * idx + 2 Max = 0 if l < n and arr[l] > arr[idx]: Max = l else: Max = idx if r < n and arr[r] > arr[Max]: Max = r # Put Maximum value at root and # recur for the child with the # Maximum value if Max != idx: arr[Max], arr[idx] = arr[idx], arr[Max] MaxHeapify(arr, n, Max) # Builds a Max heap of given arr[0..n-1] def buildMaxHeap(arr, n): # building the heap from first non-leaf # node by calling Max heapify function for i in range(int(n / 2) - 1, -1, -1): MaxHeapify(arr, n, i) # Merges Max heaps a[] and b[] into merged[] def mergeHeaps(merged, a, b, n, m): # Copy elements of a[] and b[] one # by one to merged[] for i in range(n): merged[i] = a[i] for i in range(m): merged[n + i] = b[i] # build heap for the modified # array of size n+m buildMaxHeap(merged, n + m) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': a = [10, 5, 6, 2] b = [12, 7, 9] n = len(a) m = len(b) merged = [0] * (m + n) mergeHeaps(merged, a, b, n, m) for i in range(n + m): print(merged[i], end = " ") # This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# program to merge two max heaps.
using System;
class GfG {
// Standard heapify function to heapify a
// subtree rooted under idx. It assumes
// that subtrees of node are already heapified.
public static void maxHeapify(int[] arr,
int n, int i)
{
// Find largest of node
// and its children
if (i >= n) {
return;
}
int l = i * 2 + 1;
int r = i * 2 + 2;
int max;
if (l < n && arr[l] > arr[i]) {
max = l;
}
else
max = i;
if (r < n && arr[r] > arr[max]) {
max = r;
}
// Put maximum value at root and
// recur for the child with the
// maximum value
if (max != i) {
int temp = arr[max];
arr[max] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
maxHeapify(arr, n, max);
}
}
// Merges max heaps a[] and b[] into merged[]
public static void mergeHeaps(int[] arr, int[] a,
int[] b, int n, int m)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
arr[n + i] = b[i];
}
n = n + m;
// Builds a max heap of given arr[0..n-1]
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
maxHeapify(arr, n, i);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] a = {10, 5, 6, 2};
int[] b = {12, 7, 9};
int n = a.Length;
int m = b.Length;
int[] merged = new int[m + n];
mergeHeaps(merged, a, b, n, m);
for (int i = 0; i < m + n; i++)
Console.Write(merged[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to merge two max heaps.
// Standard heapify function to heapify a
// subtree rooted under idx. It assumes
// that subtrees of node are already heapified.
function maxHeapify(arr , n , i)
{
// Find largest of node and its children
if (i >= n) {
return;
}
var l = i * 2 + 1;
var r = i * 2 + 2;
var max;
if (l < n && arr[l] > arr[i]) {
max = l;
} else
max = i;
if (r < n && arr[r] > arr[max]) {
max = r;
}
// Put maximum value at root and
// recur for the child with the
// maximum value
if (max != i) {
var temp = arr[max];
arr[max] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
maxHeapify(arr, n, max);
}
}
// Merges max heaps a and b into merged
function mergeHeaps(arr, a, b , n , m) {
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = a[i];
}
for (var i = 0; i < m; i++) {
arr[n + i] = b[i];
}
n = n + m;
// Builds a max heap of given arr[0..n-1]
for (var i = parseInt(n / 2 - 1); i >= 0; i--) {
maxHeapify(arr, n, i);
}
}
// Driver Code
var a = [ 10, 5, 6, 2 ];
var b = [ 12, 7, 9 ];
var n = a.length;
var m = b.length;
var merged = Array(m + n).fill(0);
mergeHeaps(merged, a, b, n, m);
for (var i = 0; i < m + n; i++)
document.write(merged[i] + " ");
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
12 10 9 2 5 7 6
Dado que la complejidad del tiempo para construir el montón a partir de una array de n elementos es O (n). La complejidad de fusionar los montones es igual a O(n + m).
Este artículo es una contribución de K Akhil Reddy . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA