Un niño sube corriendo una escalera de n peldaños y puede saltar 1 peldaño, 2 peldaños o 3 peldaños a la vez. Implemente un método para contar de cuántas maneras posibles el niño puede subir corriendo las escaleras.
Ejemplos:
Input : 4 Output : 7 Explanation: Below are the seven ways 1 step + 1 step + 1 step + 1 step 1 step + 2 step + 1 step 2 step + 1 step + 1 step 1 step + 1 step + 2 step 2 step + 2 step 3 step + 1 step 1 step + 3 step Input : 3 Output : 4 Explanation: Below are the four ways 1 step + 1 step + 1 step 1 step + 2 step 2 step + 1 step 3 step
Hay dos métodos para resolver este problema:
- Método recursivo
- Programación dinámica
Método 1 : recursivo.
Hay n escaleras, y una persona puede saltar la siguiente escalera, saltarse una escalera o saltarse dos escaleras. Entonces hay n escaleras. Entonces, si una persona está parada en el i-ésimo escalón, la persona puede moverse al i+1, i+2, i+3-ésimo escalón. Se puede formar una función recursiva donde en el índice actual i la función se llama recursivamente para i+1, i+2 e i+3 th escalera.
Hay otra forma de formar la función recursiva. Para llegar a una escalera i, una persona tiene que saltar desde i-1, i-2 o i-3 la escalera o i es la escalera inicial.
Algoritmo:
- Cree una función recursiva (count(int n)) que tome solo un parámetro.
- Revisa los casos base. Si el valor de n es menor que 0, devuelva 0, y si el valor de n es igual a cero, devuelva 1, ya que es la escalera de inicio.
- Llame a la función recursivamente con valores n-1, n-2 y n-3 y sume los valores que se devuelven, es decir, sum = count(n-1) + count(n-2) + count(n-3)
- Devuelve el valor de la suma.
C++
// C++ Program to find n-th stair using step size
// 1 or 2 or 3.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class GFG {
// Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair
// using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
public:
int findStep(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n < 0)
return 0;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2)
+ findStep(n - 1);
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
GFG g;
int n = 4;
cout << g.findStep(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SoM15242
C
// Program to find n-th stair using step size
// 1 or 2 or 3.
#include <stdio.h>
// Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair
// using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
int findStep(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n < 0)
return 0;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2)
+ findStep(n - 1);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 4;
printf("%d\n", findStep(n));
return 0;
}
Java
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
public class GfG {
// Returns count of ways to reach
// n-th stair using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
public static int findStep(int n)
{
if ( n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n < 0)
return 0;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2)
+ findStep(n - 1);
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String argc[])
{
int n = 4;
System.out.println(findStep(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Sagar Shukla */
Python
# Python program to find n-th stair # using step size 1 or 2 or 3. # Returns count of ways to reach n-th # stair using 1 or 2 or 3 steps. def findStep(n): if ( n == 0 ): return 1 elif (n < 0): return 0 else: return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2) + findStep(n - 1) # Driver code n = 4 print(findStep(n)) # This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C#
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
using System;
public class GfG {
// Returns count of ways to reach
// n-th stair using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
public static int findStep(int n)
{
if ( n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n < 0)
return 0;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2)
+ findStep(n - 1);
}
// Driver function
public static void Main()
{
int n = 4;
Console.WriteLine(findStep(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by vt_m */
PHP
<?php
// PHP Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
// Returns count of ways to
// reach n-th stair using
// 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
function findStep($n)
{
if ( $n == 0)
return 1;
else if ($n < 0)
return 0;
else
return findStep($n - 3) +
findStep($n - 2) +
findStep($n - 1);
}
// Driver code
$n = 4;
echo findStep($n);
// This code is contributed by m_kit
?>
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to find n-th stair using step size
// 1 or 2 or 3.
// Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair
// using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
function findStep(n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n < 0)
return 0;
else
return findStep(n - 3) + findStep(n - 2)
+ findStep(n - 1);
}
// Driver code
let n = 4;
document.write(findStep(n));
// This code is contributed by Surbhi Tyagi.
</script>
7
Laboral:
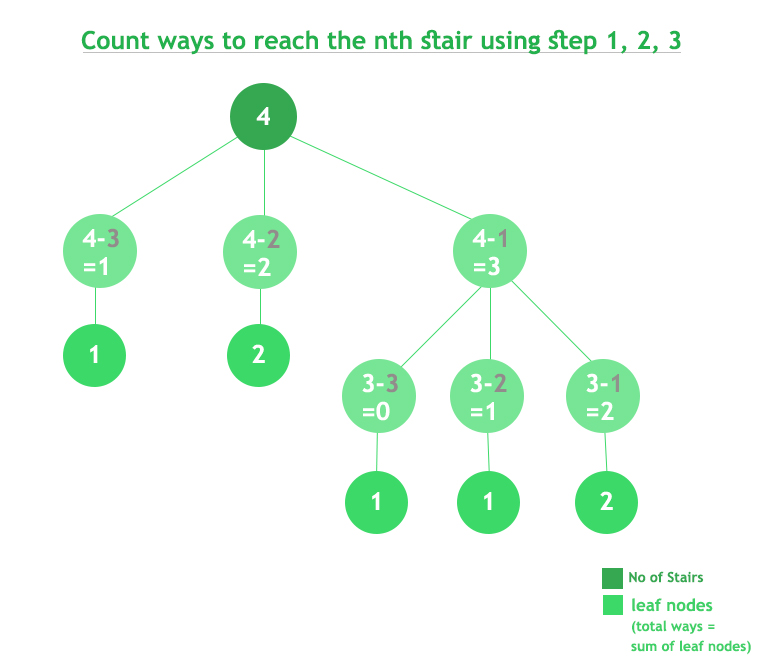
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(3 n ).
La complejidad temporal de la solución anterior es exponencial, un límite superior cercano será O(3 n ). De cada estado, se llaman 3 funciones recursivas. Entonces, el límite superior para n estados es O(3 n ). - Complejidad espacial: O(1).
Como no se requiere espacio adicional.
Nota: La Complejidad de Tiempo del programa se puede optimizar usando Programación Dinámica.
Método 2 : Programación Dinámica.
La idea es similar, pero se puede observar que hay n estados pero la función recursiva se llama 3^n veces. Eso significa que algunos estados son llamados repetidamente. Así que la idea es almacenar el valor de los estados. Esto se puede hacer de dos formas.
- Enfoque de arriba hacia abajo: la primera forma es mantener intacta la estructura recursiva y simplemente almacenar el valor en un HashMap y cada vez que se vuelve a llamar a la función, devolver el valor almacenado sin computar().
- Enfoque ascendente: la segunda forma es tomar un espacio adicional de tamaño n y comenzar a calcular los valores de los estados de 1, 2 .. a n, es decir, calcular los valores de i, i+1, i+2 y luego usarlos para calcular el valor de i+3.
Algoritmo:
- Cree una array de tamaño n + 1 e inicialice las primeras 3 variables con 1, 1, 2. Los casos base.
- Ejecute un ciclo de 3 a n.
- Para cada índice i, computar el valor de la i-ésima posición como dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2] + dp[i-3].
- Imprime el valor de dp[n], como el recuento del número de formas de llegar al paso n.
C++
// A C++ program to count number of ways
// to reach n't stair when
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// A recursive function used by countWays
int countWays(int n)
{
int res[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2] + res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int n = 4;
cout << countWays(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10
C
// A C program to count number of ways
// to reach n't stair when
#include <stdio.h>
// A recursive function used by countWays
int countWays(int n)
{
int res[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2] + res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int n = 4;
printf("%d", countWays(n));
return 0;
}
Java
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
public class GfG {
// A recursive function used by countWays
public static int countWays(int n)
{
int[] res = new int[n + 1];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2] + res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String argc[])
{
int n = 4;
System.out.println(countWays(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Sagar Shukla */
Python
# Python program to find n-th stair # using step size 1 or 2 or 3. # A recursive function used by countWays def countWays(n): res = [0] * (n + 2) res[0] = 1 res[1] = 1 res[2] = 2 for i in range(3, n + 1): res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2] + res[i - 3] return res[n] # Driver code n = 4 print(countWays(n)) # This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C#
// Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
using System;
public class GfG {
// A recursive function used by countWays
public static int countWays(int n)
{
int[] res = new int[n + 2];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2] + res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
// Driver function
public static void Main()
{
int n = 4;
Console.WriteLine(countWays(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by vt_m */
PHP
<?php
// A PHP program to count
// number of ways to reach
// n'th stair when
// A recursive function
// used by countWays
function countWays($n)
{
$res[0] = 1;
$res[1] = 1;
$res[2] = 2;
for ($i = 3; $i <= $n; $i++)
$res[$i] = $res[$i - 1] +
$res[$i - 2] +
$res[$i - 3];
return $res[$n];
}
// Driver Code
$n = 4;
echo countWays($n);
// This code is contributed by ajit
?>
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to find n-th stair
// using step size 1 or 2 or 3.
// A recursive function used by countWays
function countWays(n)
{
let res = new Array(n + 2);
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 1;
res[2] = 2;
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++)
res[i] = res[i - 1] + res[i - 2] + res[i - 3];
return res[n];
}
let n = 4;
document.write(countWays(n));
// This code is contributed by rameshtravel07.
</script>
7
- Laboral:
1 -> 1 -> 1 -> 1 1 -> 1 -> 2 1 -> 2 -> 1 1 -> 3 2 -> 1 -> 1 2 -> 2 3 -> 1 So Total ways: 7
- Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n).
Solo se necesita un recorrido de la array. Entonces la Complejidad del Tiempo es O(n). - Complejidad espacial: O(n).
Para almacenar los valores en un DP, se necesita n espacio extra.
- Complejidad temporal: O(n).
Método 3: Exponenciación matricial (enfoque O(logn))
La exponenciación de arrays es una forma matemática de resolver el problema de DP en una mejor complejidad de tiempo. La técnica de exponenciación de arrays tiene una array de transformación de tamaño KXK y un vector funcional (KX 1). Tomando la potencia n-1 de la array de transformación y multiplicándola con el vector funcional, proporcione el vector resultante, dígalo Res de tamaño KX 1. El primer elemento de Res será la respuesta para un valor de n dado. Este enfoque tomará una complejidad de tiempo O (K ^ 3logn), que es la complejidad de encontrar (n-1) el poder de la array de transformación.
Términos clave:
K = No de términos de los que depende F(n), de la relación de recurrencia podemos decir que F(n) depende de F(n-1) y F(n-2). => K =3
F1 = Vector (array 1D) que contiene el valor F(n) de los primeros K términos. Dado que K=3 =>F1 tendrá el valor F(n) de los primeros 2 términos. F1=[1,2,4]
T = Array de transformación que es una array 2D de tamaño KXK y consta de todo 1 después de la diagonal y resto cero excepto la última fila. La última fila tendrá el coeficiente de todos los K términos de los que depende F(n) en orden inverso. => T =[ [0 1 0] ,[0 0 1], [1 1 1] ].
Algoritmos:
1)Take Input N 2)If N < K then Return Precalculated Answer //Base Condition 3)construct F1 Vector and T (Transformation Matrix) 4)Take N-1th power of T by using Optimal Power(T,N) Methods and assign it in T 5)return (TXF)[1]
para métodos de potencia óptima (T, N), consulte el siguiente artículo: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/write-ac-program-to-calculate-powxn/
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define k 3
using namespace std;
// Multiply Two Matrix Function
vector<vector<int> > multiply(vector<vector<int> > A,
vector<vector<int> > B)
{
// third matrix to store multiplication of Two matrix9*
vector<vector<int> > C(k + 1, vector<int>(k + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
for (int x = 1; x <= k; x++) {
C[i][j] = (C[i][j] + (A[i][x] * B[x][j]));
}
}
}
return C;
}
// Optimal Way For finding pow(t,n)
// If n Is Odd then It Will be t*pow(t,n-1)
// else return pow(t,n/2)*pow(t,n/2)
vector<vector<int> > pow(vector<vector<int> > t, int n)
{
// base Case
if (n == 1) {
return t;
}
// Recurrence Case
if (n & 1) {
return multiply(t, pow(t, n - 1));
}
else {
vector<vector<int> > X = pow(t, n / 2);
return multiply(X, X);
}
}
int compute(int n)
{
// base Case
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 1)
return 1;
if (n == 2)
return 2;
// Function Vector(indexing 1 )
// that is [1,2]
int f1[k + 1] = {};
f1[1] = 1;
f1[2] = 2;
f1[3] = 4;
// Constructing Transformation Matrix that will be
/*[[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[3,2,1]]
*/
vector<vector<int> > t(k + 1, vector<int>(k + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
if (i < k) {
// Store 1 in cell that is next to diagonal
// of Matrix else Store 0 in cell
if (j == i + 1) {
t[i][j] = 1;
}
else {
t[i][j] = 0;
}
continue;
}
// Last Row - store the Coefficients in reverse
// order
t[i][j] = 1;
}
}
// Computing T^(n-1) and Setting Transformation matrix T
// to T^(n-1)
t = pow(t, n - 1);
int sum = 0;
// Computing first cell (row=1,col=1) For Resultant
// Matrix TXF
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += t[1][i] * f1[i];
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int n = 4;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
n = 5;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
n = 10;
cout << compute(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int k = 3;
// Multiply Two Matrix Function
static int[][] multiply(int[][] A, int[][] B)
{
// Third matrix to store multiplication
// of Two matrix9*
int[][] C = new int[k + 1][k + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
for (int x = 1; x <= k; x++) {
C[i][j]
= (C[i][j] + (A[i][x] * B[x][j]));
}
}
}
return C;
}
// Optimal Way For finding pow(t,n)
// If n Is Odd then It Will be t*pow(t,n-1)
// else return pow(t,n/2)*pow(t,n/2)
static int[][] pow(int[][] t, int n)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 1) {
return t;
}
// Recurrence Case
if ((n & 1) != 0) {
return multiply(t, pow(t, n - 1));
}
else {
int[][] X = pow(t, n / 2);
return multiply(X, X);
}
}
static int compute(int n)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 1)
return 1;
if (n == 2)
return 2;
// Function int(indexing 1 )
// that is [1,2]
int f1[] = new int[k + 1];
f1[1] = 1;
f1[2] = 2;
f1[3] = 4;
// Constructing Transformation Matrix that will be
/*[[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[3,2,1]]
*/
int[][] t = new int[k + 1][k + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
if (i < k) {
// Store 1 in cell that is next to
// diagonal of Matrix else Store 0 in
// cell
if (j == i + 1) {
t[i][j] = 1;
}
else {
t[i][j] = 0;
}
continue;
}
// Last Row - store the Coefficients
// in reverse order
t[i][j] = 1;
}
}
// Computing T^(n-1) and Setting
// Transformation matrix T to T^(n-1)
t = pow(t, n - 1);
int sum = 0;
// Computing first cell (row=1,col=1)
// For Resultant Matrix TXF
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += t[1][i] * f1[i];
}
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input
int n = 4;
System.out.println(compute(n));
n = 5;
System.out.println(compute(n));
n = 10;
System.out.println(compute(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shubhamsingh10
Python3
k = 3 # Multiply Two Matrix Function def multiply(A, B): # third matrix to store multiplication of Two matrix9* C = [[0 for x in range(k+1)] for y in range(k+1)] for i in range(1, k+1): for j in range(1, k+1): for x in range(1, k+1): C[i][j] = (C[i][j] + (A[i][x] * B[x][j])) return C # Optimal Way For finding pow(t,n) # If n Is Odd then It Will be t*pow(t,n-1) # else return pow(t,n/2)*pow(t,n/2) def pow(t, n): # base Case if (n == 1): return t # Recurrence Case if (n & 1): return multiply(t, pow(t, n - 1)) else: X = pow(t, n // 2) return multiply(X, X) def compute(n): # base Case if (n == 0): return 1 if (n == 1): return 1 if (n == 2): return 2 # Function Vector(indexing 1 ) # that is [1,2] f1 = [0]*(k + 1) f1[1] = 1 f1[2] = 2 f1[3] = 4 # Constructing Transformation Matrix that will be # [[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[3,2,1]] t = [[0 for x in range(k+1)] for y in range(k+1)] for i in range(1, k+1): for j in range(1, k+1): if (i < k): # Store 1 in cell that is next to diagonal of Matrix else Store 0 in # cell if (j == i + 1): t[i][j] = 1 else: t[i][j] = 0 continue # Last Row - store the Coefficients in reverse order t[i][j] = 1 # Computing T^(n-1) and Setting Transformation matrix T to T^(n-1) t = pow(t, n - 1) sum = 0 # Computing first cell (row=1,col=1) For Resultant Matrix TXF for i in range(1, k+1): sum += t[1][i] * f1[i] return sum # Driver Code n = 4 print(compute(n)) n = 5 print(compute(n)) n = 10 print(compute(n)) # This code is contributed by Shubhamsingh10
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG {
static int k = 3;
// Multiply Two Matrix Function
static int[, ] multiply(int[, ] A, int[, ] B)
{
// Third matrix to store multiplication
// of Two matrix9*
int[, ] C = new int[k + 1, k + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
for (int x = 1; x <= k; x++) {
C[i, j]
= (C[i, j] + (A[i, x] * B[x, j]));
}
}
}
return C;
}
// Optimal Way For finding pow(t,n)
// If n Is Odd then It Will be t*pow(t,n-1)
// else return pow(t,n/2)*pow(t,n/2)
static int[, ] pow(int[, ] t, int n)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 1) {
return t;
}
// Recurrence Case
if ((n & 1) != 0) {
return multiply(t, pow(t, n - 1));
}
else {
int[, ] X = pow(t, n / 2);
return multiply(X, X);
}
}
static int compute(int n)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 1)
return 1;
if (n == 2)
return 2;
// Function int(indexing 1 )
// that is [1,2]
int[] f1 = new int[k + 1];
f1[1] = 1;
f1[2] = 2;
f1[3] = 4;
// Constructing Transformation Matrix that will be
/*[[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[3,2,1]]
*/
int[, ] t = new int[k + 1, k + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
if (i < k) {
// Store 1 in cell that is next to
// diagonal of Matrix else Store 0 in
// cell
if (j == i + 1) {
t[i, j] = 1;
}
else {
t[i, j] = 0;
}
continue;
}
// Last Row - store the Coefficients
// in reverse order
t[i, j] = 1;
}
}
// Computing T^(n-1) and Setting
// Transformation matrix T to T^(n-1)
t = pow(t, n - 1);
int sum = 0;
// Computing first cell (row=1,col=1)
// For Resultant Matrix TXF
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += t[1, i] * f1[i];
}
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main()
{
// Input
int n = 4;
Console.WriteLine(compute(n));
n = 5;
Console.WriteLine(compute(n));
n = 10;
Console.WriteLine(compute(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shubhamsingh10
Javascript
<script>
let k = 3;
// Multiply Two Matrix Function
function multiply(A,B)
{
// Third matrix to store multiplication
// of Two matrix9*
let C = new Array(k + 1);
for(let i=0;i<k+1;i++)
{
C[i]=new Array(k+1);
for(let j=0;j<k+1;j++)
{
C[i][j]=0;
}
}
for(let i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
for(let j = 1; j <= k; j++)
{
for(let x = 1; x <= k; x++)
{
C[i][j] = (C[i][j] + (A[i][x] * B[x][j]));
}
}
}
return C;
}
// Optimal Way For finding pow(t,n)
// If n Is Odd then It Will be t*pow(t,n-1)
// else return pow(t,n/2)*pow(t,n/2)
function pow(t,n)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 1)
{
return t;
}
// Recurrence Case
if ((n & 1) != 0)
{
return multiply(t, pow(t, n - 1));
}
else
{
let X = pow(t, n / 2);
return multiply(X, X);
}
}
function compute(n)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0) return 1;
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
// Function int(indexing 1 )
// that is [1,2]
let f1=new Array(k + 1);
f1[1] = 1;
f1[2] = 2;
f1[3] = 4;
// Constructing Transformation Matrix that will be
/*[[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[3,2,1]]
*/
let t = new Array(k + 1);
for(let i=0;i<k+1;i++)
{
t[i]=new Array(k+1);
for(let j=0;j<k+1;j++)
{
t[i][j]=0;
}
}
for(let i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
for(let j = 1; j <= k; j++)
{
if (i < k)
{
// Store 1 in cell that is next to
// diagonal of Matrix else Store 0 in
// cell
if (j == i + 1)
{
t[i][j] = 1;
}
else
{
t[i][j] = 0;
}
continue;
}
// Last Row - store the Coefficients
// in reverse order
t[i][j] = 1;
}
}
// Computing T^(n-1) and Setting
// Transformation matrix T to T^(n-1)
t = pow(t, n - 1);
let sum = 0;
// Computing first cell (row=1,col=1)
// For Resultant Matrix TXF
for(let i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
sum += t[1][i] * f1[i];
}
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
// Input
let n = 4;
document.write(compute(n)+"<br>");
n = 5;
document.write(compute(n)+"<br>");
n = 10;
document.write(compute(n)+"<br>");
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
7 13 274
Explanation:
We Know For This Question
Transformation Matrix M= [[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Functional Vector F1 = [1,2,4]
for n=2 :
ans = (M X F1)[1]
ans = [2,4,7][1]
ans = 2 //[2,4,7][1] = First cell value of [2,4,7] i.e 2
for n=3 :
ans = (M X M X F1)[1] //M^(3-1) X F1 = M X M X F1
ans = (M X [2,4,7])[1]
ans = [4,7,13][1]
ans = 4
for n = 4 :
ans = (M^(4-1) X F1)[1]
ans = (M X M X M X F1) [1]
ans = (M X [4,7,13])[1]
ans = [7,13,24][1]
ans = 7
for n = 5 :
ans = (M^4 X F1)[1]
ans = (M X [7,13,24])[1]
ans = [13,24,44][1]
ans = 13
Complejidad del tiempo:
O(K^3log(n)) //For Computing pow(t,n-1) For this question K is 3 So Overall Time Complexity is O(27log(n))=O(logn)
Método 4: Usando cuatro variables
La idea se basa en la serie de Fibonacci pero aquí con 3 sumas. mantendremos los valores de los tres primeros escalones en 3 variables y usaremos la cuarta variable para encontrar el número de vías.
C++
// A C++ program to count number of ways
// to reach nth stair when
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// A recursive function used by countWays
int countWays(int n)
{
int a = 1, b = 2, c = 4; // declaring three variables
// and holding the ways
// for first three stairs
int d = 0; // fourth variable
if (n == 0 || n == 1 || n == 2)
return n;
if (n == 3)
return c;
for (int i = 4; i <= n; i++) { // starting from 4 as
d = c + b + a; // already counted for 3 stairs
a = b;
b = c;
c = d;
}
return d;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int n = 4;
cout << countWays(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Naveen Shah
Java
// A Java program to count number of ways
// to reach nth stair when
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// A recursive function used by countWays
static int countWays(int n)
{
// Declaring three variables
// and holding the ways
// for first three stairs
int a = 1, b = 2, c = 4;
// Fourth variable
int d = 0;
if (n == 0 || n == 1 || n == 2)
return n;
if (n == 3)
return c;
for(int i = 4; i <= n; i++)
{
// Starting from 4 as
// already counted for 3 stairs
d = c + b + a;
a = b;
b = c;
c = d;
}
return d;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
System.out.println(countWays(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Python3
# A Python program to count number of ways # to reach nth stair when # A recursive function used by countWays def countWays(n): # declaring three variables # and holding the ways # for first three stairs a = 1 b = 2 c = 4 d = 0 # fourth variable if (n == 0 or n == 1 or n == 2): return n if (n == 3): return c for i in range(4,n+1): # starting from 4 as d = c + b + a # already counted for 3 stairs a = b b = c c = d return d # Driver program to test above functions n = 4 print(countWays(n)) # This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C#
// A C# program to count number of ways
// to reach nth stair when
using System;
class GFG{
// A recursive function used by countWays
static int countWays(int n)
{
// Declaring three variables
// and holding the ways
// for first three stairs
int a = 1, b = 2, c = 4;
// Fourth variable
int d = 0;
if (n == 0 || n == 1 || n == 2)
return n;
if (n == 3)
return c;
for(int i = 4; i <= n; i++)
{
// Starting from 4 as
// already counted for 3 stairs
d = c + b + a;
a = b;
b = c;
c = d;
}
return d;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
Console.Write(countWays(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Javascript
<script>
// A JavaScript program to count number of ways
// to reach nth stair when
// A recursive function used by countWays
function countWays( n)
{
// Declaring three variables
// and holding the ways
// for first three stairs
var a = 1, b = 2, c = 4;
// Fourth variable
var d = 0;
if (n == 0 || n == 1 || n == 2)
return n;
if (n == 3)
return c;
for(var i = 4; i <= n; i++)
{
// Starting from 4 as
// already counted for 3 stairs
d = c + b + a;
a = b;
b = c;
c = d;
}
return d;
}
// Driver code
var n = 4;
document.write(countWays(n));
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
</script>
7
Complejidad Temporal: O(n) Espacio
Auxiliar : O(1).
Método 5: DP usando memorización (enfoque de arriba hacia abajo)
Podemos evitar el trabajo repetido realizado en el método 1 (recursión) almacenando el número de formas calculadas hasta ahora.
Solo necesitamos almacenar todos los valores en una array.
C++
// C++ Program to find n-th stair using step size
// 1 or 2 or 3.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class GFG {
private:
int findStepHelper(int n, vector<int>& dp)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n < 0)
return 0;
// If subproblems are already calculated
//then return it
if (dp[n] != -1) {
return dp[n];
}
// store the subproblems in the vector
return dp[n] = findStepHelper(n - 3, dp)
+ findStepHelper(n - 2, dp)
+ findStepHelper(n - 1, dp);
}
// Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair
// using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
public:
int findStep(int n)
{
vector<int> dp(n + 1, -1);
return findStepHelper(n, dp);
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
GFG g;
int n = 4;
cout << g.findStep(n);
return 0;
}
Java
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Java Program to find n-th stair using step size
// 1 or 2 or 3.
static class gfg {
private int findStepHelper(int n, int[] dp)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n < 0)
return 0;
// If subproblems are already calculated
//then return it
if (dp[n] != -1) {
return dp[n];
}
// store the subproblems in the vector
return dp[n] = findStepHelper(n - 3, dp)
+ findStepHelper(n - 2, dp)
+ findStepHelper(n - 1, dp);
}
// Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair
// using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
public int findStep(int n)
{
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp,-1);
return findStepHelper(n, dp);
}
};
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void main(String args[])
{
gfg g = new gfg();
int n = 4;
System.out.println(g.findStep(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
Python3
# Python Program to find n-th stair using step size # 1 or 2 or 3. class GFG: def findStepHelper(self, n, dp): # Base Case if (n == 0): return 1 elif (n < 0): return 0 # If subproblems are already calculated #then return it if (dp[n] != -1): return dp[n] # store the subproblems in the vector dp[n] = self.findStepHelper(n - 3, dp) + self.findStepHelper(n - 2, dp) + self.findStepHelper(n - 1, dp) return dp[n] # Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair # using 1 or 2 or 3 steps. def findStep(self, n): dp = [-1 for i in range(n + 1)] return self.findStepHelper(n, dp) # Driver code g = GFG() n = 4 print(g.findStep(n)) # This code is contributed by shinjanpatra.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to find n-th stair using step size
// 1 or 2 or 3.
class GFG {
findStepHelper(n,dp)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n < 0)
return 0;
// If subproblems are already calculated
//then return it
if (dp[n] != -1) {
return dp[n];
}
// store the subproblems in the vector
return dp[n] = this.findStepHelper(n - 3, dp)
+ this.findStepHelper(n - 2, dp)
+ this.findStepHelper(n - 1, dp);
}
// Returns count of ways to reach n-th stair
// using 1 or 2 or 3 steps.
findStep(n)
{
let dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(-1);
return this.findStepHelper(n, dp);
}
};
// Driver code
let g = new GFG();
let n = 4;
document.write(g.findStep(n));
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra.
</script>
7
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n). Solo se necesita un recorrido de la array. Entonces la Complejidad del Tiempo es O(n).
- Complejidad espacial: O(n). Para almacenar los valores en un DP, se necesita n espacio extra. Además, se necesita espacio de pila para la recursividad, que nuevamente es O (n)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por prakhargvp y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA