Se da un tablero de largo m y ancho n, necesitamos dividir este tablero en m*n cuadrados de manera que el costo de romperlo sea mínimo. el costo de corte para cada borde se dará para el tablero. En resumen, debemos elegir una secuencia de corte tal que se minimice el costo.
Ejemplos:
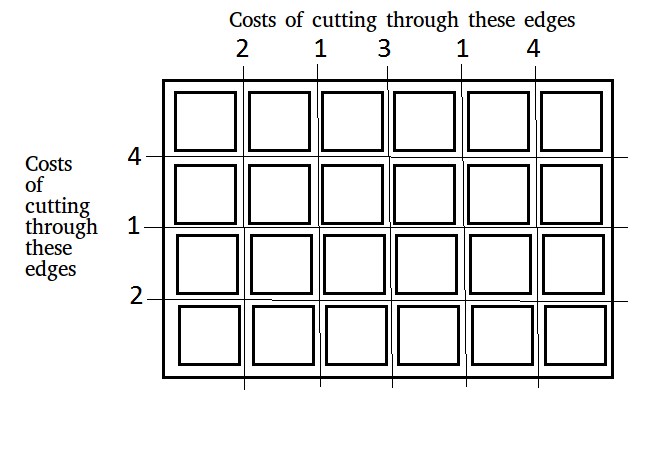
For above board optimal way to cut into square is: Total minimum cost in above case is 42. It is evaluated using following steps. Initial Value : Total_cost = 0 Total_cost = Total_cost + edge_cost * total_pieces Cost 4 Horizontal cut Cost = 0 + 4*1 = 4 Cost 4 Vertical cut Cost = 4 + 4*2 = 12 Cost 3 Vertical cut Cost = 12 + 3*2 = 18 Cost 2 Horizontal cut Cost = 18 + 2*3 = 24 Cost 2 Vertical cut Cost = 24 + 2*3 = 30 Cost 1 Horizontal cut Cost = 30 + 1*4 = 34 Cost 1 Vertical cut Cost = 34 + 1*4 = 38 Cost 1 Vertical cut Cost = 38 + 1*4 = 42
Este problema se puede resolver utilizando un enfoque codicioso. Si el costo total se denota por S, entonces S = a1w1 + a2w2 … + akwk, donde wi es el costo de cierto corte de filo y ai es el coeficiente correspondiente. El coeficiente ai está determinado por el total número de cortes que hemos competido utilizando edge wi al final del proceso de corte. Tenga en cuenta que la suma de los coeficientes siempre es constante, por lo tanto, queremos encontrar una distribución de ai obtenible tal que S sea mínimo. Para hacerlo , realizamos cortes en el borde de mayor costo lo antes posible , lo que alcanzará la S óptima. Si encontramos varios bordes que tienen el mismo costo, podemos cortar cualquiera de ellos primero.
A continuación se muestra la solución que usa el enfoque anterior, primero clasificamos los costos de corte de borde en orden inverso, luego los recorremos de mayor costo a menor costo para construir nuestra solución. Cada vez que elegimos un borde, el recuento de contrapartes se incrementa en 1, que se multiplicará cada vez con el costo de corte del borde correspondiente.
Observe a continuación el método de ordenación utilizado, que envía mayor() como tercer argumento para ordenar el número de ordenación del método en orden no creciente, es una función predefinida de la biblioteca.
C++
// C++ program to divide a board into m*n squares
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// method returns minimum cost to break board into
// m*n squares
int minimumCostOfBreaking(int X[], int Y[], int m, int n)
{
int res = 0;
// sort the horizontal cost in reverse order
sort(X, X + m, greater<int>());
// sort the vertical cost in reverse order
sort(Y, Y + n, greater<int>());
// initialize current width as 1
int hzntl = 1, vert = 1;
// loop until one or both cost array are processed
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (X[i] > Y[j])
{
res += X[i] * vert;
// increase current horizontal part count by 1
hzntl++;
i++;
}
else
{
res += Y[j] * hzntl;
// increase current vertical part count by 1
vert++;
j++;
}
}
// loop for horizontal array, if remains
int total = 0;
while (i < m)
total += X[i++];
res += total * vert;
// loop for vertical array, if remains
total = 0;
while (j < n)
total += Y[j++];
res += total * hzntl;
return res;
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
int m = 6, n = 4;
int X[m-1] = {2, 1, 3, 1, 4};
int Y[n-1] = {4, 1, 2};
cout << minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to divide a
// board into m*n squares
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG
{
// method returns minimum cost to break board into
// m*n squares
static int minimumCostOfBreaking(Integer X[], Integer Y[],
int m, int n)
{
int res = 0;
// sort the horizontal cost in reverse order
Arrays.sort(X, Collections.reverseOrder());
// sort the vertical cost in reverse order
Arrays.sort(Y, Collections.reverseOrder());
// initialize current width as 1
int hzntl = 1, vert = 1;
// loop until one or both
// cost array are processed
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (X[i] > Y[j])
{
res += X[i] * vert;
// increase current horizontal
// part count by 1
hzntl++;
i++;
}
else
{
res += Y[j] * hzntl;
// increase current vertical
// part count by 1
vert++;
j++;
}
}
// loop for horizontal array,
// if remains
int total = 0;
while (i < m)
total += X[i++];
res += total * vert;
// loop for vertical array,
// if remains
total = 0;
while (j < n)
total += Y[j++];
res += total * hzntl;
return res;
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String arg[])
{
int m = 6, n = 4;
Integer X[] = {2, 1, 3, 1, 4};
Integer Y[] = {4, 1, 2};
System.out.print(minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.
Python3
# Python program to divide a board into m*n squares # Method returns minimum cost to # break board into m*n squares def minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m, n): res = 0 # sort the horizontal cost in reverse order X.sort(reverse = True) # sort the vertical cost in reverse order Y.sort(reverse = True) # initialize current width as 1 hzntl = 1; vert = 1 # loop until one or both # cost array are processed i = 0; j = 0 while (i < m and j < n): if (X[i] > Y[j]): res += X[i] * vert # increase current horizontal # part count by 1 hzntl += 1 i += 1 else: res += Y[j] * hzntl # increase current vertical # part count by 1 vert += 1 j += 1 # loop for horizontal array, if remains total = 0 while (i < m): total += X[i] i += 1 res += total * vert #loop for vertical array, if remains total = 0 while (j < n): total += Y[j] j += 1 res += total * hzntl return res # Driver program m = 6; n = 4 X = [2, 1, 3, 1, 4] Y = [4, 1, 2] print(minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1)) # This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.
C#
// C# program to divide a
// board into m*n squares
using System;
class GFG
{
// method returns minimum cost to break board into
// m*n squares
static int minimumCostOfBreaking(int[] X, int[] Y,
int m, int n)
{
int res = 0;
// sort the horizontal cost in reverse order
Array.Sort<int>(X, new Comparison<int>(
(i1, i2) => i2.CompareTo(i1)));
// sort the vertical cost in reverse order
Array.Sort<int>(Y, new Comparison<int>(
(i1, i2) => i2.CompareTo(i1)));
// initialize current width as 1
int hzntl = 1, vert = 1;
// loop until one or both
// cost array are processed
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (X[i] > Y[j])
{
res += X[i] * vert;
// increase current horizontal
// part count by 1
hzntl++;
i++;
}
else
{
res += Y[j] * hzntl;
// increase current vertical
// part count by 1
vert++;
j++;
}
}
// loop for horizontal array,
// if remains
int total = 0;
while (i < m)
total += X[i++];
res += total * vert;
// loop for vertical array,
// if remains
total = 0;
while (j < n)
total += Y[j++];
res += total * hzntl;
return res;
}
// Driver program
public static void Main(String []arg)
{
int m = 6, n = 4;
int []X = {2, 1, 3, 1, 4};
int []Y = {4, 1, 2};
Console.WriteLine(minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to divide a
// board into m*n squares
// method returns minimum cost to break board into
// m*n squares
function minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m, n)
{
let res = 0;
// sort the horizontal cost in reverse order
X.sort();
X.reverse();
// sort the vertical cost in reverse order
Y.sort();
Y.reverse();
// initialize current width as 1
let hzntl = 1, vert = 1;
// loop until one or both
// cost array are processed
let i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (X[i] > Y[j])
{
res += X[i] * vert;
// increase current horizontal
// part count by 1
hzntl++;
i++;
}
else
{
res += Y[j] * hzntl;
// increase current vertical
// part count by 1
vert++;
j++;
}
}
// loop for horizontal array,
// if remains
let total = 0;
while (i < m)
total += X[i++];
res += total * vert;
// loop for vertical array,
// if remains
total = 0;
while (j < n)
total += Y[j++];
res += total * hzntl;
return res;
}
// Driver Code
let m = 6, n = 4;
let X = [2, 1, 3, 1, 4];
let Y = [4, 1, 2];
document.write(minimumCostOfBreaking(X, Y, m-1, n-1));
</script>
Producción:
42
Este artículo es una contribución de Utkarsh Trivedi . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA