Normalmente, muchas empresas fracasan debido a la falta de ganancias, la falta de medidas de mejora adecuadas. En su mayoría, los propietarios de restaurantes enfrentan muchas dificultades para mejorar su productividad. Este proyecto realmente ayuda a quienes desean aumentar su productividad, lo que a su vez aumenta las ganancias de su negocio. Este es el objetivo principal de este proyecto.
Lo que hace el proyecto es que el propietario del restaurante se entera de los inconvenientes de su restaurante, como los alimentos que más le disgustan de su restaurante, mediante la revisión de texto del cliente que se procesa con el algoritmo de clasificación ML (Naive Bayes) y sus resultados se almacenan en la base de datos usando SQLite.
Herramientas y tecnologías utilizadas:
- NLTK
- Aprendizaje automático
- Python
- Tkinter
- Sqlite3
- pandas
Implementación paso a paso:
Paso 1: Importación de bibliotecas e inicialización de datos
En primer lugar, importamos las bibliotecas NumPy , matplotlib , pandas , nltk, re, sklearn, Tkinter , sqlite3 que se utilizan para la manipulación de datos, procesamiento de datos de texto, reconocimiento de patrones, entrenamiento de datos, interfaces gráficas de usuario y manipulación de datos en la base de datos.
Python3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import re
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from tkinter import *
import sqlite3
dataset = pd.read_csv('Restaurant_Reviews.tsv',
delimiter='\t', quoting=3)
corpus = []
rras_code = "Wyd^H3R"
food_rev = {}
food_perc = {}
conn = sqlite3.connect('Restaurant_food_data.db')
c = conn.cursor()
for i in range(0, 1000):
review = re.sub('[^a-zA-Z]', ' ', dataset['Review'][i])
review = review.lower()
review = review.split()
ps = PorterStemmer()
all_stopwords = stopwords.words('english')
all_stopwords.remove('not')
review = [ps.stem(word)
for word in review if not word in set(all_stopwords)]
review = ' '.join(review)
corpus.append(review)
cv = CountVectorizer(max_features=1500)
X = cv.fit_transform(corpus).toarray()
y = dataset.iloc[:, -1].values
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.20, random_state=0)
classifier = GaussianNB()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
variables = []
clr_variables = []
foods = ["Idly", "Dosa", "Vada", "Roti", "Meals", "Veg Biryani",
"Egg Biryani", "Chicken Biryani", "Mutton Biryani",
"Ice Cream", "Noodles", "Manchooriya", "Orange juice",
"Apple Juice", "Pineapple juice", "Banana juice"]
for i in foods:
food_rev[i] = []
food_perc[i] = [0.0, 0.0]
def init_data():
conn = sqlite3.connect('Restaurant_food_data.db')
c = conn.cursor()
for i in range(len(foods)):
c.execute("INSERT INTO item VALUES(:item_name,:no_of_customers,\
:no_of_positives,:no_of_negatives,:pos_perc,:neg_perc)",
{
'item_name': foods[i],
'no_of_customers': "0",
'no_of_positives': "0",
'no_of_negatives': "0",
'pos_perc': "0.0%",
'neg_perc': "0.0%"
}
)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
Paso 2: Aclarar al usuario
Inicialmente, nuestra aplicación GUI pregunta al usuario si es propietario o cliente para decidir qué acción realizar.
Python3
root1 = Tk()
main = "Restaurant Review Analysis System/"
root1.title(main+"Welcome Page")
label = Label(root1, text="RESTAURANT REVIEW ANALYSIS SYSTEM",
bd=2, font=('Arial', 47, 'bold', 'underline'))
ques = Label(root1, text="Are you a Customer or Owner ???")
cust = Button(root1, text="Customer", font=('Arial', 20),
padx=80, pady=20, command=take_review)
owner = Button(root1, text="Owner", font=('Arial', 20),
padx=100, pady=20, command=login)
'''conn=sqlite3.connect('Restaurant_food_data.db')
c=conn.cursor()
c.execute("CREATE TABLE item (Item_name text,No_of_customers text,\
No_of_positive_reviews text,No_of_negative_reviews text,Positive_percentage \
text,Negative_percentage text) ")
conn.commit()
conn.close()'''
#c.execute("DELETE FROM item")
root1.attributes("-zoomed", True)
label.grid(row=0, column=0)
ques.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky=W+E)
ques.config(font=("Helvetica", 30))
cust.grid(row=2, column=0)
owner.grid(row=3, column=0)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
root1.mainloop()
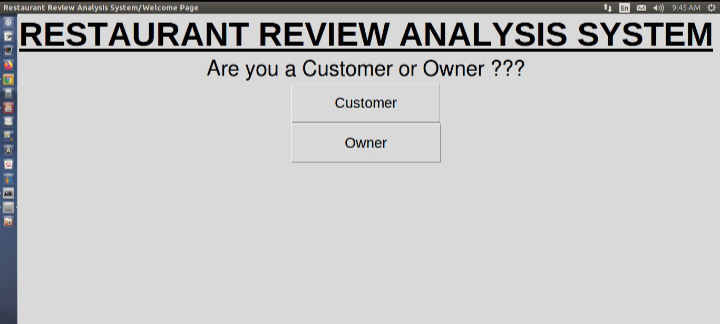
aclarando usuario
Paso 3: Recopilación de datos
Una vez que el sistema asegura que el usuario es un cliente, solicita la revisión de alimentos en formato de texto. El cliente debe seleccionar los alimentos que ha tomado del restaurante y luego dar su opinión sobre los alimentos seleccionados. Cuando hace clic en el botón Enviar, la revisión de texto se trata con el algoritmo ML para predecir si se trata de una revisión positiva o negativa. Y luego, todos los datos se insertan en la base de datos.
Python3
def take_review():
root2 = Toplevel()
root2.title(main+"give review")
label = Label(root2, text="RESTAURANT REVIEW ANALYSIS SYSTEM",
bd=2, font=('Arial', 47, 'bold', 'underline'))
req1 = Label(root2, text="Select the item(s) you have taken.....")
conn = sqlite3.connect('Restaurant_food_data.db')
c = conn.cursor()
chk_btns = []
selected_foods = []
req2 = Label(root2, text="Give your review below....")
rev_tf = Entry(root2, width=125, borderwidth=5)
req3 = Label(root2, text="NOTE : Use not instead of n't.")
global variables
variables = []
chk_btns = []
for i in range(len(foods)):
var = IntVar()
chk = Checkbutton(root2, text=foods[i], variable=var)
variables.append(var)
chk_btns.append(chk)
label.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=4)
req1.grid(row=1, column=0, columnspan=4, sticky=W+E)
req1.config(font=("Helvetica", 30))
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
c = chk_btns[i*4+j]
c.grid(row=i+3, column=j, columnspan=1, sticky=W)
selected_foods = []
submit_review = Button(root2, text="Submit Review", font=(
'Arial', 20), padx=100, pady=20, command=lambda: [
estimate(rev_tf.get()), root2.destroy()])
root2.attributes("-zoomed", True)
req2.grid(row=7, column=0, columnspan=4, sticky=W+E)
req2.config(font=("Helvetica", 20))
rev_tf.grid(row=8, column=1, rowspan=3, columnspan=2, sticky=S)
req3.grid(row=11, column=1, columnspan=2)
submit_review.grid(row=12, column=0, columnspan=4)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
# Processing and storing the data
def estimate(s):
conn = sqlite3.connect('Restaurant_food_data.db')
c = conn.cursor()
review = re.sub('[^a-zA-Z]', ' ', s)
review = review.lower()
review = review.split()
ps = PorterStemmer()
all_stopwords = stopwords.words('english')
all_stopwords.remove('not')
review = [ps.stem(word)
for word in review if not word in set(all_stopwords)]
review = ' '.join(review)
X = cv.transform([review]).toarray()
res = classifier.predict(X) # list
if "not" in review:
res[0] = abs(res[0]-1)
selected_foods = []
for i in range(len(foods)):
if variables[i].get() == 1:
selected_foods.append(foods[i])
c.execute("SELECT *,oid FROM item")
records = c.fetchall()
for i in records:
rec = list(i)
if rec[0] in selected_foods:
n_cust = int(rec[1])+1
n_pos = int(rec[2])
n_neg = int(rec[3])
if res[0] == 1:
n_pos += 1
else:
n_neg += 1
pos_percent = round((n_pos/n_cust)*100, 1)
neg_percent = round((n_neg/n_cust)*100, 1)
c.execute("""UPDATE item SET Item_name=:item_name,No_of_customers\
=:no_of_customers,No_of_positive_reviews=:no_of_positives,\
No_of_negative_reviews=:no_of_negatives,Positive_percentage\
=:pos_perc,Negative_percentage=:neg_perc where oid=:Oid""",
{
'item_name': rec[0],
'no_of_customers': str(n_cust),
'no_of_positives': str(n_pos),
'no_of_negatives': str(n_neg),
'pos_perc': str(pos_percent)+"%",
'neg_perc': str(neg_percent)+"%",
'Oid': foods.index(rec[0])+1
}
)
selected_foods = []
conn.commit()
conn.close()
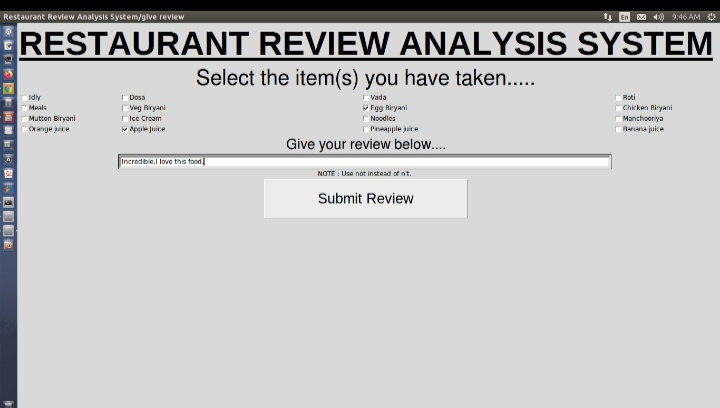
tomando revisión
Paso 4: Verificación de propiedad
Si el usuario actual del sistema es el propietario del restaurante, entonces el sistema verifica al propietario preguntando rras_code (es decir, un código que identifica de forma única a un restaurante en todo el mundo. Y es altamente confidencial, no se debe compartir este código con otros excepto los copropietarios del restaurante).
Python3
def login():
root3 = Toplevel()
root3.title(main+"owner verification")
label = Label(root3, text="RESTAURANT REVIEW ANALYSIS SYSTEM",
bd=2, font=('Arial', 47, 'bold', 'underline'))
label2 = Label(root3, text="VERIFY OWNERSHIP", bd=1,
font=('Helvetica', 30, 'bold', 'underline'))
label3 = Label(root3, text="To verify your ownership, please \
enter your restaurant's private rras code....",
bd=1, font=('Helvetica', 20, 'bold'))
ent = Entry(root3, show="*", borderwidth=2)
submit_code = Button(root3, text="Submit", font=('Arial', 20), padx=80,
pady=20, command=lambda: [
view_details(ent.get()), root3.destroy()])
root3.attributes("-zoomed", True)
label.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=3)
label2.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky=W+E, columnspan=3)
label3.grid(row=2, column=0, sticky=W, columnspan=3)
ent.grid(row=3, column=1, columnspan=1)
submit_code.grid(row=4, column=1, columnspan=1)
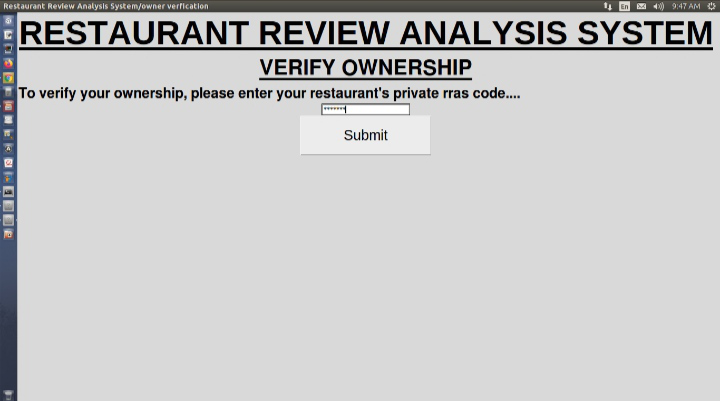
Verificando la propiedad
Paso 5: Acceder a los datos
Cuando se verifica la propiedad, el propietario tiene 3 opciones descritas en una nueva página como se menciona a continuación:
Python3
def popup():
messagebox.showerror("Error Message!", "Incorrect code!")
def view_details(s):
if(s != rras_code):
popup()
else:
root4 = Toplevel()
root4.title(main+"view_details")
label = Label(root4, text="RESTAURANT REVIEW ANALYSIS SYSTEM",
bd=2, font=('Arial', 47, 'bold', 'underline'))
sug1 = Label(
root4, text="Click the below button, if you want to view\
the data from your database....")
acc_btn = Button(root4, text="View Data", font=(
'Arial', 20), padx=100, pady=20, command=access_data)
sug2 = Label(root4, text="Click the below button, if you want \
to clear specific item data...")
itemclr_btn = Button(root4, text="Clear Item Data", font=(
'Arial', 20), padx=100, pady=20, command=clr_itemdata)
sug3 = Label(root4, text="Click the below button, if you want to\
clear all item data...")
allclr_btn = Button(root4, text="Clear All Data", font=(
'Arial', 20), padx=100, pady=20, command=clr_alldata)
exit_btn = Button(root4, text="Exit", command=root4.destroy)
root4.attributes("-zoomed", True)
label.grid(row=0, column=0)
sug1.grid(row=1, column=0)
sug1.config(font=("Helvetica", 30))
acc_btn.grid(row=2, column=0)
sug2.grid(row=3, column=0)
sug2.config(font=("Helvetica", 30))
itemclr_btn.grid(row=4, column=0)
sug3.grid(row=5, column=0)
sug3.config(font=("Helvetica", 30))
allclr_btn.grid(row=6, column=0)
exit_btn.grid(row=9, column=0, sticky=S)
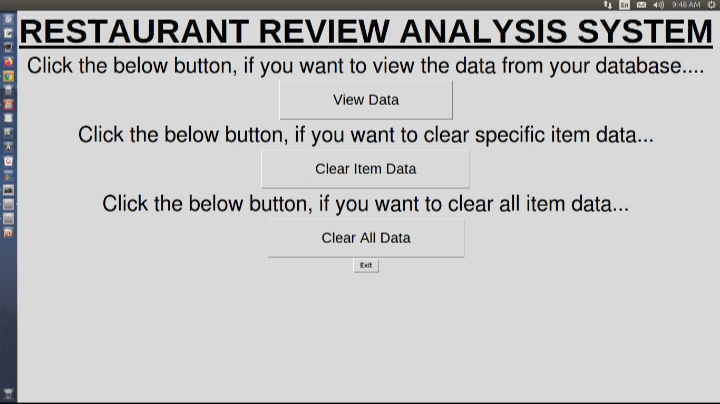
Opciones
Paso 6: Ver los datos
El propietario puede ver los datos en la base de datos donde cada alimento tiene atributos como número de clientes, número de críticas positivas, número de críticas negativas, tasa positiva, tasa negativa. Los alimentos con calificación altamente positiva están etiquetados en color verde, y los alimentos con calificación menos positiva están etiquetados en color rojo para comprender fácilmente el resumen de datos. Ahora, el propietario puede identificar alimentos de baja calificación e intenta mejorar el sabor del alimento tomando algunas medidas, como llamar a nuevos chefs, etc., lo que definitivamente mejora su negocio.
Python3
def access_data():
root5 = Toplevel()
root5.title(main+"Restaurant_Database")
label = Label(root5, text="RESTAURANT REVIEW ANALYSIS SYSTEM",
bd=2, font=('Arial', 47, 'bold', 'underline'))
title1 = Label(root5, text="S.NO", font=('Arial', 10, 'bold', 'underline'))
title2 = Label(root5, text="FOOD ITEM", font=(
'Arial', 10, 'bold', 'underline'))
title3 = Label(root5, text="NO.OF CUSTOMERS",
font=('Arial', 10, 'bold', 'underline'))
title4 = Label(root5, text="NO.OF POSITIVE REVIEWS",
font=('Arial', 10, 'bold', 'underline'))
title5 = Label(root5, text="NO.OF NEGATIVE REVIEWS",
font=('Arial', 10, 'bold', 'underline'))
title6 = Label(root5, text="POSITIVE RATE",
font=('Arial', 10, 'bold', 'underline'))
title7 = Label(root5, text="NEGATIVE RATE",
font=('Arial', 10, 'bold', 'underline'))
label.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=7)
title1.grid(row=1, column=0)
title2.grid(row=1, column=1)
title3.grid(row=1, column=2)
title4.grid(row=1, column=3)
title5.grid(row=1, column=4)
title6.grid(row=1, column=5)
title7.grid(row=1, column=6)
conn = sqlite3.connect('Restaurant_food_data.db')
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute("SELECT *,oid from item")
records = c.fetchall()
pos_rates = []
for record in records:
record = list(record)
pos_rates.append(float(record[-3][:-1]))
max_pos = max(pos_rates)
min_pos = min(pos_rates)
for i in range(len(records)):
rec_list = list(records[i])
if str(max_pos)+"%" == rec_list[-3]:
rec_lab = [Label(root5, text=str(rec_list[-1]), fg="green")]
for item in rec_list[:-1]:
lab = Label(root5, text=item, fg="green")
rec_lab.append(lab)
elif str(min_pos)+"%" == rec_list[-3]:
rec_lab = [Label(root5, text=str(rec_list[-1]), fg="red")]
for item in rec_list[:-1]:
lab = Label(root5, text=item, fg="red")
rec_lab.append(lab)
else:
rec_lab = [Label(root5, text=str(rec_list[-1]))]
for item in rec_list[:-1]:
lab = Label(root5, text=item)
rec_lab.append(lab)
for j in range(len(rec_lab)):
rec_lab[j].grid(row=i+2, column=j)
exit_btn = Button(root5, text="Exit", command=root5.destroy)
exit_btn.grid(row=len(records)+5, column=3)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
root5.attributes("-zoomed", True)
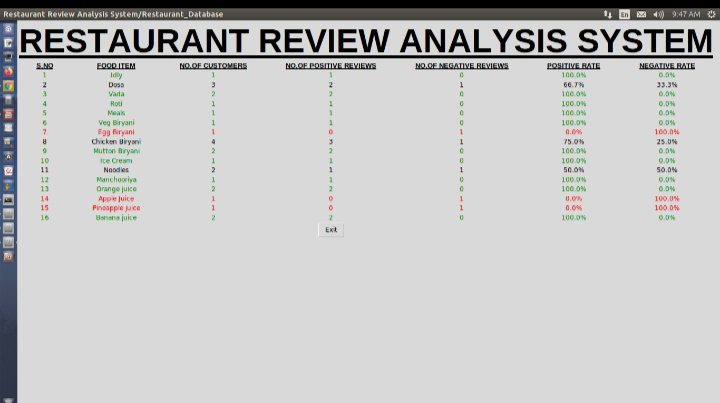
Contenido de la base de datos
Paso 7: Borrar los datos:
Cuando se han realizado algunos ajustes o modificaciones, el propietario puede borrar esos datos específicos del artículo para que pueda observar rápidamente el rendimiento del alimento. Si el propietario lo desea, también puede borrar todos los datos de los alimentos.
Python3
def clr_itemdata():
root6 = Toplevel()
root6.title(main+"clear_item_data")
label = Label(root6, text="RESTAURANT REVIEW ANALYSIS SYSTEM",
bd=2, font=('Arial', 47, 'bold', 'underline'))
req1 = Label(root6, text="Pick the items to clear their corresponding\
item data....")
chk_list = []
global clr_variables
clr_variables = []
for i in range(len(foods)):
var = IntVar()
chk = Checkbutton(root6, text=foods[i], variable=var)
clr_variables.append(var)
chk_list.append(chk)
label.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=4)
req1.grid(row=1, column=0, columnspan=4, sticky=W+E)
req1.config(font=("Helvetica", 30))
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
c = chk_list[i*4+j]
c.grid(row=i+3, column=j, columnspan=1, sticky=W)
clr_item = Button(root6, text="Clear", font=(
'Arial', 20), padx=100, pady=20, command=lambda: [
clr_data(), root6.destroy()])
clr_item.grid(row=8, column=0, columnspan=4)
root6.attributes("-zoomed", True)
def clr_alldata():
confirm = messagebox.askquestion(
"Confirmation", "Are you sure to delete all data??")
if confirm == "yes":
conn = sqlite3.connect('Restaurant_food_data.db')
c = conn.cursor()
for i in range(len(foods)):
c.execute("""UPDATE item SET Item_name=:item_name,No_of_customers\
=:no_of_customers,No_of_positive_reviews=:no_of_positives,\
No_of_negative_reviews=:no_of_negatives,Positive_percentage=:\
pos_perc,Negative_percentage=:neg_perc where oid=:Oid""",
{
'item_name': foods[i],
'no_of_customers': "0",
'no_of_positives': "0",
'no_of_negatives': "0",
'pos_perc': "0.0%",
'neg_perc': "0.0%",
'Oid': i+1
}
)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
Borrado de datos de alimentos
Finalmente, esta es mi idea para aumentar la productividad de las empresas con tecnología. Con esto, los problemas comerciales se cierran por la mejora de la productividad.
Aplicaciones de proyectos en la vida real:
- Se puede utilizar en cualquier restaurante/hotel de comida.
- Eficaz en medidas de mejora de alimentos que mejoran directamente el negocio.
- Fácil de usar.
- No hay posibilidad de pérdida de negocio.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por plrcprabhu y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA