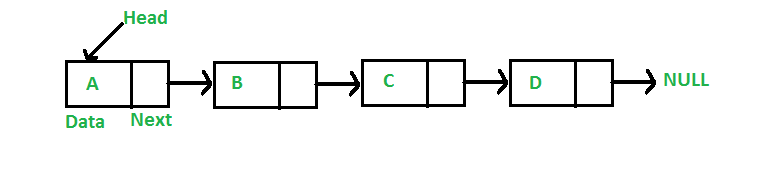
La lista enlazada almacena datos en almacenamiento secuencial, como arrays . Aunque los datos se almacenan secuencialmente, las ubicaciones de memoria no son contiguas.
A diferencia de una array, la lista vinculada puede almacenar datos de diferentes tipos de datos.
El siguiente diagrama representa la estructura de lista enlazada.
En C++, la lista enlazada se puede representar con una clase y una clase de Node por separado, que tiene dos miembros, a saber, datos y un puntero siguiente que apunta al siguiente Node.
InsertNode : en este artículo, la inserción se realiza al final de la lista . Siga los pasos para insertar un Node en la lista vinculada.
- Digamos que se va a insertar 4 en la lista enlazada existente, es decir, 1 -> 2 -> 3. La lista enlazada resultante será 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4.
- Para insertar un nuevo Node, recorra hasta el final de la lista hasta encontrar el Node NULO.
- Cree un nuevo Node y vincule el nuevo Node al último Node de la lista vinculada.
DeleteNode : en este artículo, la eliminación se realiza utilizando el índice del Node. Siga los pasos para eliminar un Node:
- Si el Node que se eliminará es el Node principal, almacene la cabeza en la variable temporal . Luego actualice head como head->next . Eliminar temp .
- Si el índice del Node a eliminar es mayor que la longitud de la lista, regrese de la función.
- Atraviese hasta el Node a eliminar. Elimine el Node y vincule el Node anterior al siguiente Node del Node eliminado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Node class to represent
// a node of the linked list.
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
// Default constructor
Node()
{
data = 0;
next = NULL;
}
// Parameterised Constructor
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
this->next = NULL;
}
};
// Linked list class to
// implement a linked list.
class Linkedlist {
Node* head;
public:
// Default constructor
Linkedlist() { head = NULL; }
// Function to insert a
// node at the end of the
// linked list.
void insertNode(int);
// Function to print the
// linked list.
void printList();
// Function to delete the
// node at given position
void deleteNode(int);
};
// Function to delete the
// node at given position
void Linkedlist::deleteNode(int nodeOffset)
{
Node *temp1 = head, *temp2 = NULL;
int ListLen = 0;
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "List empty." << endl;
return;
}
// Find length of the linked-list.
while (temp1 != NULL) {
temp1 = temp1->next;
ListLen++;
}
// Check if the position to be
// deleted is less than the length
// of the linked list.
if (ListLen < nodeOffset) {
cout << "Index out of range"
<< endl;
return;
}
// Declare temp1
temp1 = head;
// Deleting the head.
if (nodeOffset == 1) {
// Update head
head = head->next;
delete temp1;
return;
}
// Traverse the list to
// find the node to be deleted.
while (nodeOffset-- > 1) {
// Update temp2
temp2 = temp1;
// Update temp1
temp1 = temp1->next;
}
// Change the next pointer
// of the previous node.
temp2->next = temp1->next;
// Delete the node
delete temp1;
}
// Function to insert a new node.
void Linkedlist::insertNode(int data)
{
// Create the new Node.
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
// Assign to head
if (head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
// Traverse till end of list
Node* temp = head;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
// Update temp
temp = temp->next;
}
// Insert at the last.
temp->next = newNode;
}
// Function to print the
// nodes of the linked list.
void Linkedlist::printList()
{
Node* temp = head;
// Check for empty list.
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "List empty" << endl;
return;
}
// Traverse the list.
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Linkedlist list;
// Inserting nodes
list.insertNode(1);
list.insertNode(2);
list.insertNode(3);
list.insertNode(4);
cout << "Elements of the list are: ";
// Print the list
list.printList();
cout << endl;
// Delete node at position 2.
list.deleteNode(2);
cout << "Elements of the list are: ";
list.printList();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Elements of the list are: 1 2 3 4 Elements of the list are: 1 3 4
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)