Dado un Node de Lista enlazada N y un valor K, la tarea es insertar el Node con valor K en la lista enlazada antes del Node N dado .
Estructura del Node:
C++
// Structure of Node
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
// Constructor of Node
Node(int val, Node* link = 0)
: data(val), next(link)
{
}
};
Java
// Structure of Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
// Constructor of Node
public Node(int val, Node link = null)
{
this.data = val;
this.next = link;
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019
Python3
# Structure of Node class Node: # Constructor of Node def __init__(self, val, link = None): self.data = val self.next = link # This code is contributed by pratham76
C#
// Structure of Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
// Constructor of Node
public Node(int val, Node link = null)
{
this.data = val;
this.next = link;
}
};
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56
Javascript
<script>
// Structure of Node
class Node {
// Constructor of Node
constructor(val, link = null) {
this.data = val;
this.next = link;
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
5 8 6
En el problema dado puede haber dos casos:
- El Node dado es el Node principal.
- El Node dado es cualquier Node válido excepto la cabeza.
Cuando el Node dado es el Node Principal :
La idea es crear un nuevo Node con el valor K dado . Luego, la siguiente parte del nuevo Node se actualizará con la cabeza del puntero. Y finalmente, el encabezado se actualizará con la dirección del nuevo Node. A continuación se muestra la imagen del mismo:
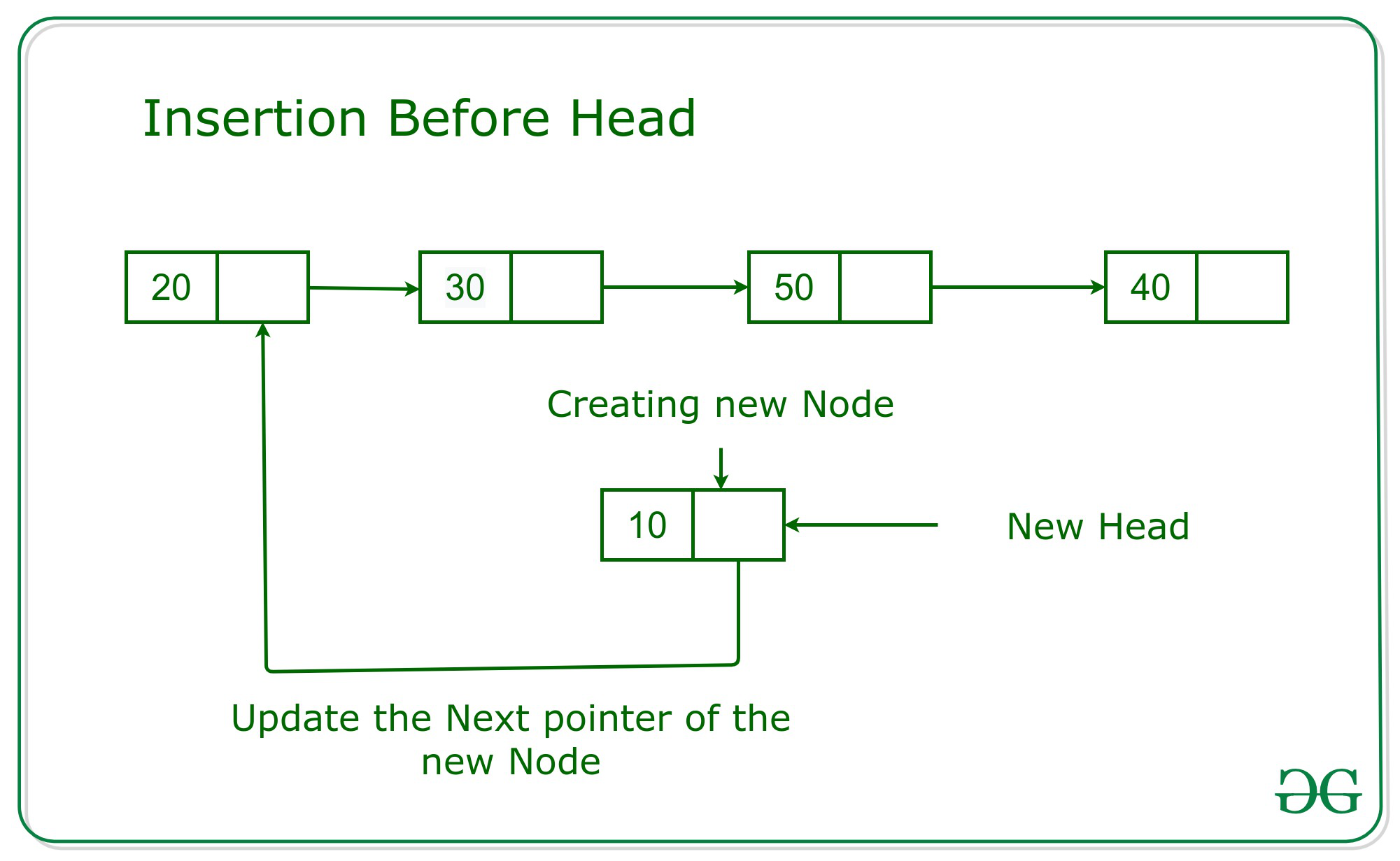
Cuando el Node dado es cualquier Node válido excepto el Node principal :
El enfoque más simple es recorrer la lista enlazada dada para buscar el Node anterior del Node dado. Luego, cree el nuevo Node con el valor K dado . Ahora, actualice la siguiente parte del nuevo Node con la dirección del Node dado y la siguiente parte del Node anterior con la dirección del nuevo Node. A continuación se muestra una ilustración del enfoque con la ayuda de la imagen:
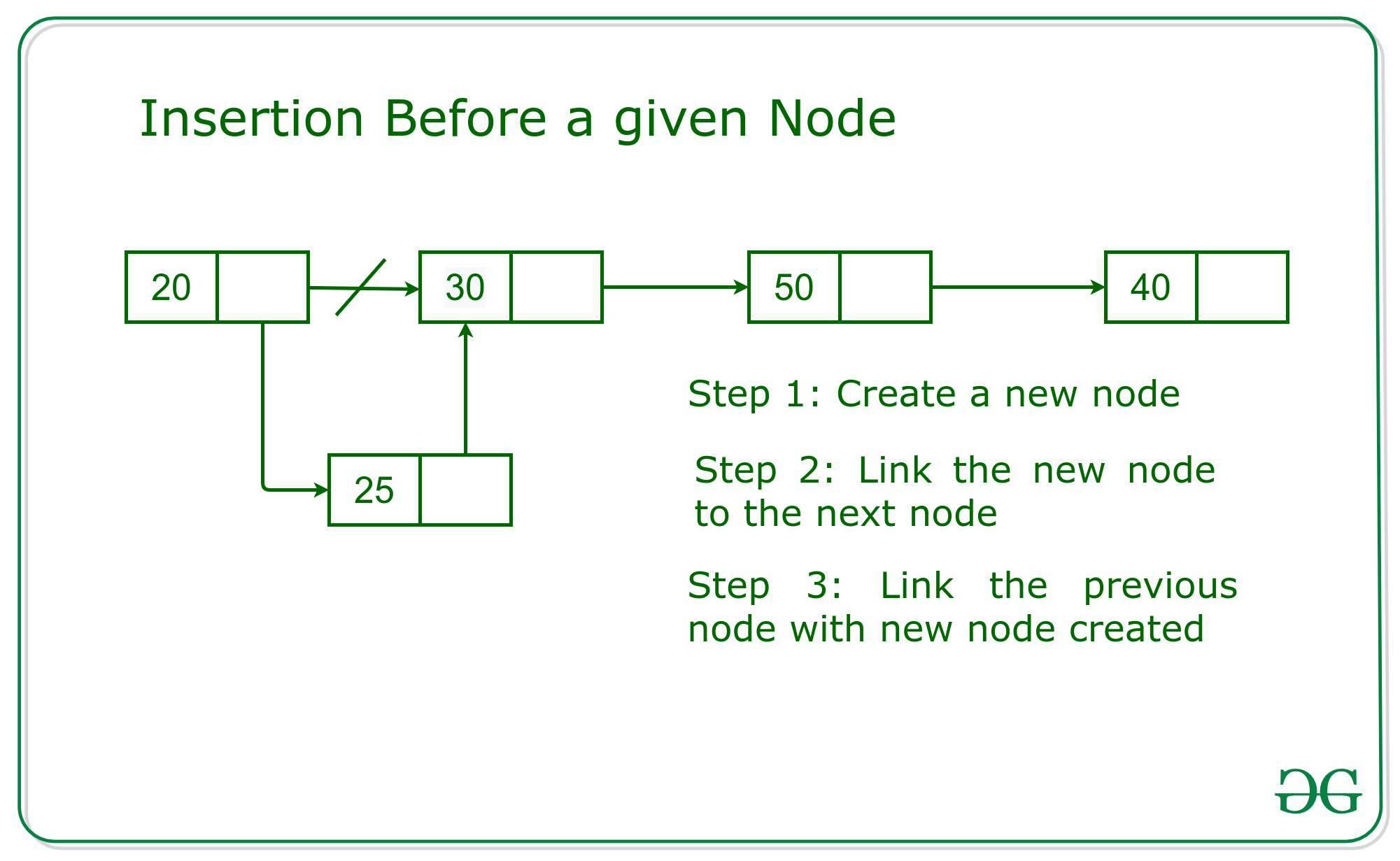
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
// Constructor of Node
Node(int val, Node* link = 0)
: data(val), next(link)
{
}
};
// Create a head node
Node* head = new Node(5);
// Function prints the linked list
// starting from the given node
void printList(Node* n)
{
// Till n is not NULL
while (n != NULL) {
// Print the data
cout << n->data << " ";
n = n->next;
}
}
// Function to add a node before the
// given node other than head node
Node* addBefore(Node* given_ptr, int val)
{
// First check if the given pointer
// is the address of head
if (head == given_ptr) {
// Create a new node
Node* n = new Node(val);
// Point to next to current head
n->next = head;
// Update the head pointer
head = n;
return n;
}
// Otherwise traverse the list to
// find previous node of given node
else {
Node *p, *n = head;
// This loop will return p with
// previous pointer of given node
for (n, p; n != given_ptr;
p = n, n = n->next)
;
// Create a new node
Node* m = new Node(val);
// Update the m->next
m->next = p->next;
// Update previous node's next
p->next = m;
return m;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Head Node
head->next = new Node(6);
// Function Call
addBefore(head->next, 8);
// Print the linked List
printList(head);
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor of Node
Node(int val)
{
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
static Node head = new Node(5);
// Function prints the linked list
// starting from the given node
static void printList(Node n)
{
// Till n is not null
while (n != null)
{
// Print the data
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// Function to add a node before the
// given node other than head node
static Node addBefore(Node given_ptr, int val)
{
// First check if the given pointer
// is the address of head
if (head == given_ptr)
{
// Create a new node
Node n = new Node(val);
// Point to next to current head
n.next = head;
// Update the head pointer
head = n;
return n;
}
// Otherwise traverse the list to
// find previous node of given node
else
{
Node p = null;
// This loop will return p with
// previous pointer of given node
for(Node n = head; n != given_ptr;
p = n, n = n.next);
// Create a new node
Node m = new Node(val);
// Update the m.next
m.next = p.next;
// Update previous node's next
p.next = m;
return m;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Head Node
head.next = new Node(6);
// Function Call
addBefore(head.next, 8);
// Print the linked List
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach class Node: # Constructor of Node def __init__(self, val, link = None): self.data = val self.next = link # Create a head node head = Node(5); # Function prints the linked list # starting from the given node def printList(n): # Till n is not NULL while (n != None): # Print the data print(n.data, end = ' ') n = n.next; # Function to add a node before the # given node other than head node def addBefore(given_ptr, val): global head # First check if the given pointer # is the address of head if (head == given_ptr): # Create a node n = Node(val); # Point to next to current head n.next = head; # Update the head pointer head = n; return n; # Otherwise traverse the list to # find previous node of given node else: p = None n = head; # This loop will return p with # previous pointer of given node while(n != given_ptr): p = n n = n.next # Create a node m = Node(val); # Update the m.next m.next = p.next; # Update previous node's next p.next = m; return m; # Driver Code if __name__=='__main__': # Head Node head.next = Node(6); # Function Call addBefore(head.next, 8); # Print the linked List printList(head); # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# program for the
// above approach
using System;
class GFG{
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
// Constructor of Node
public Node(int val)
{
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
static Node head = new Node(5);
// Function prints the linked list
// starting from the given node
static void printList(Node n)
{
// Till n is not null
while (n != null)
{
// Print the data
Console.Write(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// Function to add a node before the
// given node other than head node
static Node addBefore(Node given_ptr,
int val)
{
// First check if the given
// pointer is the address of
// head
if (head == given_ptr)
{
// Create a new node
Node n = new Node(val);
// Point to next to current
// head
n.next = head;
// Update the head pointer
head = n;
return n;
}
// Otherwise traverse the list
// to find previous node of
// given node
else
{
Node p = null;
// This loop will return p with
// previous pointer of given node
for(Node n = head; n != given_ptr;
p = n, n = n.next);
// Create a new node
Node m = new Node(val);
// Update the m.next
m.next = p.next;
// Update previous node's next
p.next = m;
return m;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Head Node
head.next = new Node(6);
// Function Call
addBefore(head.next, 8);
// Print the linked List
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
class Node {
// Constructor of Node
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head = new Node(5);
// Function prints the linked list
// starting from the given node
function printList(n) {
// Till n is not null
while (n != null) {
// Print the data
document.write(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// Function to add a node before the
// given node other than head node
function addBefore(given_ptr , val) {
// First check if the given pointer
// is the address of head
if (head == given_ptr) {
// Create a new node
var n = new Node(val);
// Point to next to current head
n.next = head;
// Update the head pointer
head = n;
return n;
}
// Otherwise traverse the list to
// find previous node of given node
else {
var p = null;
// This loop will return p with
// previous pointer of given node
for (n = head; n != given_ptr; p = n, n = n.next)
;
// Create a new node
var m = new Node(val);
// Update the m.next
m.next = p.next;
// Update previous node's next
p.next = m;
return m;
}
}
// Driver Code
// Head Node
head.next = new Node(6);
// Function Call
addBefore(head.next, 8);
// Print the linked List
printList(head);
// This code is contributed by todaysgaurav
</script>
5 8 6
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por tenacious39 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
