Hashing es una técnica que usa menos comparaciones clave y busca el elemento en tiempo O(n) en el peor de los casos y en tiempo O(1) en el caso promedio.
- La tarea es implementar todas las funciones del directorio telefónico:
- crear_registro
- mostrar_registro
- eliminar el registro
- registro_de_búsqueda
- actualizar_registro
Se tomarán los siguientes datos del cliente:
ID, Name, Telephone number
Enfoque:
estamos creando una tabla hash e insertando registros. Para eliminar, buscar o actualizar una entidad, se solicita la identificación del cliente y, en función del operador de igualdad, se muestran o procesan los detalles. Si no se encuentra el registro, se muestra un mensaje apropiado.
La colisión es el principal problema en la técnica hash. En el direccionamiento abierto (hashing cerrado), todas las colisiones se resuelven en el área principal, es decir, el área que contiene todas las direcciones de las casas.
Cuando ocurre una colisión, las direcciones de área principal se buscan en busca de un elemento abierto o desocupado mediante un sondeo lineal.
Pasos para insertar entidades en una tabla hash:
1 . Si la ubicación está vacía, inserte directamente la entidad.
2 . Si la ubicación asignada está ocupada, siga sondeando hasta que encuentre una ranura vacía. Una vez que se encuentra una ranura vacía, inserte la entidad.
- Crear registro: este método toma detalles del usuario como ID, nombre y número de teléfono y crea un nuevo registro en la tabla hash.
- Mostrar registro: esta función se crea para mostrar todo el registro del diario.
- Borrar Registro: Este método toma la clave del registro a borrar. Luego, busca en la tabla hash si la identificación del registro coincide con la clave. Entonces, ese registro se elimina.
- Buscar Registro: Este método toma la clave del registro a buscar. Luego, atraviesa la tabla hash, si la identificación del registro coincide con la clave, muestra el detalle del registro.
- Actualizar Registro: Este método toma la clave del registro a buscar. Luego, atraviesa la tabla hash, si la identificación del registro coincide con la clave, muestra el detalle del registro.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Class to store contact
// details
class node {
string name;
long int tel;
int id;
public:
node()
{
tel = 0;
id = 0;
}
friend class hashing;
};
class hashing {
// Maximum size of
// directory is 100
node data[100];
string n;
long int t;
int i, index;
public:
hashing()
{
i = 0;
t = 0;
}
// This method takes details
// from the user like ID,
// Name and Telephone number
// and create new record in
// the hashtable.
void create_record(int size)
{
// Enter ID
i = 4;
// Enter Name
n = "XYZ Gupta";
// Enter telephone number
t = 23451234;
cout << "\nEnter id :";
cout << " \t\t\t"
<< i;
cout << "\nEnter name :";
cout << " \t\t\t " << n;
cout
<< "\nEnter telephone";
cout << " number :\t"
<< t;
index = i % size;
// Inserting record using linear
// probing in case of collision
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
if (data[index].id == 0) {
data[index].id = i;
data[index].name = n;
data[index].tel = t;
break;
}
else
index
= (index + 1) % size;
}
}
// This method takes the key of
// the record to be searched.
// Then, it traverses the hash
// table, if record id matches
// with the key it displays the
// record detail.
void search_record(int size)
{
int index1, key, flag = 0;
key = 4;
cout << "\nEnter record";
cout << " id to search : "
<< key;
index1 = key % size;
// Traversing the directory
// linearly inorder to search
// record detail
for (int a = 0; a < size; a++) {
if (data[index1].id == key) {
flag = 1;
cout << "\nRecord found:";
cout << "\n\tID ";
cout << "\tNAME ";
cout << "\t\tTELEPHONE ";
cout << "\n\t"
<< data[index1].id
<< " \t"
<< data[index1].name
<< " \t"
<< data[index1].tel;
break;
}
else
index1
= (index1 + 1) % size;
}
if (flag == 0)
cout << "\nRecord";
cout << " not found";
}
// This method takes the key
// of the record to be deleted.
// Then, it searches in hash
// table if record id matches
// with the key. Then, that
// record is deleted.
void delete_record(int size)
{
int index1, key, flag = 0;
key = 4;
cout << "\nEnter record";
cout << " id to delete : "
<< key << "\n ";
index1 = key % size;
// Traversing the directory
// linearly inorder to delete
// the record detail
for (int a = 0; a < size; a++) {
if (data[index1].id
== key) {
flag = 1;
data[index1].id = 0;
data[index1].name = " ";
data[index1].tel = 0;
cout << "\nRecord";
cout << " deleted";
cout << " successfully";
break;
}
else
index1
= (index1 + 1) % size;
}
if (flag == 0)
cout << "\nRecord";
cout << " not found";
}
// This method takes the key
// of the record to be searched.
// Then, it traverses the hash table,
// if record id matches with the
// key then it displays the record
// detail.
void update_record(int size)
{
int index1, key, flag = 0;
key = 4;
cout << "\nEnter record";
cout << " id to update : "
<< key;
index1 = key % size;
// Traversing the directory
// linearly inorder to search
// record detail
for (int a = 0; a < size; a++) {
if (data[index1].id
== key) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
else
index1
= (index1 + 1) % size;
}
// If the record is found
// the details are updated
if (flag == 1) {
n = "XYZ Agarwal";
t = 23413421;
data[index1].name = n;
data[index1].tel = t;
cout << "\nEnter";
cout << " name: \t\t\t"
<< n;
cout << "\nEnter";
cout << " telephone number: \t"
<< t;
cout << "\nDetails updated: ";
cout << "\n\tID \tNAME";
cout << " \t\tTELEPHONE ";
cout << "\n\t"
<< data[index1].id
<< " \t"
<< data[index1].name
<< " \t"
<< data[index1].tel;
}
}
// This function is created to
// display all the record of
// the diary.
void display_record(int size)
{
cout << "\n\tID \tNAME";
cout << " \t\tTELEPHONE ";
// Displaying the details of
// all records of the directory.
for (int a = 0; a < size; a++) {
if (data[a].id != 0) {
cout << "\n\t"
<< data[a].id
<< " \t"
<< data[a].name
<< " \t"
<< data[a].tel;
}
}
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
// size of directory
int size;
// creating object of hashing
// class
hashing s;
size = 20;
// Creating a record in
// directory
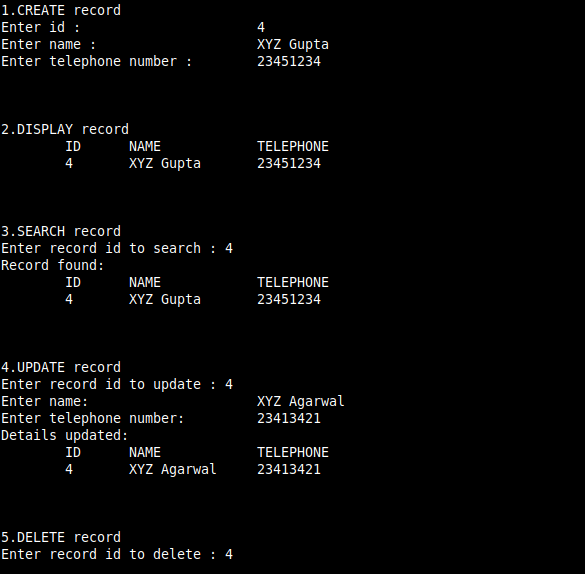
cout << "\n1.CREATE record ";
s.create_record(size);
// Display available
// record details
cout << "\n\n\n\n2.DISPLAY";
cout << " record ";
s.display_record(size);
// Searching a record detail
// in the directory
cout << "\n\n\n\n3.SEARCH";
cout << " record";
s.search_record(size);
// Updating the existing
// details of a record
cout << "\n\n\n\n4.UPDATE";
cout << " record ";
s.update_record(size);
// Removing specified
// existing record
// from dictionary
cout << "\n\n\n\n5.DELETE";
cout << " record ";
s.delete_record(size);
return 0;
}
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por shweta24hiremath y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA