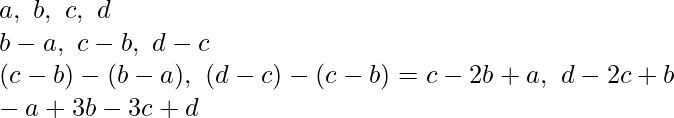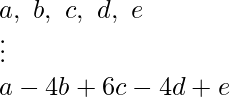Dada una array arr[] que consta de N enteros, la tarea es encontrar el elemento restante de la array después de restar cada elemento de su siguiente elemento adyacente y eliminar el último elemento de la array repetidamente.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {3, 4, 2, 1}
Salida: 4
Explicación:
Operación 1: La array arr[] se modifica a {4 – 3, 2 – 4, 1 – 2} = {1, -2, -1}.
Operación 2: La array arr[] se modifica a {-2 – 1, -1 + 2} = {-3, 1}.
Operación 3: La array arr[] se modifica a {1 + 3} = {4}.
Por lo tanto, el último elemento restante de la array es 4.Entrada: arr[] = {1, 8, 4}
Salida: -11
Explicación:
Operación 1: La array arr[] se modifica a {1 – 8, 4 – 8} = {7, -4}.
Operación 2: La array arr[] se modifica a {-4 – 7 } = {-11}.
Por lo tanto, el último elemento restante de la array es -11.
Enfoque ingenuo: el enfoque más simple es recorrer la array hasta que su tamaño se reduzca a 1 y realizar las operaciones dadas en la array. Después de completar el recorrido, imprima los elementos restantes.
Complejidad de Tiempo: O(N 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Enfoque eficiente: el enfoque anterior se puede optimizar en función de las siguientes observaciones:
- Supongamos que la array dada es arr[] = {a, b, c, d} . Luego, realizando las operaciones:
- Ahora, supongamos que la array arr[] = {a, b, c, d, e} . Luego, realizando las operaciones:
- De las dos observaciones anteriores, se puede concluir que la respuesta es la suma de la multiplicación de los coeficientes de los términos en la expansión de (x – y) (N – 1) y cada elemento del arreglo arr[i] .
- Por lo tanto, la idea es encontrar la suma de la array arr[] después de actualizar cada elemento de la array como (arr[i]* (N – 1) C (i-1) * (-1) i ) .
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Recorra la array arr[] y actualice arr[i] como arr[i] = arr[i]* (N – 1) C (i – 1) * (-1) i después de calcular N C r usando el triángulo de Pascal .
- Imprime la suma de la array arr[] .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Function to find the last remaining
// array element after performing
// the given operations repeatedly
int lastElement(const int arr[], int n)
{
// Stores the resultant sum
int sum = 0;
int multiplier = n % 2 == 0 ? -1 : 1;
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Increment sum by arr[i]
// * coefficient of i-th term
// in (x - y) ^ (N - 1)
sum += arr[i] * multiplier;
// Update multiplier
multiplier
= multiplier * (n - 1 - i)
/ (i + 1) * (-1);
}
// Return the resultant sum
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 4, 2, 1 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << lastElement(arr, N);
return 0;
}
Java
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Function to find the last remaining
// array element after performing
// the given operations repeatedly
public static int lastElement(int arr[], int n)
{
// Stores the resultant sum
int sum = 0;
int multiplier = n % 2 == 0 ? -1 : 1;
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Increment sum by arr[i]
// * coefficient of i-th term
// in (x - y) ^ (N - 1)
sum += arr[i] * multiplier;
// Update multiplier
multiplier
= multiplier * (n - 1 - i) / (i + 1) * (-1);
}
// Return the resultant sum
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 4, 2, 1 };
int N = 4;
System.out.println(lastElement(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by aditya7409.
Python3
# Python 3 program for the above approach # Function to find the last remaining # array element after performing # the given operations repeatedly def lastElement(arr, n): # Stores the resultant sum sum = 0 if n % 2 == 0: multiplier = -1 else: multiplier = 1 # Traverse the array for i in range(n): # Increment sum by arr[i] # * coefficient of i-th term # in (x - y) ^ (N - 1) sum += arr[i] * multiplier # Update multiplier multiplier = multiplier * (n - 1 - i) / (i + 1) * (-1) # Return the resultant sum return sum # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [3, 4, 2, 1] N = len(arr) print(int(lastElement(arr, N))) # This code is contributed by SURENDRA_GANGWAR.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to find the last remaining
// array element after performing
// the given operations repeatedly
public static int lastElement(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Stores the resultant sum
int sum = 0;
int multiplier = n % 2 == 0 ? -1 : 1;
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Increment sum by arr[i]
// * coefficient of i-th term
// in (x - y) ^ (N - 1)
sum += arr[i] * multiplier;
// Update multiplier
multiplier
= multiplier * (n - 1 - i) / (i + 1) * (-1);
}
// Return the resultant sum
return sum;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 4, 2, 1 };
int N = 4;
Console.WriteLine(lastElement(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by susmitakundugoaldanga.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Function to find the last remaining
// array element after performing
// the given operations repeatedly
function lastElement(arr, n)
{
// Stores the resultant sum
let sum = 0;
let multiplier = n % 2 == 0 ? -1 : 1;
// Traverse the array
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Increment sum by arr[i]
// * coefficient of i-th term
// in (x - y) ^ (N - 1)
sum += arr[i] * multiplier;
// Update multiplier
multiplier
= multiplier * (n - 1 - i)
/ (i + 1) * (-1);
}
// Return the resultant sum
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
let arr = [ 3, 4, 2, 1 ];
let N = arr.length;
document.write(lastElement(arr, N));
// This code is contributed by Surbhi Tyagi.
</script>
4
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)