La función shader() en p5.js hace posible usar un shader personalizado para rellenar formas en el modo WEBGL. Se puede cargar un sombreador personalizado mediante el método loadShader(), e incluso se puede programar para que tenga gráficos en movimiento.
Sintaxis:
shader( [s] )
Parámetro: Esta función tiene un solo parámetro como se mencionó anteriormente y se analiza a continuación:
- s: es un objeto p5.Shader que contiene el sombreador deseado que se utilizará para rellenar formas.
El siguiente ejemplo demuestra la función shader() en p5.js:
Ejemplo: Este ejemplo muestra cómo dibujar un círculo con un sombreador.
Javascript
// Variable to hold the shader object
let circleShader;
function preload() {
// Load the shader files with loadShader()
circleShader = loadShader('basic.vert', 'basic.frag');
}
function setup() {
// Shaders require WEBGL mode to work
createCanvas(400, 400, WEBGL);
noStroke();
}
function draw() {
// The shader() function sets the active
// shader with our shader
shader(circleShader);
// Setting the time and resolution of our shader
circleShader.setUniform(
'resolution', [width, height]
);
circleShader.setUniform(
'time', frameCount * 0.05
);
// Using rect() to give some
// geometry on the screen
rect(0, 0, width, height);
}
function windowResized() {
resizeCanvas(windowWidth, windowHeight);
}
básico.vert
attribute vec3 aPosition;
attribute vec2 aTexCoord;
void main() {
// Copy the position data into a vec4,
// using 1.0 as the w component
vec4 positionVec4 = vec4(aPosition, 1.0);
// Scale the rect by two, and move it to
// the center of the screen
positionVec4.xy = positionVec4.xy * 2.0 - 1.0;
// Send the vertex information on to
// the fragment shader
gl_Position = positionVec4;
}
básico.frag
precision mediump float;
varying vec2 vTexCoord;
// We need the sketch resolution to
// perform some calculations
uniform vec2 resolution;
uniform float time;
// Function that turns an rgb value that
// goes from 0 - 255 into 0.0 - 1.0
vec3 rgb(float r, float g, float b){
return vec3(r / 255.0, g / 255.0, b / 255.0);
}
vec4 circle(float x, float y, float diam, vec3 col){
vec2 coord = gl_FragCoord.xy;
// Flip the y coordinates for p5
coord.y = resolution.y - coord.y;
// Store the x and y in a vec2
vec2 p = vec2(x, y);
// Calculate the circle
// First get the difference of the circles
// location and the screen coordinates
// compute the length of that result and
// subtract the radius
// this creates a black and white mask that
// we can use to multiply against our colors
float c = length( p - coord) - diam*0.5;
// Restrict the results to be between
// 0.0 and 1.0
c = clamp(c, 0.0,1.0);
// Send out the color, with the circle
// as the alpha channel
return vec4(rgb(col.r, col.g, col.b), 1.0 - c);
}
void main() {
// The width and height of our rectangle
float width = 100.0;
float height = 200.0;
// the center of the screen is just the
// resolution divided in half
vec2 center = resolution * 0.5;
// Lets make our rect in the center of the
// screen. We have to subtract half of it's
// width and height just like in p5
float x = center.x ;
float y = center.y ;
// add an oscillation to x
x += sin(time) * 200.0;
// A color for the rect
vec3 grn = vec3(200.0, 240.0, 200.0);
// A color for the bg
vec3 magenta = rgb(240.0,150.0,240.0);
// Call our circle function
vec4 circ = circle(x, y, 200.0, grn);
// out put the final image
// Mix the circle with the background color
// using the circles alpha
circ.rgb = mix(magenta, circ.rgb, circ.a);
gl_FragColor = vec4( circ.rgb ,1.0);
}
Producción:
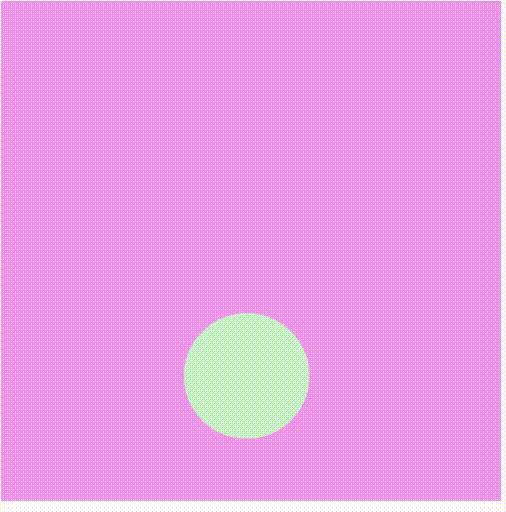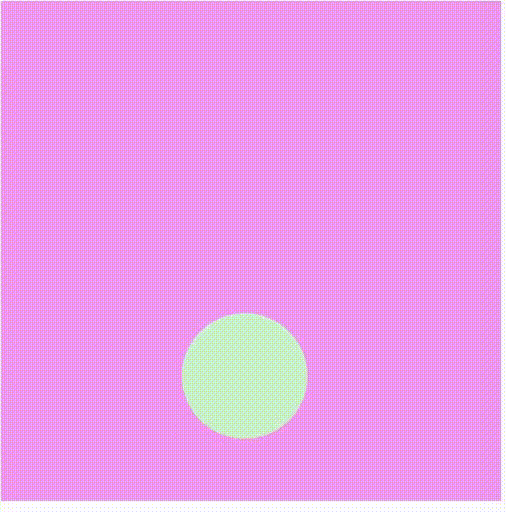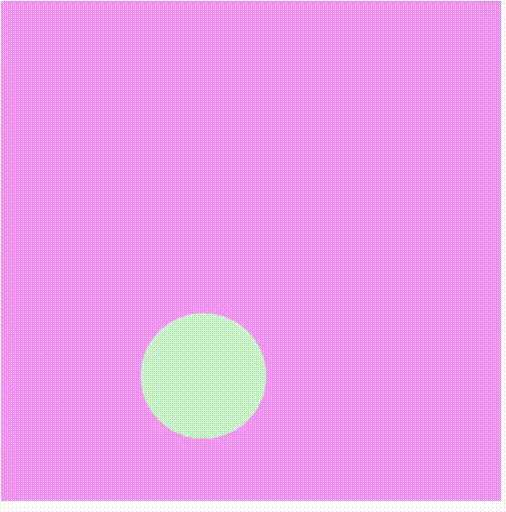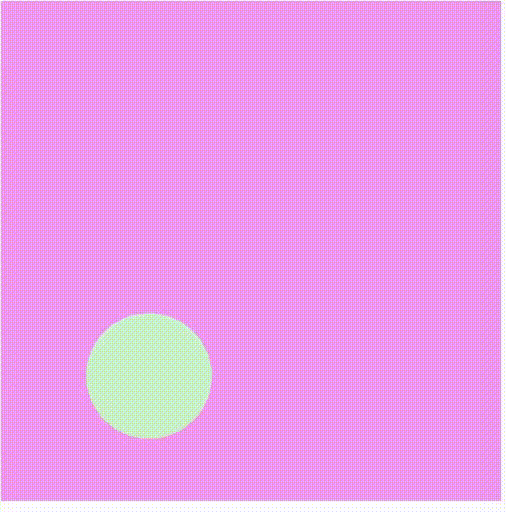
Referencia: https://p5js.org/reference/#/p5/shader
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por _sh_pallavi y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA