Hay dos métodos para desplazarse suavemente por una página web después de hacer clic en el enlace de anclaje que se analizan a continuación:
Método 1: Usar scrollIntoView() con el comportamiento ‘suave’: El método scrollIntoView() se usa para desplazar la vista del usuario al elemento al que se llama. Contiene varias opciones que se pueden definir para modificar el comportamiento del scroll. Una de ellas es la propiedad de ‘comportamiento’. El valor predeterminado de esta propiedad hace que el desplazamiento salte instantáneamente a su destino, en lugar de desplazarse suavemente. Establecer este valor en ‘suave’ cambia este comportamiento y hace que la página se desplace sin problemas.
La parte hash del vínculo ancla se extrae primero mediante la propiedad hash y se selecciona con el método querySelector(). Luego se llama al método scrollIntoView() en este elemento seleccionado para desplazar suavemente la página a esta ubicación.
Ejemplo:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
How to set smooth scrolling after
clicking an anchor link using
JavaScript?
</title>
<style>
.scroll {
height: 1000px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color: green">
GeeksforGeeks
</h1>
<b>
How to set smooth scrolling after
clicking an anchor link using
JavaScript?
</b>
<p id="dest">
Click on the button below to
scroll to the top of the page.
</p>
<p class="scroll">
GeeksforGeeks is a computer science
portal. This is a large scrollable
area.
</p>
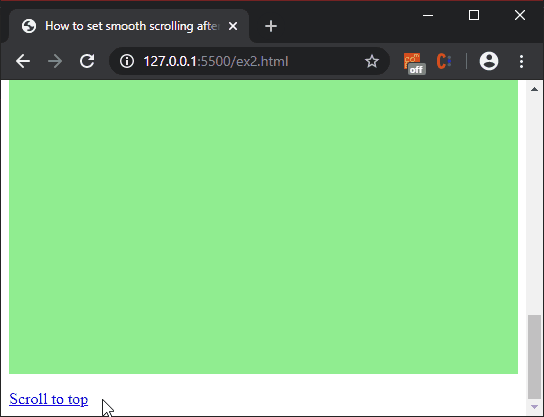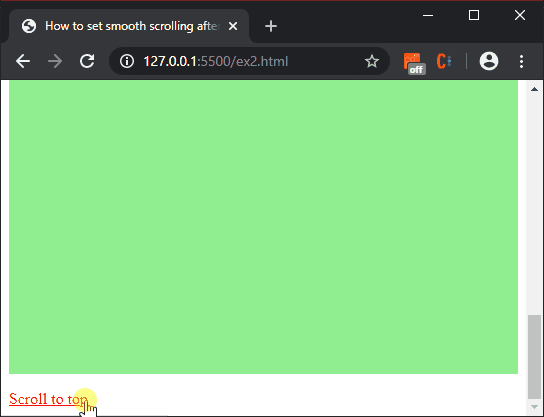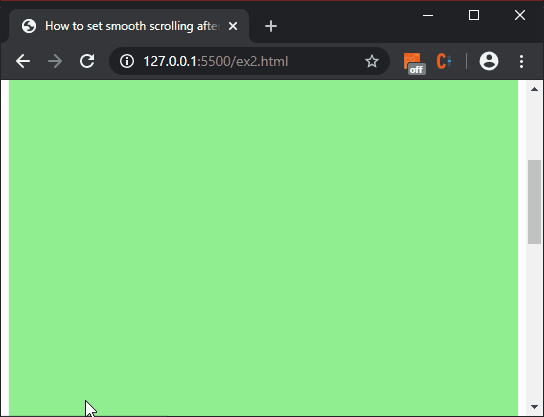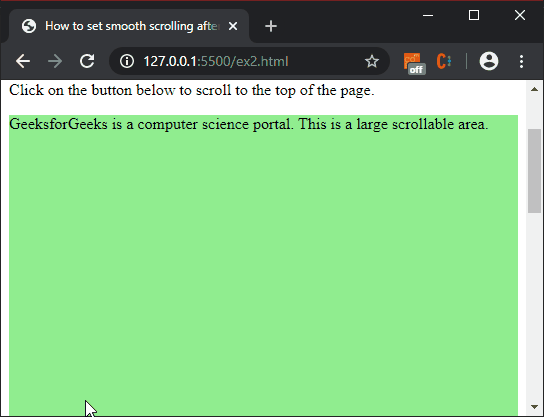
<a href="#dest">
Scroll to top
</a>
<script>
// Define selector for selecting
// anchor links with the hash
let anchorSelector = 'a[href^="#"]';
// Collect all such anchor links
let anchorList =
document.querySelectorAll(anchorSelector);
// Iterate through each of the links
anchorList.forEach(link => {
link.onclick = function (e) {
// Prevent scrolling if the
// hash value is blank
e.preventDefault();
// Get the destination to scroll to
// using the hash property
let destination =
document.querySelector(this.hash);
// Scroll to the destination using
// scrollIntoView method
destination.scrollIntoView({
behavior: 'smooth'
});
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:

Método 2: Usar el método jQuery scrollTop(): El método scrollTop() en jQuery se usa para desplazarse a una parte particular de la página. Animar este método con las animaciones integradas disponibles puede hacer que el desplazamiento sea más fluido.
La parte hash del enlace ancla se extrae primero usando la propiedad hash y su posición en la página se encuentra usando el método offset() . Luego se llama al método scrollTop() en este valor hash para desplazarse a esa ubicación. Este método se anima encerrándolo dentro del método animate() y especificando la duración de la animación que se usará en milisegundos. Un valor mayor haría que la animación se completara más lentamente que un valor menor. Esto animará suavemente todos los enlaces de anclaje en la página cuando se haga clic en ellos.
Ejemplo:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
How to set smooth scrolling after
clicking an anchor link using
JavaScript?
</title>
<script src=
"https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.4.1.min.js">
</script>
<style>
.scroll {
height: 1000px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color: green">
GeeksforGeeks
</h1>
<b>
How to set smooth scrolling after
clicking an anchor link using
JavaScript?
</b>
<p id="dest">
Click on the button below to
scroll to the top of the page.
</p>
<p class="scroll">
GeeksforGeeks is a computer science
portal. This is a large scrollable
area.
</p>
<a href="#dest">
Scroll to top
</a>
<script>
// Define selector for selecting
// anchor links with the hash
let anchorSelector = 'a[href^="#"]';
$(anchorSelector).on('click', function (e) {
// Prevent scrolling if the
// hash value is blank
e.preventDefault();
// Get the destination to scroll to
// using the hash property
let destination = $(this.hash);
// Get the position of the destination
// using the coordinates returned by
// offset() method
let scrollPosition
= destination.offset().top;
// Specify animation duration
let animationDuration = 500;
// Animate the html/body with
// the scrollTop() method
$('html, body').animate({
scrollTop: scrollPosition
}, animationDuration);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sayantanm19 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA