Dado un árbol binario , un Node objetivo y un número entero K , la tarea es encontrar todos los Nodes que están a una distancia K del Node objetivo dado.
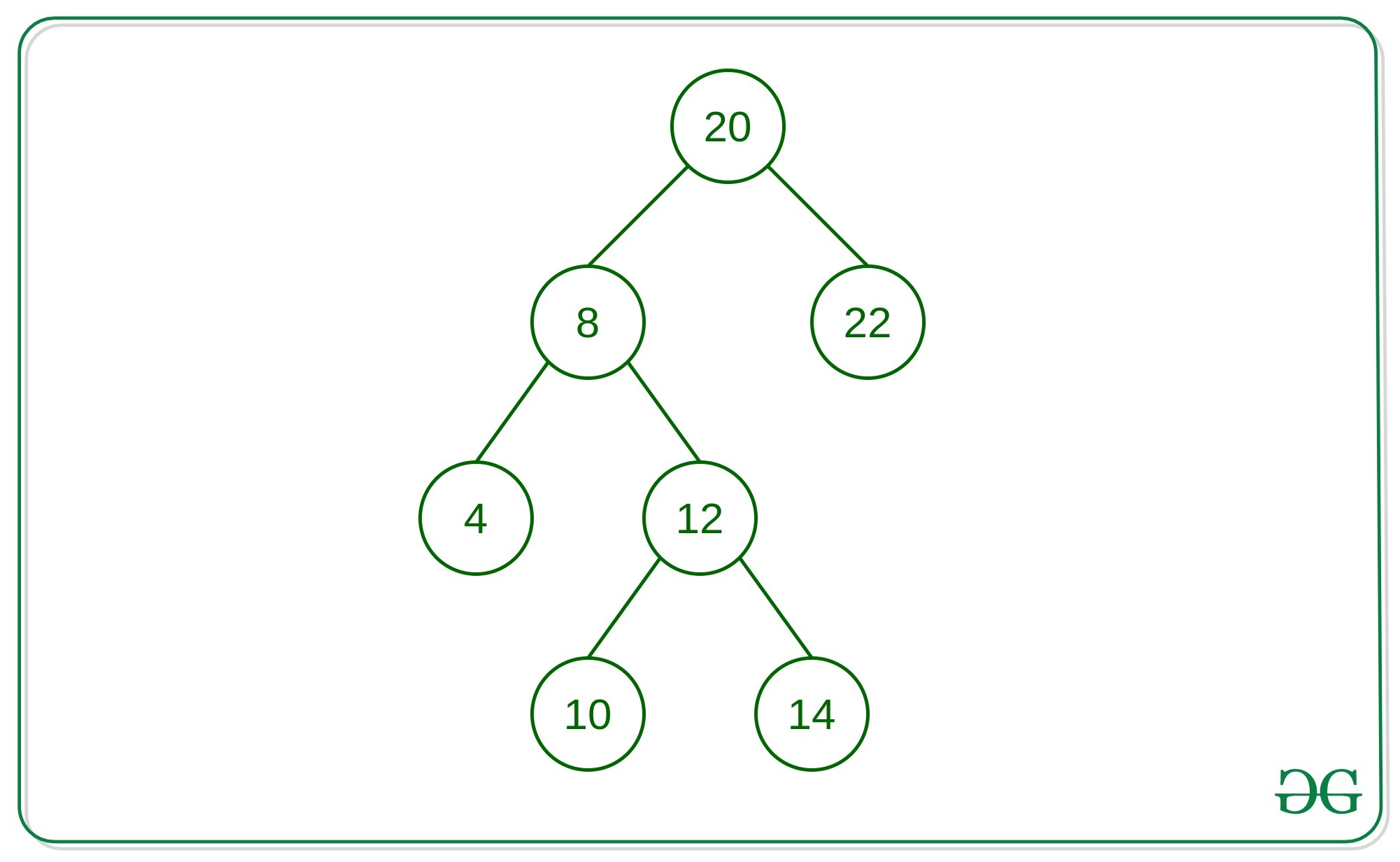
Considere el árbol anterior, para el Node de destino 12.
Entrada: K = 1
Salida: 8 10 14Entrada: K = 2
Salida: 4 20Entrada: K = 3
salida: 22
Aproximación:
Generalmente hay dos casos para los Nodes a una distancia de K:
- El Node a una distancia K es un Node secundario del Node de destino.
- El Node a una distancia K es el ancestro del Node de destino.
La idea es almacenar el Node principal de cada Node en un mapa hash con la ayuda del recorrido de orden de niveles en el árbol. Luego, simplemente recorra los Nodes desde el Node de destino utilizando la búsqueda en anchura en el Node secundario izquierdo, secundario derecho y principal. En cualquier instante, cuando la distancia de un Node desde el Node de destino sea igual a K , imprima todos los Nodes de la cola.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to print all
// the nodes from the given target
// node iterative approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Node
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left, *right;
};
// Map to store the parent
// node of every node of
// the given Binary Tree
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> um;
// Function to store all nodes
// parent in unordered_map
void storeParent(Node* root)
{
// Make a queue to do level-order
// Traversal and store parent
// of each node in unordered map
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
// Loop to iterate until the
// queue is not empty
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* p = q.front();
q.pop();
// Condition if the node is a
/// root node that storing its
// parent as NULL
if (p == root) {
um[p] = NULL;
}
// if left child exist of
// popped out node then store
// parent as value and node as key
if (p->left) {
um[p->left] = p;
q.push(p->left);
}
if (p->right) {
um[p->right] = p;
q.push(p->right);
}
}
}
// Function to find the nodes
// at distance K from give node
void nodeAtDistK(Node* root,
Node* target, int k)
{
// Keep track of each node
// which are visited so that
// while doing BFS we will
// not traverse it again
unordered_set<Node*> s;
int dist = 0;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(target);
s.insert(target);
// Loop to iterate over the nodes
// until the queue is not empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// if distance is equal to K
// then we found a node in tree
// which is distance K
if (dist == k) {
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front()->val << " ";
q.pop();
}
// no need to traverse further since we found the answer
break ;
}
// BFS on node's left,
// right and parent node
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* p = q.front();
q.pop();
// if the left of node is not
// visited yet then push it in
// queue and insert it in set as well
if (p->left &&
s.find(p->left) == s.end()) {
q.push(p->left);
s.insert(p->left);
}
// if the right of node is not visited
// yet then push it in queue
// and insert it in set as well
if (p->right &&
s.find(p->right) == s.end()) {
q.push(p->right);
s.insert(p->right);
}
// if the parent of node is not visited
// yet then push it in queue and
// insert it in set as well
if (um[p] && s.find(um[p]) == s.end()) {
q.push(um[p]);
s.insert(um[p]);
}
}
dist++;
}
}
// Function to create a newnode
Node* newnode(int val)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->val = val;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = newnode(20);
root->left = newnode(8);
root->right = newnode(22);
root->right->left = newnode(5);
root->right->right = newnode(8);
root->left->left = newnode(4);
root->left->left->left = newnode(25);
root->left->right = newnode(12);
root->left->right->left =
newnode(10);
root->left->right->left->left =
newnode(15);
root->left->right->left->right =
newnode(18);
root->left->right->left->right->right =
newnode(23);
root->left->right->right =
newnode(14);
Node* target = root->left->right;
storeParent(root);
nodeAtDistK(root, target, 3);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to print all
// the nodes from the given target
// node iterative approach
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class GFG{
// Structure of the Node
static class Node
{
int val;
Node left, right;
public Node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
};
// Map to store the parent
// node of every node of
// the given Binary Tree
static HashMap<Node, Node> um = new HashMap<>();
// Function to store all nodes
// parent in unordered_map
static void storeParent(Node root)
{
// Make a queue to do level-order
// Traversal and store parent
// of each node in unordered map
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
// Loop to iterate until the
// queue is not empty
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
Node p = q.poll();
// Condition if the node is a
/// root node that storing its
// parent as NULL
if (p == root)
{
um.put(p, null);
}
// if left child exist of
// popped out node then store
// parent as value and node as key
if (p.left != null)
{
um.put(p.left, p);
q.add(p.left);
}
if (p.right != null)
{
um.put(p.right, p);
q.add(p.right);
}
}
}
// Function to find the nodes
// at distance K from give node
static void nodeAtDistK(Node root,
Node target, int k)
{
// Keep track of each node
// which are visited so that
// while doing BFS we will
// not traverse it again
HashSet<Node> s = new HashSet<>();
int dist = 0;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(target);
s.add(target);
// Loop to iterate over the nodes
// until the queue is not empty
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// If distance is equal to K
// then we found a node in tree
// which is distance K
if (dist == k)
{
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
System.out.print(q.peek().val + " ");
q.poll();
}
}
// BFS on node's left,
// right and parent node
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
Node p = q.poll();
// If the left of node is not
// visited yet then add it in
// queue and insert it in set as well
if (p.left != null && !s.contains(p.left))
{
q.add(p.left);
s.add(p.left);
}
// If the right of node is not visited
// yet then add it in queue
// and insert it in set as well
if (p.right != null && !s.contains(p.right))
{
q.add(p.right);
s.add(p.right);
}
// If the parent of node is not visited
// yet then add it in queue and
// insert it in set as well
if (um.get(p) != null &&
!s.contains(um.get(p)))
{
q.add(um.get(p));
s.add(um.get(p));
}
}
dist++;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(20);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(22);
root.right.left = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(8);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(12);
root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
root.left.right.left.left = new Node(15);
root.left.right.left.right = new Node(18);
root.left.right.left.right.right = new Node(23);
root.left.right.right = new Node(14);
Node target = root.left.right;
storeParent(root);
nodeAtDistK(root, target, 3);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552
C#
// C# implementation to print all
// the nodes from the given target
// node iterative approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Structure of the Node
public class Node
{
public int val;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
};
// Map to store the parent
// node of every node of
// the given Binary Tree
static Dictionary<Node,
Node> um = new Dictionary<Node,
Node>();
// Function to store all nodes
// parent in unordered_map
static void storeParent(Node root)
{
// Make a queue to do level-order
// Traversal and store parent
// of each node in unordered map
List<Node> q = new List<Node>();
q.Add(root);
// Loop to iterate until the
// queue is not empty
while (q.Count != 0)
{
Node p = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
// Condition if the node is a
/// root node that storing its
// parent as NULL
if (p == root)
{
um.Add(p, null);
}
// If left child exist of
// popped out node then store
// parent as value and node as key
if (p.left != null)
{
um.Add(p.left, p);
q.Add(p.left);
}
if (p.right != null)
{
um.Add(p.right, p);
q.Add(p.right);
}
}
}
// Function to find the nodes
// at distance K from give node
static void nodeAtDistK(Node root,
Node target, int k)
{
// Keep track of each node
// which are visited so that
// while doing BFS we will
// not traverse it again
HashSet<Node> s = new HashSet<Node>();
int dist = 0;
List<Node> q = new List<Node>();
q.Add(target);
s.Add(target);
// Loop to iterate over the nodes
// until the queue is not empty
while (q.Count != 0)
{
// If distance is equal to K
// then we found a node in tree
// which is distance K
if (dist == k)
{
while (q.Count != 0)
{
Console.Write(q[0].val + " ");
q.RemoveAt(0);
}
}
// BFS on node's left,
// right and parent node
int size = q.Count;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
Node p = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
// If the left of node is not
// visited yet then add it in
// queue and insert it in set as well
if (p.left != null && !s.Contains(p.left))
{
q.Add(p.left);
s.Add(p.left);
}
// If the right of node is not visited
// yet then add it in queue and insert
// it in set as well
if (p.right != null && !s.Contains(p.right))
{
q.Add(p.right);
s.Add(p.right);
}
// If the parent of node is not visited
// yet then add it in queue and
// insert it in set as well
if (um[p] != null &&
!s.Contains(um[p]))
{
q.Add(um[p]);
s.Add(um[p]);
}
}
dist++;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(20);
root.left = new Node(8);
root.right = new Node(22);
root.right.left = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(8);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(12);
root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
root.left.right.left.left = new Node(15);
root.left.right.left.right = new Node(18);
root.left.right.left.right.right = new Node(23);
root.left.right.right = new Node(14);
Node target = root.left.right;
storeParent(root);
nodeAtDistK(root, target, 3);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
23 25 22
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n) donde n = Número de Nodes
- Complejidad espacial: O(n)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ranaanku39 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA