Dado un gráfico dirigido y no ponderado que consta de N vértices y una array arr[] donde i-ésimo vértice tiene una arista dirigida a arr[i] . La tarea es encontrar el número de formas de cambiar la dirección de los bordes de modo que el gráfico dado sea acíclico.
Ejemplos:
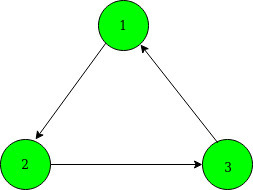
Entrada: N = 3, arr[] = {2, 3, 1}
La forma gráfica dirigida por la información dada es:
Salida: 6
Explicación:
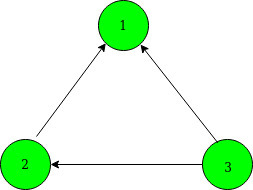
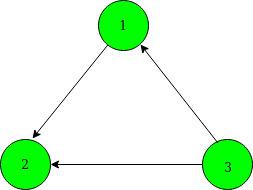
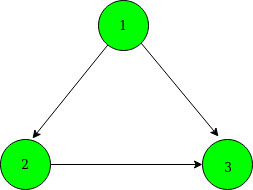
Hay 6 formas posibles de cambiar la dirección de los bordes para hacer que el gráfico sea acíclico:
Planteamiento: La idea es comprobar si los Componentes Conectados forman un ciclo o no.
- Si el componente es un camino, sin importar cómo orientemos los bordes, no formaremos un ciclo.
- Si el componente tiene un ciclo con N aristas, entonces hay 2 N formas de organizar todas las aristas, de las cuales solo 2 formas van a formar un ciclo. Entonces, hay (2 N – 2) formas de cambiar los bordes para que el gráfico se vuelva acíclico.
Pasos :
- Utilizando el recorrido de primera búsqueda en profundidad (DFS) , encuentre los ciclos en el gráfico dado y el número de vértices asociados con cada ciclo.
- Después del recorrido DFS , el número total de formas de cambiar la dirección de los bordes es el producto de lo siguiente:
- El número de formas que se forman por cada ciclo de X vértices viene dado por (2 X – 2) .
- El número de caminos formados por cada camino de Y vértices viene dado por (2 Y ) .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to count the
// number of ways to change
// the direction of edges
// such that no cycle is
// present in the graph
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Vector cycles[] to store
// the cycle with vertices
// associated with each cycle
vector<int> cycles;
// Count of cycle
int cyclecnt;
// Function to count the
// number of vertices in the
// current cycle
void DFSUtil(int u, int arr[], int vis[])
{
cycles[cyclecnt]++;
vis[u] = 3;
// Returns when the same
// initial vertex is found
if (vis[arr[u]] == 3) {
return;
}
// Recurr for next vertex
DFSUtil(arr[u], arr, vis);
}
// DFS traversal to detect
// the cycle in graph
void DFS(int u, int arr[], int vis[])
{
// Marke vis[u] to 2 to
// check for any cycle form
vis[u] = 2;
// If the vertex arr[u]
// is not visited
if (vis[arr[u]] == 0) {
// Call DFS
DFS(arr[u], arr, vis);
}
// If current node is
// processed
else if (vis[arr[u]] == 1) {
vis[u] = 1;
return;
}
// Cycle found, call DFSUtil
// to count the number of
// vertices in the current
// cycle
else {
cycles.push_back(0);
// Count number of
// vertices in cycle
DFSUtil(u, arr, vis);
cyclecnt++;
}
// Current Node is processed
vis[u] = 1;
}
// Function to count the
// number of ways
int countWays(int arr[], int N)
{
int i, ans = 1;
// To precompute the power
// of 2
int dp[N + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
// Storing power of 2
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * 2);
}
// Array vis[] created for
// DFS traversal
int vis[N + 1] = { 0 };
// DFS traversal from Node 1
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (vis[i] == 0) {
// Calling DFS
DFS(i, arr, vis);
}
}
int cnt = N;
// Traverse the cycles array
for (i = 0; i < cycles.size(); i++) {
// Remove the vertices
// which are part of a
// cycle
cnt -= cycles[i];
// Count form by number
// vertices form cycle
ans *= dp[cycles[i]] - 2;
}
// Count form by number of
// vertices not forming
// cycle
ans = (ans * dp[cnt]);
return ans;
}
// Driver's Code
int main()
{
int N = 3;
int arr[] = { 0, 2, 3, 1 };
// Function to count ways
cout << countWays(arr, N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to count the number
// of ways to change the direction
// of edges such that no cycle is
// present in the graph
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Vector cycles[] to store
// the cycle with vertices
// associated with each cycle
static ArrayList<Integer> cycles;
// Count of cycle
static int cyclecnt;
// Function to count the
// number of vertices in the
// current cycle
static void DFSUtil(int u, int arr[],
int vis[])
{
cycles.set(cyclecnt,
cycles.get(cyclecnt) + 1);
vis[u] = 3;
// Returns when the same
// initial vertex is found
if (vis[arr[u]] == 3)
{
return;
}
// Recurr for next vertex
DFSUtil(arr[u], arr, vis);
}
// DFS traversal to detect
// the cycle in graph
static void DFS(int u, int arr[], int vis[])
{
// Marke vis[u] to 2 to
// check for any cycle form
vis[u] = 2;
// If the vertex arr[u]
// is not visited
if (vis[arr[u]] == 0)
{
// Call DFS
DFS(arr[u], arr, vis);
}
// If current node is
// processed
else if (vis[arr[u]] == 1)
{
vis[u] = 1;
return;
}
// Cycle found, call DFSUtil
// to count the number of
// vertices in the current
// cycle
else
{
cycles.add(0);
// Count number of
// vertices in cycle
DFSUtil(u, arr, vis);
cyclecnt++;
}
// Current Node is processed
vis[u] = 1;
}
// Function to count the
// number of ways
static int countWays(int arr[], int N)
{
int i, ans = 1;
// To precompute the power
// of 2
int[] dp = new int[N + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
// Storing power of 2
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * 2);
}
// Array vis[] created for
// DFS traversal
int[] vis = new int[N + 1];
// DFS traversal from Node 1
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
if (vis[i] == 0)
{
// Calling DFS
DFS(i, arr, vis);
}
}
int cnt = N;
// Traverse the cycles array
for(i = 0; i < cycles.size(); i++)
{
// Remove the vertices
// which are part of a
// cycle
cnt -= cycles.get(i);
// Count form by number
// vertices form cycle
ans *= dp[cycles.get(i)] - 2;
}
// Count form by number of
// vertices not forming
// cycle
ans = (ans * dp[cnt]);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3;
int arr[] = { 0, 2, 3, 1 };
cycles = new ArrayList<>();
// Function to count ways
System.out.println(countWays(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Python3
# Python3 program to count the # number of ways to change # the direction of edges # such that no cycle is # present in the graph # List cycles[] to store # the cycle with vertices # associated with each cycle cycles = [] # Function to count the # number of vertices in the # current cycle def DFSUtil(u, arr, vis, cyclecnt): cycles[cyclecnt] += 1 vis[u] = 3 # Returns when the same # initial vertex is found if (vis[arr[u]] == 3) : return # Recurr for next vertex DFSUtil(arr[u], arr, vis, cyclecnt) # DFS traversal to detect # the cycle in graph def DFS( u, arr, vis, cyclecnt): # Marke vis[u] to 2 to # check for any cycle form vis[u] = 2 # If the vertex arr[u] # is not visited if (vis[arr[u]] == 0) : # Call DFS DFS(arr[u], arr, vis, cyclecnt) # If current node is # processed elif (vis[arr[u]] == 1): vis[u] = 1 return # Cycle found, call DFSUtil # to count the number of # vertices in the current # cycle else : cycles.append(0) # Count number of # vertices in cycle DFSUtil(u, arr, vis,cyclecnt) cyclecnt += 1 # Current Node is processed vis[u] = 1 # Function to count the # number of ways def countWays(arr, N,cyclecnt): ans = 1 # To precompute the power # of 2 dp = [0]*(N + 1) dp[0] = 1 # Storing power of 2 for i in range(1, N + 1): dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * 2) # Array vis[] created for # DFS traversal vis = [0]*(N + 1) # DFS traversal from Node 1 for i in range(1, N + 1) : if (vis[i] == 0) : # Calling DFS DFS(i, arr, vis, cyclecnt) cnt = N # Traverse the cycles array for i in range(len(cycles)) : # Remove the vertices # which are part of a # cycle cnt -= cycles[i] # Count form by number # vertices form cycle ans *= dp[cycles[i]] - 2 # Count form by number of # vertices not forming # cycle ans = (ans * dp[cnt]) return ans # Driver's Code if __name__ == "__main__": N = 3 cyclecnt = 0 arr = [ 0, 2, 3, 1 ] # Function to count ways print(countWays(arr, N,cyclecnt)) # This code is contributed by chitranayal
C#
// C# program to count the number
// of ways to change the direction
// of edges such that no cycle is
// present in the graph
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Vector cycles[] to store
// the cycle with vertices
// associated with each cycle
static ArrayList cycles;
// Count of cycle
static int cyclecnt;
// Function to count the
// number of vertices in the
// current cycle
static void DFSUtil(int u, int []arr,
int []vis)
{
cycles[cyclecnt] = (int)cycles[cyclecnt] + 1;
vis[u] = 3;
// Returns when the same
// initial vertex is found
if (vis[arr[u]] == 3)
{
return;
}
// Recurr for next vertex
DFSUtil(arr[u], arr, vis);
}
// DFS traversal to detect
// the cycle in graph
static void DFS(int u, int []arr, int []vis)
{
// Marke vis[u] to 2 to
// check for any cycle form
vis[u] = 2;
// If the vertex arr[u]
// is not visited
if (vis[arr[u]] == 0)
{
// Call DFS
DFS(arr[u], arr, vis);
}
// If current node is
// processed
else if (vis[arr[u]] == 1)
{
vis[u] = 1;
return;
}
// Cycle found, call DFSUtil
// to count the number of
// vertices in the current
// cycle
else
{
cycles.Add(0);
// Count number of
// vertices in cycle
DFSUtil(u, arr, vis);
cyclecnt++;
}
// Current Node is processed
vis[u] = 1;
}
// Function to count the
// number of ways
static int countWays(int []arr, int N)
{
int i, ans = 1;
// To precompute the power
// of 2
int[] dp = new int[N + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
// Storing power of 2
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * 2);
}
// Array vis[] created for
// DFS traversal
int[] vis = new int[N + 1];
// DFS traversal from Node 1
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
if (vis[i] == 0)
{
// Calling DFS
DFS(i, arr, vis);
}
}
int cnt = N;
// Traverse the cycles array
for(i = 0; i < cycles.Count; i++)
{
// Remove the vertices
// which are part of a
// cycle
cnt -= (int)cycles[i];
// Count form by number
// vertices form cycle
ans *= dp[(int)cycles[i]] - 2;
}
// Count form by number of
// vertices not forming
// cycle
ans = (ans * dp[cnt]);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int N = 3;
int []arr = new int[]{ 0, 2, 3, 1 };
cycles = new ArrayList();
// Function to count ways
Console.Write(countWays(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to count the number
// of ways to change the direction
// of edges such that no cycle is
// present in the graph
// Vector cycles[] to store
// the cycle with vertices
// associated with each cycle
let cycles;
// Count of cycle
let cyclecnt=0;
// Function to count the
// number of vertices in the
// current cycle
function DFSUtil(u,arr,vis)
{
cycles[cyclecnt]++;
vis[u] = 3;
// Returns when the same
// initial vertex is found
if (vis[arr[u]] == 3)
{
return;
}
// Recurr for next vertex
DFSUtil(arr[u], arr, vis);
}
// DFS traversal to detect
// the cycle in graph
function DFS(u,arr,vis)
{
// Marke vis[u] to 2 to
// check for any cycle form
vis[u] = 2;
// If the vertex arr[u]
// is not visited
if (vis[arr[u]] == 0)
{
// Call DFS
DFS(arr[u], arr, vis);
}
// If current node is
// processed
else if (vis[arr[u]] == 1)
{
vis[u] = 1;
return;
}
// Cycle found, call DFSUtil
// to count the number of
// vertices in the current
// cycle
else
{
cycles.push(0);
// Count number of
// vertices in cycle
DFSUtil(u, arr, vis);
cyclecnt++;
}
// Current Node is processed
vis[u] = 1;
}
// Function to count the
// number of ways
function countWays(arr,N)
{
let i, ans = 1;
// To precompute the power
// of 2
let dp = new Array(N + 1);
for(let i=0;i<dp.length;i++)
{
dp[i]=0;
}
dp[0] = 1;
// Storing power of 2
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * 2);
}
// Array vis[] created for
// DFS traversal
let vis = new Array(N + 1);
for(let i=0;i<vis.length;i++)
{
vis[i]=0;
}
// DFS traversal from Node 1
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
if (vis[i] == 0)
{
// Calling DFS
DFS(i, arr, vis);
}
}
let cnt = N;
// Traverse the cycles array
for(i = 0; i < cycles.length; i++)
{
// Remove the vertices
// which are part of a
// cycle
cnt -= cycles[i];
// Count form by number
// vertices form cycle
ans *= dp[cycles[i]] - 2;
}
// Count form by number of
// vertices not forming
// cycle
ans = (ans * dp[cnt]);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
let N = 3;
let arr=[0, 2, 3, 1];
cycles =[];
// Function to count ways
document.write(countWays(arr, N));
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
6
Tiempo Complejidad : O(V + E)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sharadgoyal y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA