Dada una array A[][] de N * M , la tarea es encontrar la suma máxima desde la fila superior hasta la fila inferior después de seleccionar un elemento de cada fila sin elemento diagonal adyacente.
Ejemplos:
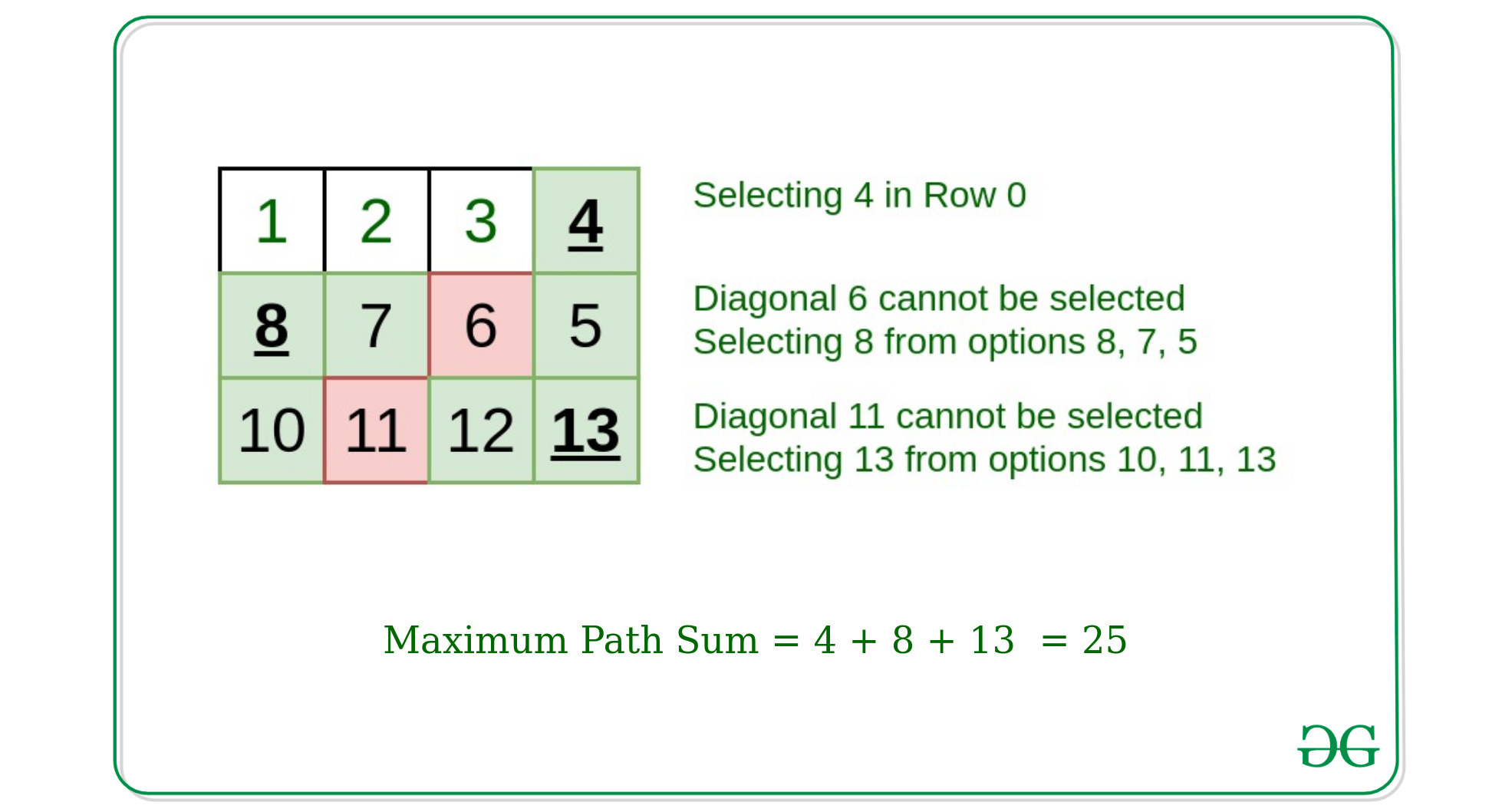
Entrada: A = { {1, 2, 3, 4}, {8, 7, 6, 5}, {10, 11, 12, 13} }
Salida: 25
Explicación:
Elementos seleccionados para dar la suma máxima –
Fila 0 = 4
Fila 1 = 8
Fila 2 = 13
Suma = 25Entrada: A = { {1, 6}, {5, 3}, {11, 7} }
Salida: 17
Explicación:
Elementos seleccionados para dar la suma máxima –
Fila 0 = 1
Fila 1 = 5
Fila 2 = 11
Explicación: Para seleccionar cualquier elemento si hemos seleccionado A[i][j], entonces los elementos A[i+1][j+1] y A[i+1][j-1] no se pueden seleccionar.
En el ejemplo dado, seleccione el elemento máximo de la fila superior donde 4 es el máximo en este caso, luego no se puede seleccionar el elemento A[1][2] que es 6, seleccione el elemento 8 cuyo máximo de las opciones disponibles. Del mismo modo, el elemento 11 no se puede seleccionar de la 3ª fila. Seleccione el elemento 13 para obtener la suma máxima que es 25.
Enfoque ingenuo: genere todas las combinaciones de N elementos después de elegir 1 elemento de cada fila y seleccione la combinación que produce la suma máxima.
Enfoque eficiente: la idea es utilizar el concepto de programación dinámica de forma ascendente. Comience con la fila más baja de la array dada y repita el proceso a continuación hasta que lleguemos a la fila más alta.
- Cree una array auxiliar de los elementos de fila más inferiores con sus índices correspondientes.
- Ordenar la array auxiliar.
- Iterar sobre la array auxiliar y para cada elemento encontrar el elemento máximo de la fila anterior que se agregará al elemento actual para producir la suma máxima tal que para cada A[i][j] el elemento seleccionado no sea A[i-1][ j+1] o A[i-1][j-1] .
- Repita esto hasta llegar a la fila superior de la array dada.
- Encuentre el elemento máximo de la fila superior para obtener la suma máxima
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ implementation to find
// maximum sum from top to bottom
// row with no adjacent diagonal elements
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the maximum
// path sum from top to bottom row
int maxSum(vector<vector<int> >& V,
int n, int m){
int ans = 0;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
// Create an auxiliary array of next row
// with the element and it's position
vector<pair<int, int> > aux;
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
aux.push_back({ V[i + 1][j],
j });
}
// Sort the auxiliary array
sort(aux.begin(), aux.end());
reverse(aux.begin(), aux.end());
// Find maximum from row above to
// be added to the current element
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
// Find the maximum element from
// the next row that can be added
// to current row element
for (int k = 0; k < m; ++k) {
if (aux[k].second - j == 0 ||
abs(aux[k].second - j) > 1) {
V[i][j] += aux[k].first;
break;
}
}
}
}
// Find the maximum sum
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
ans = max(ans, V[0][i]);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
vector<vector<int> > V{{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 8, 7, 6, 5 },
{ 10, 11, 12, 13 }};
int n = V.size();
int m = V[0].size();
// Function to find maximum path
cout << maxSum(V, n, m);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to find maximum
// sum from top to bottom row with no
// adjacent diagonal elements
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find the maximum
// path sum from top to bottom row
static int maxSum(int[][] V,
int n, int m)
{
int ans = 0;
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i)
{
// Create an auxiliary array of next row
// with the element and it's position
ArrayList<int[]> aux = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j)
{
aux.add(new int[]{V[i + 1][j], j});
}
// Sort the auxiliary array
Collections.sort(aux, (a, b) -> b[0] - a[0]);
// Find maximum from row above to
// be added to the current element
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j)
{
// Find the maximum element from
// the next row that can be added
// to current row element
for(int k = 0; k < m; ++k)
{
if (aux.get(k)[1] - j == 0 ||
Math.abs(aux.get(k)[1] - j) > 1)
{
V[i][j] += aux.get(k)[0];
break;
}
}
}
}
// Find the maximum sum
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
ans = Math.max(ans, V[0][i]);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] V = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 8, 7, 6, 5 },
{ 10, 11, 12, 13 } };
int n = V.length;
int m = V[0].length;
// Function to find maximum path
System.out.println(maxSum(V, n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Python3
# Python3 implementation to find # maximum sum from top to bottom # row with no adjacent diagonal elements # Function to find the maximum # path sum from top to bottom row def maxSum(V, n, m): ans = 0 for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1): # Create an auxiliary array of next row # with the element and it's position aux = [] for j in range(m): aux.append([V[i + 1][j], j]) # Sort the auxiliary array aux = sorted(aux) aux = aux[::-1] # Find maximum from row above to # be added to the current element for j in range(m): # Find the maximum element from # the next row that can be added # to current row element for k in range(m): if (aux[k][1] - j == 0 or abs(aux[k][1] - j) > 1): V[i][j] += aux[k][0] break # Find the maximum sum for i in range(m): ans = max(ans, V[0][i]) return ans # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': V=[[ 1, 2, 3, 4 ], [ 8, 7, 6, 5 ], [ 10, 11, 12, 13]] n = len(V) m = len(V[0]) # Function to find maximum path print(maxSum(V, n, m)) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# implementation to find
// maximum sum from top to bottom
// row with no adjacent diagonal elements
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Function to find the maximum
// path sum from top to bottom row
static int maxSum(int[,] V, int n, int m){
int ans = 0;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
// Create an auxiliary array of next row
// with the element and it's position
List<Tuple<int,int>> aux = new List<Tuple<int,int>>();
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
aux.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(V[i + 1, j], j));
}
// Sort the auxiliary array
aux.Sort();
aux.Reverse();
// Find maximum from row above to
// be added to the current element
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
// Find the maximum element from
// the next row that can be added
// to current row element
for (int k = 0; k < m; ++k) {
if (aux[k].Item2 - j == 0 ||
Math.Abs(aux[k].Item2 - j) > 1) {
V[i, j] += aux[k].Item1;
break;
}
}
}
}
// Find the maximum sum
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
ans = Math.Max(ans, V[0,i]);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[,] V = {{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 8, 7, 6, 5 },
{ 10, 11, 12, 13 }};
int n = V.GetLength(0);
int m = V.GetLength(1);
// Function to find maximum path
Console.WriteLine(maxSum(V, n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to find
// maximum sum from top to bottom
// row with no adjacent diagonal elements
// Function to find the maximum
// path sum from top to bottom row
function maxSum(V, n, m){
let ans = 0;
for (let i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
// Create an auxiliary array of next row
// with the element and it's position
let aux = new Array();
for (let j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
aux.push([ V[i + 1][j], j ]);
}
// Sort the auxiliary array
aux.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
aux.reverse();
// Find maximum from row above to
// be added to the current element
for (let j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
// Find the maximum element from
// the next row that can be added
// to current row element
for (let k = 0; k < m; ++k) {
if (aux[k][1] - j == 0 ||
Math.abs(aux[k][1] - j) > 1) {
V[i][j] += aux[k][0];
break;
}
}
}
}
// Find the maximum sum
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
ans = Math.max(ans, V[0][i]);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
let V = [[ 1, 2, 3, 4 ],
[ 8, 7, 6, 5 ],
[ 10, 11, 12, 13 ]];
let n = V.length;
let m = V[0].length;
// Function to find maximum path
document.write(maxSum(V, n, m));
// This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal
</script>
25
Complejidad de Tiempo: O(n*m 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(m)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Sanjit_Prasad y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA