Un montón de izquierda es una cola de prioridad implementada con un montón binario. Cada Node tiene un sValue que está a la Distancia más cercana a los otros Nodes. Ahora escribiremos un programa java para realizar ciertas operaciones en un Heap de izquierda (Inorder Traversal) como insertar, eliminar, borrar y verificar si está vacío.
Un árbol izquierdista es un árbol binario con propiedades:
- Propiedad de almacenamiento dinámico mínimo normal: clave (i)> = clave (padre (i))
- Más pesado en el lado izquierdo: dist(right(i)) <= dist(left(i)). Aquí, dist(i) es el número de aristas en la ruta más corta desde el Node i hasta un Node hoja en una representación de árbol binario extendida (en esta representación, un hijo nulo se considera un Node externo u hoja). El camino más corto a un Node externo descendiente es a través del hijo derecho. Cada subárbol también es un árbol de izquierda y dist( i ) = 1 + dist( right( i ) ).
Ejemplo: El siguiente árbol de la izquierda se presenta con su distancia calculada para cada Node con el procedimiento mencionado anteriormente. El Node más a la derecha tiene un rango de 0 ya que el subárbol derecho de este Node es nulo y su padre tiene una distancia de 1 por dist( i ) = 1 + dist( right( i )). Se sigue lo mismo para cada Node y se calcula su valor s (o rango).
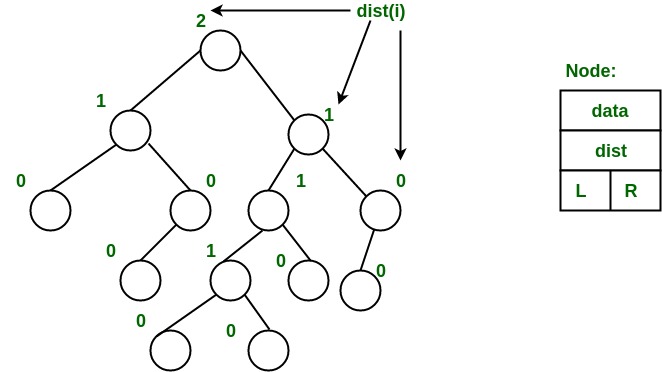
De la segunda propiedad anterior, podemos sacar dos conclusiones:
- El camino desde la raíz hasta la hoja más a la derecha es el camino más corto desde la raíz hasta la hoja.
- Si la ruta a la hoja más a la derecha tiene x Nodes, entonces el montón de la izquierda tiene al menos 2 x – 1 Node. Esto significa que la longitud de la ruta a la hoja más a la derecha es O (log n) para un montón a la izquierda con n Nodes.
Ejemplo:
LEFTIST HEAP Functions to do 2. delete min 3. check empty 4. clear 2 Inorder Traversal: 53 52 54 If you wish to continue type Y or y y Functions to do 2. delete min 3. check empty 4. clear 3 Empty status = false Inorder Traversal: 53 52 54 If you wish to continue type Y or y y Functions to do 2. delete min 3. check empty 4. clear 4 Inorder Traversal: If you wish to continue type Y or y
Acercarse:
- Primero tomaremos un Node de clase y crearemos su constructor y varios parámetros.
- Luego crearemos una clase LeftHeap. En esta clase, crearemos varios métodos e intentaremos realizar sus operaciones.
- Crearemos un constructor, donde mantendremos la raíz nula.
- Crearemos un método isEmpty() para verificar si el Heap está vacío.
- Crearemos un método clear(), para limpiar el montón.
- Creamos un método para fusionar:
- Aquí necesitamos tomar dos Nodes, y luego verificaríamos que ambos estén vacíos
- Luego estableceríamos los valores a derecha o izquierda según nuestra conveniencia.
- Esta función se utiliza para encontrar el elemento mínimo en el montón
- Luego declaramos una función llamada del().
- Esta función se usa para encontrar el número mínimo y luego lo eliminamos.
- Luego declaramos la función principal y llamamos a la función y realizamos operaciones con la ayuda de un caso de cambio. Las operaciones realizadas son si verificar si está vacío o vaciar el montón o eliminar el elemento mínimo.
Implementación:
Java
// Java Program to Implement Leftist Heap
// Declare all libraries
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
// Class Node
class Node {
// elements, and sValue are the variables in class Node
int element, sValue;
// class has two parameters
Node left, right;
public Node(int element) { this(element, null, null); }
// Function Node where we are using this keyword
// Which will help us to avoid confusion if we are having
// same elements
public Node(int element, Node left, Node right)
{
this.element = element;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.sValue = 0;
}
}
// Class Left heap
class LeftHeap {
// Now parameter is created named head.
private Node head;
// Its constructor is created named left heap
// Returns null
public LeftHeap() { head = null; }
// Now we will write function to check if the list is
// empty
public boolean isEmpty()
{
// If head is null returns true
return head == null;
}
// Now we will write a function clear
public void clear()
{
// We will put head is null
head = null;
}
// Now let us create a function merge which will
// help us merge
public void merge(LeftHeap rhs)
{
// If the present function is rhs
// then we return it
if (this == rhs)
return;
// Here we call the function merge
// And make rhs is equal to null
head = merge(head, rhs.head);
rhs.head = null;
}
// Function merge with two Nodes a and b
public Node merge(Node a, Node b)
{
// If A is null
// We return b
if (a == null)
return b;
// If b is null
// we return A
if (b == null)
return a;
// If we put a element greater than b element
if (a.element > b.element) {
// We write the swap code
Node temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// Now we call the function merge to merge a and b
a.right = merge(a.right, b);
// If a is null we swap right with left and empty
// right
if (a.left == null) {
a.left = a.right;
a.right = null;
}
// else
// if value in a is less than the svalue of right
// If the condition is satisfied , we swap the left
// with right
else {
if (a.left.sValue < a.right.sValue) {
Node temp = a.left;
a.left = a.right;
a.right = temp;
}
// we store the value in a s Value of right
// SValue
a.sValue = a.right.sValue + 1;
}
// We now return the value of a
return a;
}
// Function insert
public void insert(int a)
{
// This root will help us insert a new variable
head = merge(new Node(a), head);
}
// The below function will help us delete minimum
// function present in the Heap
public int del()
{
// If is empty return -1
if (isEmpty())
return -1;
// Now we will store the element in variable and
// Call the merge function to del that is converging
// to head then we return min
int min = head.element;
head = merge(head.left, head.right);
return min;
}
// Function order
// will print the starting and ending points in order.
public void order()
{
order(head);
System.out.println();
}
// Function order with Node r
// If r not equal to r
// It prints all the elements iterating from order left
// to right
private void order(Node r)
{
if (r != null) {
order(r.left);
System.out.print(r.element + " ");
order(r.right);
}
}
}
// Class gfg
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating the scanner object
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("LEFTIST HEAP");
// Creating object for class LeftHeap
LeftHeap h = new LeftHeap();
// Char ch
char ch;
// Now taking the loop
do {
// Now writing down all the functions
System.out.println("Functions to do");
System.out.println("1. insert");
System.out.println("2. delete min");
System.out.println("3. check empty");
System.out.println("4. clear");
// Scanning the choice to be used in switch
int choice = sc.nextInt();
// Using switch
switch (choice) {
// Case 1
// to insert the elements in the heap
// call the insert func
case 1:
System.out.println("Enter integer element to insert");
h.insert(sc.nextInt());
break;
// Delete the minimum element in the func
case 2:
h.del();
break;
// To check the empty status of the heap
case 3:
System.out.println("Empty status = "
+ h.isEmpty());
break;
// Cleaning the heap
case 4:
h.clear();
break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong entry");
break;
}
// Prints the inorder traversal
// Calling the func
System.out.print("\n Inorder Traversal: ");
h.order();
// Whether to continue or not
System.out.println("\n If you wish to continue type Y or y");
ch = sc.next().charAt(0);
}
// Closing of loop
while (ch == 'Y' || ch == 'y');
}
}
Producción:

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por saransh9342 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA