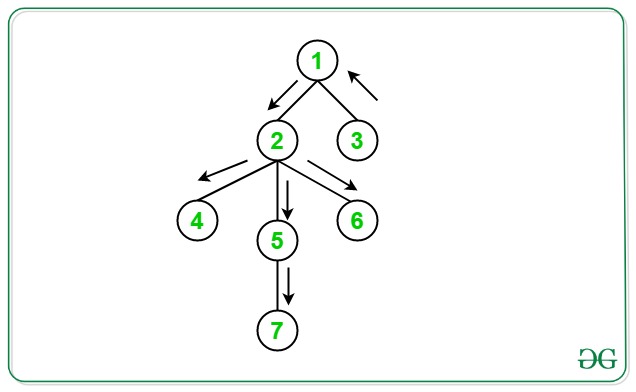
Dado un árbol que tiene N Nodes conectados por N − 1 arista y un solo Node desconectado , la tarea es encontrar los diámetros para cada Node del Árbol dado después de conectarlo con el componente desconectado dado.
Ejemplo:
Aporte:
Salida: 3 3 4 4 4 4
Explicación:
Inicialmente diámetro del árbol = 3 .
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 1 y el Node 7 , entonces el diámetro del árbol es igual a 3 (7 -> 1 -> 2 -> 5).
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 2 y el Node 7 , entonces el diámetro del árbol es igual a 3 (3 -> 1 -> 2 -> 5).
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 3 y el Node 7 , entonces el diámetro del árbol es igual a 4 (7 -> 3 -> 1 -> 2 -> 5).
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 4 y el Node 7, entonces el diámetro del nuevo árbol es igual a 4 (7-> 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3).
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 5 y el Node 7 , entonces el diámetro del nuevo árbol será 4 (7-> 5 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3).
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 6 y el Node 7 , entonces el diámetro del nuevo árbol será 4 ((7-> 6 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3)).
Aporte:
Salida: 3 2 3
Explicación:
Diámetro inicial del árbol = 2
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 1 y el Node 4 , entonces el diámetro del árbol es igual a 3 (4 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3).
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 2 y el Node 4 , entonces el diámetro del árbol es igual a 2 (4 -> 2 -> 3).
Si se agrega un borde entre el Node 3 y el Node 4 , entonces el diámetro del árbol es igual a 3 (4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1).
Planteamiento: Para resolver el problema, es necesario hacer las siguientes observaciones:
- El diámetro aumenta en 1 cuando el Node desconectado se conecta a un borde que forma el final del diámetro.
- Para todos los demás Nodes, el diámetro permanece sin cambios al conectar el Node desconectado.
Siga los pasos que se dan a continuación para resolver el problema basado en las observaciones anteriores:
- Realice el recorrido DFS del árbol dado.
- Mientras atraviesa, mantenga un registro de la distancia más lejana recorrida y el Node más lejano.
- Ahora, realice DFS desde el Node más lejano obtenido del paso anterior y realice un seguimiento del Node más alejado de este Node.
- Ahora, realice DFS y siga agregando Nodes en un Mapa que esté más alejado de los dos Nodes obtenidos de los pasos anteriores por separado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Keeps track of the farthest
// end of the diameter
int X = 1;
// Keeps track of the length of
// the diameter
int diameter = 0;
// Stores the nodes which are at
// ends of the diameter
map<int, bool> mp;
// Perform DFS on the given tree
void dfs(int current_node, int prev_node,
int len, bool add_to_map,
vector<vector<int> >& adj)
{
// Update diameter and X
if (len > diameter) {
diameter = len;
X = current_node;
}
// If current node is an end of diameter
if (add_to_map && len == diameter) {
mp[current_node] = 1;
}
// Traverse its neighbors
for (auto& it : adj[current_node]) {
if (it != prev_node)
dfs(it, current_node, len + 1,
add_to_map, adj);
}
}
// Function to call DFS for the
// required purposes
void dfsUtility(vector<vector<int> >& adj)
{
// DFS from a random node and find
// the node farthest from it
dfs(1, -1, 0, 0, adj);
int farthest_node = X;
// DFS from X to calculate diameter
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, 0, adj);
// DFS from farthest_node to find
// the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, 1, adj);
// DFS from X (other end of diameter) and
// check the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(X, -1, 0, 1, adj);
}
void printDiameters(vector<vector<int> >& adj)
{
dfsUtility(adj);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
// If node i is the end of
// a diameter
if (mp[i] == 1)
// Increase diameter by 1
cout << diameter + 1 << ", ";
// Otherwise
else
// Remains unchanged
cout << diameter << ", ";
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3 7
/|\
/ | \
4 5 6 */
vector<vector<int> > adj(7);
// creating undirected edges
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(1);
adj[1].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(1);
adj[2].push_back(4);
adj[4].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(5);
adj[5].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(6);
adj[6].push_back(2);
printDiameters(adj);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Keeps track of the farthest
// end of the diameter
static int X = 1;
// Keeps track of the length of
// the diameter
static int diameter = 0;
// Stores the nodes which are at
// ends of the diameter
static HashMap<Integer,
Boolean> mp = new HashMap<>();
// Perform DFS on the given tree
static void dfs(int current_node, int prev_node,
int len, boolean add_to_map,
Vector<Integer> [] adj)
{
// Update diameter and X
if (len > diameter)
{
diameter = len;
X = current_node;
}
// If current node is an end of diameter
if (add_to_map && len == diameter)
{
mp.put(current_node, true);
}
// Traverse its neighbors
for (int it : adj[current_node])
{
if (it != prev_node)
dfs(it, current_node, len + 1,
add_to_map, adj);
}
}
// Function to call DFS for the
// required purposes
static void dfsUtility(Vector<Integer> [] adj)
{
// DFS from a random node and find
// the node farthest from it
dfs(1, -1, 0, false, adj);
int farthest_node = X;
// DFS from X to calculate diameter
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, false, adj);
// DFS from farthest_node to find
// the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, true, adj);
// DFS from X (other end of diameter) and
// check the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(X, -1, 0, true, adj);
}
static void printDiameters(Vector<Integer> [] adj)
{
dfsUtility(adj);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
// If node i is the end of
// a diameter
if (mp.containsKey(i) &&
mp.get(i) == true)
// Increase diameter by 1
System.out.print(diameter + 1 + ", ");
// Otherwise
else
// Remains unchanged
System.out.print(diameter + ", ");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3 7
/|\
/ | \
4 5 6 */
Vector<Integer> []adj = new Vector[7];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
// creating undirected edges
adj[1].add(2);
adj[2].add(1);
adj[1].add(3);
adj[3].add(1);
adj[2].add(4);
adj[4].add(2);
adj[2].add(5);
adj[5].add(2);
adj[2].add(6);
adj[6].add(2);
printDiameters(adj);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3
# Python3 program to implement # the above approach from collections import defaultdict # Keeps track of the farthest # end of the diameter X = 1 # Keeps track of the length of # the diameter diameter = 0 # Stores the nodes which are at # ends of the diameter mp = defaultdict(lambda :0) # Perform DFS on the given tree def dfs(current_node, prev_node, len, add_to_map, adj): global diameter, X # Update diameter and X if len > diameter: diameter = len X = current_node # If current node is an end of diameter if add_to_map and len == diameter: mp[current_node] = 1 # Traverse its neighbors for it in adj[current_node]: if it != prev_node: dfs(it, current_node, len + 1, add_to_map, adj) # Function to call DFS for the # required purposes def dfsUtility(adj): # DFS from a random node and find # the node farthest from it dfs(1, -1, 0, 0, adj) farthest_node = X # DFS from X to calculate diameter dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, 0, adj) # DFS from farthest_node to find # the farthest node(s) from it dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, 1, adj) # DFS from X (other end of diameter) and # check the farthest node(s) from it dfs(X, -1, 0, 1, adj) def printDiameters(adj): global diameter dfsUtility(adj) for i in range(1, 6 + 1): # If node i is the end of # a diameter if mp[i] == 1: # Increase diameter by 1 print(diameter + 1, end = ", ") # Otherwise else: # Remains unchanged print(diameter, end = ", ") # Driver code # constructed tree is # 1 # / \ # 2 3 # / | \ # 4 5 6 # | # 7 adj = [] for i in range(7): adj.append([]) # Creating undirected edges adj[1].append(2) adj[2].append(1) adj[1].append(3) adj[3].append(1) adj[2].append(4) adj[4].append(2) adj[2].append(5) adj[5].append(2) adj[2].append(6) adj[6].append(2) printDiameters(adj) # This code is contributed by Stuti Pathak
C#
// C# Program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Keeps track of the farthest
// end of the diameter
static int X = 1;
// Keeps track of the
// length of the diameter
static int diameter = 0;
// Stores the nodes which are at
// ends of the diameter
static Dictionary<int, Boolean> mp
= new Dictionary<int, Boolean>();
// Perform DFS on the given tree
static void dfs(int current_node, int prev_node,
int len, bool add_to_map,
List<int>[] adj)
{
// Update diameter and X
if (len > diameter)
{
diameter = len;
X = current_node;
}
// If current node is an end of diameter
if (add_to_map && len == diameter)
{
mp.Add(current_node, true);
}
// Traverse its neighbors
foreach(int it in adj[current_node])
{
if (it != prev_node)
dfs(it, current_node, len + 1,
add_to_map, adj);
}
}
// Function to call DFS for
// the required purposes
static void dfsUtility(List<int>[] adj)
{
// DFS from a random node and find
// the node farthest from it
dfs(1, -1, 0, false, adj);
int farthest_node = X;
// DFS from X to calculate diameter
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, false, adj);
// DFS from farthest_node to find
// the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, true, adj);
// DFS from X (other end of diameter) and
// check the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(X, -1, 0, true, adj);
}
static void printDiameters(List<int>[] adj)
{
dfsUtility(adj);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
// If node i is the end
// of a diameter
if (mp.ContainsKey(i) && mp[i] == true)
// Increase diameter by 1
Console.Write(diameter + 1 + ", ");
// Otherwise
else
// Remains unchanged
Console.Write(diameter + ", ");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3 7
/|\
/ | \
4 5 6 */
List<int>[] adj = new List<int>[ 7 ];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List<int>();
// creating undirected edges
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[1].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(4);
adj[4].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(5);
adj[5].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(6);
adj[6].Add(2);
printDiameters(adj);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Keeps track of the farthest
// end of the diameter
let X = 1;
// Keeps track of the
// length of the diameter
let diameter = 0;
// Stores the nodes which are at
// ends of the diameter
let mp = new Map();
// Perform DFS on the given tree
function dfs(current_node, prev_node, len, add_to_map, adj)
{
// Update diameter and X
if (len > diameter)
{
diameter = len;
X = current_node;
}
// If current node is an end of diameter
if (add_to_map && len == diameter)
{
mp.set(current_node, true);
}
// Traverse its neighbors
for(let it = 0; it < adj[current_node].length; it++)
{
if (adj[current_node][it] != prev_node)
dfs(adj[current_node][it], current_node, len + 1,
add_to_map, adj);
}
}
// Function to call DFS for
// the required purposes
function dfsUtility(adj)
{
// DFS from a random node and find
// the node farthest from it
dfs(1, -1, 0, false, adj);
let farthest_node = X;
// DFS from X to calculate diameter
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, false, adj);
// DFS from farthest_node to find
// the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, true, adj);
// DFS from X (other end of diameter) and
// check the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(X, -1, 0, true, adj);
}
function printDiameters(adj)
{
dfsUtility(adj);
for (let i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
// If node i is the end
// of a diameter
if (mp.has(i) && mp.get(i) == true)
// Increase diameter by 1
document.write(diameter + 1 + ", ");
// Otherwise
else
// Remains unchanged
document.write(diameter + ", ");
}
}
/* constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3 7
/|\
/ | \
4 5 6 */
let adj = new Array(7);
for (let i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = [];
// creating undirected edges
adj[1].push(2);
adj[2].push(1);
adj[1].push(3);
adj[3].push(1);
adj[2].push(4);
adj[4].push(2);
adj[2].push(5);
adj[5].push(2);
adj[2].push(6);
adj[6].push(2);
printDiameters(adj);
</script>
3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4,
Complejidad temporal: O(V + E) , donde V es el número de vértices y E es el número de aristas en el gráfico.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(V)