Dada una Lista Vinculada Circular, la tarea es agregar un Nuevo Node en el Medio de la Lista. Consideremos la siguiente lista circular enlazada:
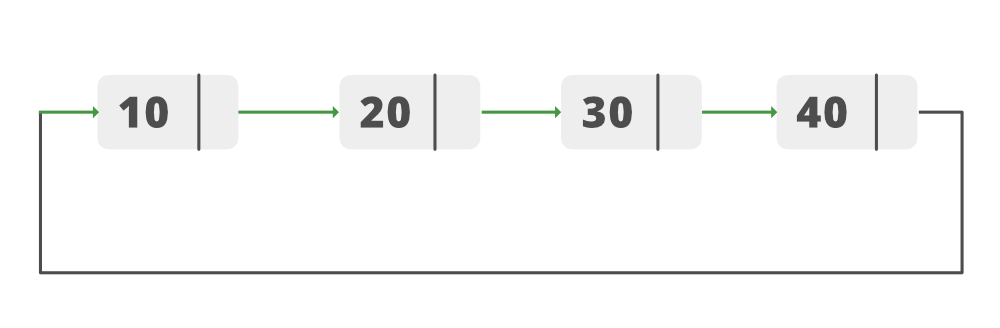
Lista antes de la inserción
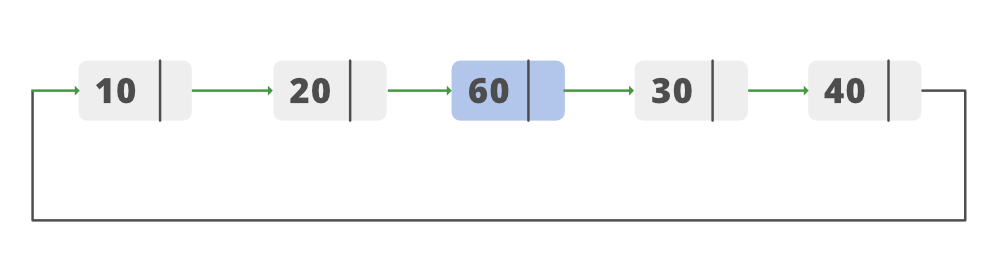
Lista después de la inserción
- Cree un nuevo Node (New_node).
- Compruebe si hay una lista vacía. Si la lista está vacía, inserte el Node como cabeza.
- Para una lista no vacía, calcule la longitud de la lista.
- Cree un medio variable y almacene la longitud media en él.
- Cree dos Nodes Temporal y Actual.
- Ahora recorra la lista hasta que Temporal alcance el punto medio de la lista usando la variable media.
- Inserte New_node después de Current.
- Haga que Current.next apunte a New node y New_node.next a Temporal.
- Se inserta el Node.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
Java
// Java Program to Insert a New Node at
// the Middle of the Circular Linked List
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
// Stores Information about Node of List
public class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
// Declaring Head of the Node
public Node head_of_node = null;
// A last pointer to help append values to our list
public Node last = null;
// keep count of size of the list
public int length_of_list;
// Add method adds values to the end of the list
public void add(int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head_of_node == null) {
head_of_node = newNode;
last = newNode;
newNode.next = head_of_node;
}
else {
last.next = newNode;
last = newNode;
last.next = head_of_node;
}
// keep count of size of list
length_of_list++;
}
// Method to insert Node in the middle of the list
public void Insert_In_Middle(int data)
{
// creating a new node that is to be inserted
Node New_node = new Node(data);
// check for empty list
if (head_of_node == null) {
head_of_node = New_node;
last = New_node;
New_node.next = head_of_node;
}
// If the list is not empty
else {
// Declaring nodes
Node temporary;
Node current;
// Checking if the length of list
// if even or odd
int mid_point_check = (length_of_list % 2);
// mid point for even length
if (mid_point_check == 0) {
length_of_list = length_of_list / 2;
}
// mid point for odd length
else {
length_of_list = (length_of_list + 1) / 2;
}
// temporary points to the head of list
temporary = head_of_node;
current = null;
// loop till we reach the mid point
while (length_of_list > 0) {
// make current point to the previous node
current = temporary;
temporary = temporary.next;
length_of_list -= 1;
}
// make the previous node point to the new node
current.next = New_node;
// make the new_node.next point to temporary
New_node.next = temporary;
}
// increasing the length of list after insertion of
// new node
length_of_list++;
}
// Print_list method iterates through the list and
// prints the values stored in the list
public void Print_List()
{
Node current = head_of_node;
if (head_of_node == null) {
System.out.println("Your list is empty");
}
else {
do {
System.out.print(" " + current.data);
current = current.next;
} while (current != head_of_node);
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GFG circular_list = new GFG();
circular_list.add(10);
circular_list.add(20);
circular_list.add(30);
circular_list.add(40);
System.out.print("Original List --> ");
circular_list.Print_List();
circular_list.Insert_In_Middle(60);
System.out.print("List after Inserting --> ");
circular_list.Print_List();
}
}
Producción
Original List --> 10 20 30 40 List after Inserting --> 10 20 60 30 40
Complejidad temporal: O(n) donde n no es ningún Node de una lista enlazada circular
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por uchiha1101 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA