Dado un árbol binario en el que los Nodes están numerados del 1 al N. Dado un Node y un entero positivo K . Tenemos que imprimir el ancestro Kth del Node dado en el árbol binario. Si no existe ningún ancestro de este tipo, imprima -1 .
Por ejemplo , en el siguiente árbol binario, el segundo antepasado de los Nodes 4 y 5 es 1 . El tercer ancestro del Node 4 será -1 .
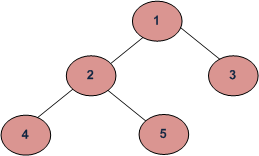
Enfoque: Primero, encontramos la ruta de los datos clave dados desde la raíz y la almacenaremos en un vector , luego simplemente devolveremos el k -ésimo índice del vector desde el último.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of Tree
struct node {
node *left, *right;
int data;
};
// To create a new node
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* temp = new node;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the path from
// root to the target node
bool RootToNode(node* root, int key, vector<int>& v)
{
if (root == NULL)
return false;
// Add current node to the path
v.push_back(root->data);
// If current node is the target node
if (root->data == key)
return true;
// If the target node exists in
// the left or the right sub-tree
if (RootToNode(root->left, key, v)
|| RootToNode(root->right, key, v))
return true;
// Remove the last inserted node as
// it is not a part of the path
// from root to target
v.pop_back();
return false;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
// Given node
int target = 4;
// Vector to store the path from
// root to the given node
vector<int> v;
// Find the path from root to the target node
RootToNode(root, target, v);
int k = 2;
// Print the Kth ancestor
if (k > v.size() - 1 || k <= 0)
cout << -1;
else
cout << v[v.size() - 1 - k];
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Structure of Tree
static class node
{
node left, right;
int data;
};
// To create a new node
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.left = temp.right = null;
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the path from
// root to the target node
static boolean RootToNode(node root, int key,
Vector<Integer> v)
{
if (root == null)
return false;
// Add current node to the path
v.add(root.data);
// If current node is the target node
if (root.data == key)
return true;
// If the target node exists in
// the left or the right sub-tree
if (RootToNode(root.left, key, v)
|| RootToNode(root.right, key, v))
return true;
// Remove the last inserted node as
// it is not a part of the path
// from root to target
v.removeElementAt(v.size()-1);
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
// Given node
int target = 4;
// Vector to store the path from
// root to the given node
Vector<Integer> v = new Vector<>();
// Find the path from root to the target node
RootToNode(root, target, v);
int k = 2;
// Print the Kth ancestor
if (k > v.size() - 1 || k <= 0)
System.out.println(-1);
else
System.out.println(v.get(v.size() - 1 - k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach # To create a node class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # Function to find the path # from root to the target node def RootToNode(root, key, v): if root == None: return False # Add current node to the path v.append(root.data) # If current node is the target node if root.data == key: return True # If the target node exists in # the left or the right sub-tree if (RootToNode(root.left, key, v) or RootToNode(root.right, key, v)): return True # Remove the last inserted node # as it is not a part of the # path from root to target v.pop() return False # Driver code if __name__ == "__main__": root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.right.left = Node(6) root.right.right = Node(7) # Given node target, k = 4, 2 # Vector to store the path # from root to the given node v = [] # Find the path from root to the target node RootToNode(root, target, v) # Print the Kth ancestor if k > len(v) - 1 or k <= 0: print(-1) else: print(v[len(v) - 1 - k]) # This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain
C#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG
{
// Structure of Tree
public class node
{
public node left, right;
public int data;
};
// To create a new node
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.left = temp.right = null;
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the path from
// root to the target node
static bool RootToNode(node root, int key,
List<int> v)
{
if (root == null)
return false;
// Add current node to the path
v.Add(root.data);
// If current node is the target node
if (root.data == key)
return true;
// If the target node exists in
// the left or the right sub-tree
if (RootToNode(root.left, key, v)
|| RootToNode(root.right, key, v))
return true;
// Remove the last inserted node as
// it is not a part of the path
// from root to target
v.Remove(v.Count-1);
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
// Given node
int target = 4;
// Vector to store the path from
// root to the given node
List<int> v = new List<int>();
// Find the path from root to the target node
RootToNode(root, target, v);
int k = 2;
// Print the Kth ancestor
if (k > v.Count - 1 || k <= 0)
Console.WriteLine(-1);
else
Console.WriteLine(v[v.Count - 1 - k]);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation of above approach
// Structure of Tree
class node
{
constructor()
{
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = 0;
}
};
// To create a new node
function newNode(data)
{
var temp = new node();
temp.left = temp.right = null;
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the path from
// root to the target node
function RootToNode(root, key, v)
{
if (root == null)
return false;
// push current node to the path
v.push(root.data);
// If current node is the target node
if (root.data == key)
return true;
// If the target node exists in
// the left or the right sub-tree
if (RootToNode(root.left, key, v)
|| RootToNode(root.right, key, v))
return true;
// Remove the last inserted node as
// it is not a part of the path
// from root to target
v.pop();
return false;
}
// Driver code
var root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
// Given node
var target = 4;
// Vector to store the path from
// root to the given node
var v = [];
// Find the path from root to the target node
RootToNode(root, target, v);
var k = 2;
// Print the Kth ancestor
if (k > v.length - 1 || k <= 0)
document.write(-1);
else
document.write(v[v.length - 1 - k]);
</script>
Producción:
1