Requisitos previos: gráfico y sus representaciones
Dada una array de adyacencia g[][] de un gráfico que consta de N vértices, la tarea es modificar la array después de la inserción de todos los bordes[] y la eliminación del borde entre los vértices (X, Y) . En una array de adyacencia, si existe una arista entre los vértices i y j del gráfico, entonces g[i][j] = 1 y g[j][i] = 1 . Si no existe ningún borde entre estos dos vértices, entonces g[i][j] = 0 y g[j][i] = 0 .
Ejemplos:
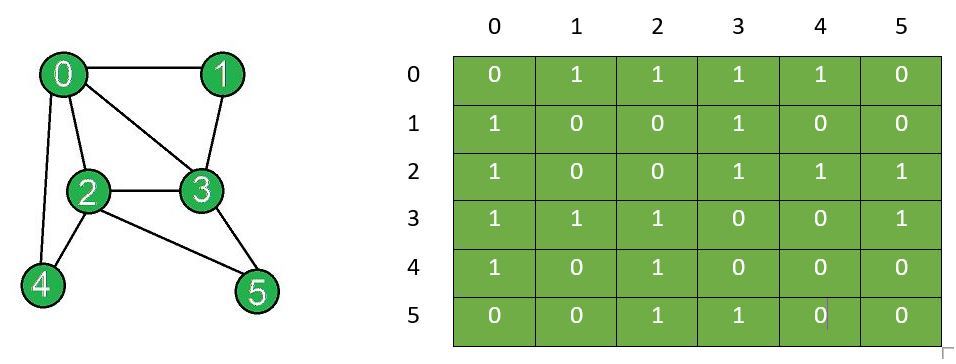
Entrada: N = 6, Bordes[] = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {0, 4}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}}, X = 2, Y = 3
Salida:
array de adyacencia después de la inserción del borde:
0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
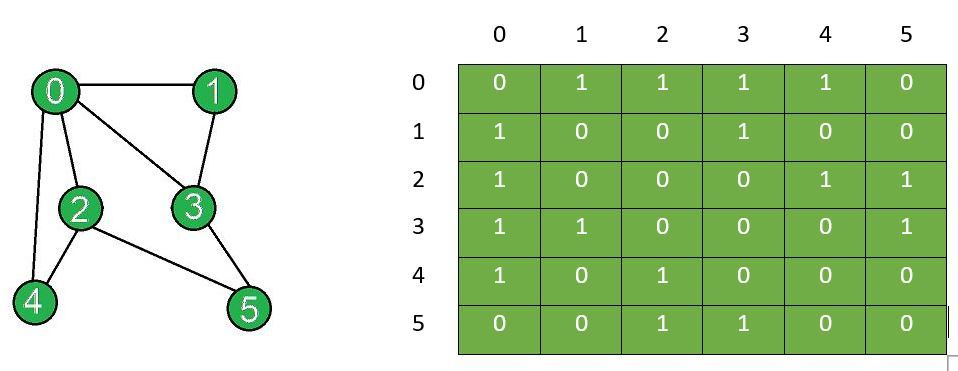
Array de adyacencia después de eliminar el borde:
0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
Explicación:
El gráfico y la array de adyacencia correspondiente después de la inserción de los bordes:El gráfico después de la eliminación y la array de adyacencia después de la eliminación del borde entre el vértice X e Y :
Entrada: N = 6, Bordes[] = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {0, 4}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}}, X = 3, Y = 5
Salida:
Array de adyacencia después de la inserción del borde:
0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
Array de adyacencia después de eliminar el borde:
0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
Enfoque:
Inicialice una array de dimensiones N x N y siga los pasos a continuación:
- Inserción de una arista: Para insertar una arista entre dos vértices suponga i y j , establezca los valores correspondientes en la array de adyacencia igual a 1, es decir, g[i][j]=1 y g[j][i]=1 si ambos los vértices i y j existen.
- Eliminación de una arista: para eliminar una arista entre dos vértices, suponga i y j , establezca los valores correspondientes en la array de adyacencia en 0. Es decir, establezca g[i][j]=0 y g[j][i]= 0 si ambos vértices i y j existen.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to add and remove edge
// in the adjacency matrix of a graph
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
private:
// Number of vertices
int n;
// Adjacency matrix
int g[10][10];
public:
// Constructor
Graph(int x)
{
n = x;
// Initializing each element of the
// adjacency matrix to zero
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to display adjacency matrix
void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
// Displaying the 2D matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << "\n";
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cout << " " << g[i][j];
}
}
}
// Function to update adjacency
// matrix for edge insertion
void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// Checks if the vertices
// exist in the graph
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n)) {
cout << "Vertex" << x
<< " does not exist!";
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n)) {
cout << "Vertex" << y
<< " does not exist!";
}
// Checks if it is a self edge
if (x == y) {
cout << "Same Vertex!";
}
else {
// Insert edge
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
// Function to update adjacency
// matrix for edge removal
void removeEdge(int x, int y)
{
// Checks if the vertices
// exist in the graph
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n)) {
cout << "Vertex" << x
<< " does not exist!";
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n)) {
cout << "Vertex" << y
<< " does not exist!";
}
// Checks if it is a self edge
if (x == y) {
cout << "Same Vertex!";
}
else {
// Remove edge
g[y][x] = 0;
g[x][y] = 0;
}
}
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 6, X = 2, Y = 3;
Graph obj(N);
// Adding edges to the graph
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(0, 3);
obj.addEdge(0, 4);
obj.addEdge(1, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 4);
obj.addEdge(2, 5);
obj.addEdge(3, 5);
cout << "Adjacency matrix after"
<< " edge insertions:\n";
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
obj.removeEdge(X, Y);
cout << "\nAdjacency matrix after"
<< " edge removal:\n";
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to add and remove edge
// in the adjacency matrix of a graph
class Graph {
// Number of vertices
private int n;
// Adjacency matrix
private int[][] g = new int[10][10];
// Constructor
Graph(int x)
{
this.n = x;
// Initializing each element of the
// adjacency matrix to zero
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to display adjacency matrix
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
// Displaying the 2D matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
System.out.print(" " + g[i][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to update adjacency
// matrix for edge insertion
public void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// Checks if the vertices exists
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n)) {
System.out.printf("Vertex " + x
+ " does not exist!");
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n)) {
System.out.printf("Vertex " + y
+ " does not exist!");
}
// Checks if it is a self edge
if (x == y) {
System.out.println("Same Vertex!");
}
else {
// Insert edge
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
// Function to update adjacency
// matrix for edge removal
public void removeEdge(int x, int y)
{
// Checks if the vertices exists
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n)) {
System.out.printf("Vertex " + x
+ " does not exist!");
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n)) {
System.out.printf("Vertex " + y
+ " does not exist!");
}
// Checks if it is a self edge
if (x == y) {
System.out.println("Same Vertex!");
}
else {
// Remove edge
g[y][x] = 0;
g[x][y] = 0;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 6, X = 2, Y = 3;
Graph obj = new Graph(N);
// Inserting edges
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(0, 3);
obj.addEdge(0, 4);
obj.addEdge(1, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 4);
obj.addEdge(2, 5);
obj.addEdge(3, 5);
System.out.println("Adjacency matrix after"
+ " edge insertions:");
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
obj.removeEdge(2, 3);
System.out.println("\nAdjacency matrix after"
+ " edge removal:");
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to add and remove edge
# in adjacency matrix representation of a graph
class Graph:
# Number of vertices
__n = 0
# Adjacency matrix
__g = [[0 for x in range(10)]
for y in range(10)]
# Constructor
def __init__(self, x):
self.__n = x
# Initializing each element of
# the adjacency matrix to zero
for i in range(0, self.__n):
for j in range(0, self.__n):
self.__g[i][j] = 0
# Function to display adjacency matrix
def displayAdjacencyMatrix(self):
# Displaying the 2D matrix
for i in range(0, self.__n):
print()
for j in range(0, self.__n):
print("", self.__g[i][j], end = "")
# Function to update adjacency
# matrix for edge insertion
def addEdge(self, x, y):
# Checks if the vertices
# exist in the graph
if (x < 0) or (x >= self.__n):
print("Vertex {} does not exist!".format(x))
if (y < 0) or (y >= self.__n):
print("Vertex {} does not exist!".format(y))
# Checks if it is a self edge
if(x == y):
print("Same Vertex!")
else:
# Adding edge between the vertices
self.__g[y][x] = 1
self.__g[x][y] = 1
# Function to update adjacency
# matrix for edge removal
def removeEdge(self, x, y):
# Checks if the vertices
# exist in the graph
if (x < 0) or (x >= self.__n):
print("Vertex {} does not exist!".format(x))
if (y < 0) or (y >= self.__n):
print("Vertex {} does not exist!".format(y))
# Checks if it is a self edge
if(x == y):
print("Same Vertex!")
else:
# Remove edge from between
# the vertices
self.__g[y][x] = 0
self.__g[x][y] = 0
# Driver code
# Creating an object of class Graph
obj = Graph(6);
# Adding edges to the graph
obj.addEdge(0, 1)
obj.addEdge(0, 2)
obj.addEdge(0, 3)
obj.addEdge(0, 4)
obj.addEdge(1, 3)
obj.addEdge(2, 3)
obj.addEdge(2, 4)
obj.addEdge(2, 5)
obj.addEdge(3, 5)
# Edges added to the adjacency matrix
print("Adjacency matrix after "
"edge insertions:\n")
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
# Removing the edge between vertices
# "2" and "3" from the graph
obj.removeEdge(2, 3);
# The adjacency matrix after
# removing the edge
print("\nAdjacency matrix after "
"edge removal:\n")
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
# This code is contributed by amarjeet_singh
C#
// C# program to add and remove edge
// in adjacency matrix representation
// of a graph
using System;
class Graph{
// Number of vertices
private int n;
// Adjacency matrix
private int[,] g = new int[10, 10];
// Constructor
public Graph(int x)
{
this.n = x;
// Initializing each element of
// the adjacency matrix to zero
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i, j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to display adjacency matrix
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
// Displaying the 2D matrix
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
Console.WriteLine();
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
Console.Write(" " + g[i, j]);
}
}
}
// Function to update adjacency
// matrix for edge insertion
public void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// Checks if the vertices exist
// in the graph
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n))
{
Console.WriteLine("Vertex {0} does " +
"not exist!", x);
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n))
{
Console.WriteLine("Vertex {0} does " +
"not exist!", y);
}
// Checks if it is a self edge
if (x == y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Same Vertex!");
}
else
{
// Adding edge between the vertices
g[y, x] = 1;
g[x, y] = 1;
}
}
// Function to update adjacency
// matrix for edge removal
public void removeEdge(int x, int y)
{
// Checks if the vertices exist
// in the graph
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n))
{
Console.WriteLine("Vertex {0} does" +
"not exist!", x);
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n))
{
Console.WriteLine("Vertex {0} does" +
"not exist!", y);
}
// Checks if it is a self edge
if (x == y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Same Vertex!");
}
else
{
// Remove edge from between
// the vertices
g[y, x] = 0;
g[x, y] = 0;
}
}
}
class GFG{
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of class Graph
Graph obj = new Graph(6);
// Adding edges to the graph
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(0, 3);
obj.addEdge(0, 4);
obj.addEdge(1, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
obj.addEdge(2, 4);
obj.addEdge(2, 5);
obj.addEdge(3, 5);
// Edges added to the adjacency matrix
Console.WriteLine("Adjacency matrix after " +
"edge insertions:\n");
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// Removing the edge between vertices
// "2" and "3" from the graph
obj.removeEdge(2, 3);
// The adjacency matrix after
// removing the edge
Console.WriteLine("\nAdjacency matrix after " +
"edge removal:");
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
}
}
// This code is contributed by amarjeet_singh
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to add and remove edge
// in adjacency matrix representation
// of a graph
// Number of vertices
var n = 0;
// Adjacency matrix
var g = Array.from(Array(10), ()=>Array(10).fill(0));
// Constructor
function initialize(x)
{
n = x;
// Initializing each element of
// the adjacency matrix to zero
for(var i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for(var j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to display adjacency matrix
function displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
// Displaying the 2D matrix
for(var i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
document.write("<br>");
for(var j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
document.write(" " + g[i][j]);
}
}
}
// Function to update adjacency
// matrix for edge insertion
function addEdge(x, y)
{
// Checks if the vertices exist
// in the graph
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n))
{
document.write(`Vertex ${x} does not exist!`);
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n))
{
document.write(`Vertex ${y} does not exist!`);
}
// Checks if it is a self edge
if (x == y)
{
document.write("Same Vertex!<br>");
}
else
{
// Adding edge between the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
// Function to update adjacency
// matrix for edge removal
function removeEdge(x, y)
{
// Checks if the vertices exist
// in the graph
if ((x < 0) || (x >= n))
{
document.write(`Vertex ${x} does not exist!`);
}
if ((y < 0) || (y >= n))
{
document.write(`Vertex ${y} does not exist!`);
}
// Checks if it is a self edge
if (x == y)
{
document.write("Same Vertex!<br>");
}
else
{
// Remove edge from between
// the vertices
g[y][x] = 0;
g[x][y] = 0;
}
}
// Driver code
// Creating an object of class Graph
initialize(6);
// Adding edges to the graph
addEdge(0, 1);
addEdge(0, 2);
addEdge(0, 3);
addEdge(0, 4);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(2, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(3, 5);
// Edges added to the adjacency matrix
document.write("Adjacency matrix after " +
"edge insertions:<br>");
displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// Removing the edge between vertices
// "2" and "3" from the graph
removeEdge(2, 3);
// The adjacency matrix after
// removing the edge
document.write("<br>Adjacency matrix after " +
"edge removal:<br>");
displayAdjacencyMatrix();
</script>
Adjacency matrix after edge insertions: 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 Adjacency matrix after edge removal: 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0
Complejidad de tiempo: la inserción y eliminación de un borde requiere una complejidad O(1), mientras que se necesita O(N 2 ) para mostrar la array de adyacencia.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N 2 )
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por amarjeet_singh y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA