La criptografía es una técnica de seguridad de la información y las comunicaciones mediante el uso de códigos para que solo aquellas personas a las que está destinada la información puedan entenderla y procesarla. Previniendo así el acceso no autorizado a la información. El prefijo «cripta» significa «oculto» y el sufijo grafía significa «escrito». En este artículo, se analiza un tipo de técnica criptográfica, el algoritmo de intercambio de secretos de Shamir.
Algoritmo de Shamir’s Secret Sharing: Shamir’s Secret Sharing es un algoritmo en criptografía creado por Adi Shamir. El objetivo principal de este algoritmo es dividir el secreto que debe cifrarse en varias partes únicas.
- Digamos que S es el secreto que deseamos codificar.
- Se divide en N partes: S1, S2, S3, …., Sn.
- Después de dividirlo, el usuario elige un número K para descifrar las partes y encontrar el secreto original.
- Se elige de tal manera que si sabemos menos de K partes, entonces no podremos encontrar el secreto S (es decir, el secreto S no se puede reconstruir con (K – 1) partes o menos.
- Si conocemos K o más partes de S1, S2, S3, …., Sn, entonces podemos calcular/reconstruir nuestro código secreto S fácilmente. Esto se denomina convencionalmente esquema de umbral (K, N).
Enfoque: La idea principal detrás del Algoritmo para Compartir el Secreto de Shamir se encuentra detrás del concepto de que para los puntos K dados podemos encontrar una ecuación polinomial con el grado (K – 1).
Ejemplo:
- Para los dos puntos dados, (x1, y1) y (x2, y2) podemos encontrar un polinomio lineal ax + by = c .
- De manera similar, para los tres puntos dados, podemos encontrar un polinomio cuadrático ax 2 + bx + cy = d .
Entonces, la idea es construir un polinomio con el grado (K – 1) tal que el término constante sea el código secreto y los números restantes sean aleatorios y este término constante se pueda encontrar usando cualquier K puntos de N puntos generados a partir de este polinomio utilizando el polinomio base de Lagrange.
Por ejemplo: Sea el código secreto S = 65, N = 4, K = 2.
- Inicialmente, para cifrar el código secreto, construimos un polinomio de grado (K – 1).
- Por lo tanto, sea el polinomio y = a + bx . Aquí, la parte constante ‘a’ es nuestro código secreto.
- Sea b cualquier número aleatorio, digamos b = 15.
- Por lo tanto, para este polinomio y = 65 + 15x, generamos N = 4 puntos a partir de él.
- Sean esos 4 puntos (1, 80), (2, 95), (3, 110), (4, 125). Claramente, podemos generar el polinomio inicial a partir de cualquiera de estos 4 puntos y en el polinomio resultante, el término constante a es el código secreto requerido.
Para reconstruir el polinomio dado, se utiliza el polinomio base de Lagrange .
El concepto principal detrás del polinomio de Lagrange es formar primero las identidades de Lagrange y la suma de estas identidades nos da la función requerida que necesitamos encontrar a partir de los puntos dados. Las siguientes ecuaciones muestran cómo calcularlos:
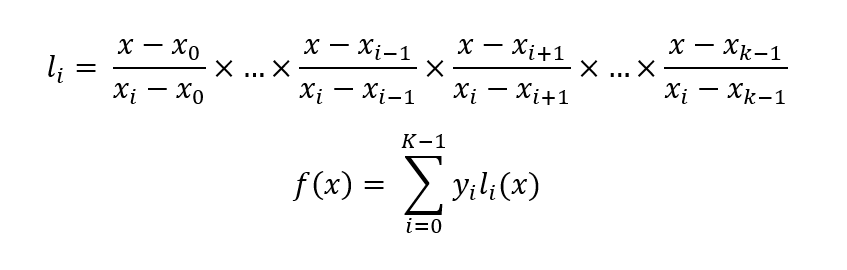
Por ejemplo, digamos que deseamos calcular la ecuación dada usando K = 2 puntos de los cuatro puntos seleccionados: (1, 80), (3, 110). La siguiente ilustración muestra la solución paso a paso para esto:
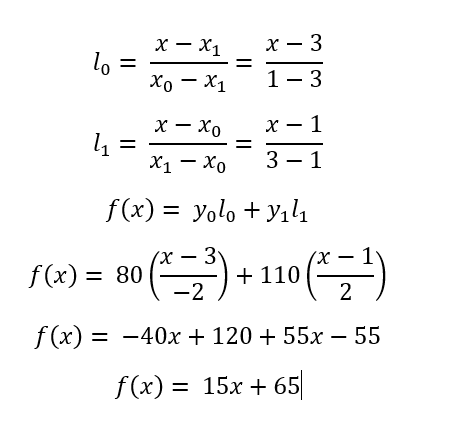
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
CPP
// C++ implementation of shamir’s
// secret sharing algorithm
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate the value
// of y
// y = poly[0] + x*poly[1] + x^2*poly[2] + ...
int calculate_Y(int x, vector<int>& poly)
{
// Initializing y
int y = 0;
int temp = 1;
// Iterating through the array
for (auto coeff : poly) {
// Computing the value of y
y = (y + (coeff * temp));
temp = (temp * x);
}
return y;
}
// Function to perform the secret
// sharing algorithm and encode the
// given secret
void secret_sharing(int S, vector<pair<int, int> >& points,
int N, int K)
{
// A vector to store the polynomial
// coefficient of K-1 degree
vector<int> poly(K);
// Randomly choose K - 1 numbers but
// not zero and poly[0] is the secret
// create polynomial for this
poly[0] = S;
for (int j = 1; j < K; ++j) {
int p = 0;
while (p == 0)
// To keep the random values
// in range not too high
// we are taking mod with a
// prime number around 1000
p = (rand() % 997);
// This is to ensure we did not
// create a polynomial consisting
// of zeroes.
poly[j] = p;
}
// Generating N points from the
// polynomial we created
for (int j = 1; j <= N; ++j) {
int x = j;
int y = calculate_Y(x, poly);
// Points created on sharing
points[j - 1] = { x, y };
}
}
// This structure is used for fraction
// part handling multiplication
// and addition of fraction
struct fraction {
int num, den;
// A fraction consists of a
// numerator and a denominator
fraction(int n, int d)
{
num = n, den = d;
}
// If the fraction is not
// in its reduced form
// reduce it by dividing
// them with their GCD
void reduce_fraction(fraction& f)
{
int gcd = __gcd(f.num, f.den);
f.num /= gcd, f.den /= gcd;
}
// Performing multiplication on the
// fraction
fraction operator*(fraction f)
{
fraction temp(num * f.num, den * f.den);
reduce_fraction(temp);
return temp;
}
// Performing addition on the
// fraction
fraction operator+(fraction f)
{
fraction temp(num * f.den + den * f.num,
den * f.den);
reduce_fraction(temp);
return temp;
}
};
// Function to generate the secret
// back from the given points
// This function will use Lagrange Basis Polynomial
// Instead of finding the complete Polynomial
// We only required the poly[0] as our secret code,
// thus we can get rid of x terms
int Generate_Secret(int x[], int y[], int M)
{
fraction ans(0, 1);
// Loop to iterate through the given
// points
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
// Initializing the fraction
fraction l(y[i], 1);
for (int j = 0; j < M; ++j) {
// Computing the lagrange terms
if (i != j) {
fraction temp(-x[j], x[i] - x[j]);
l = l * temp;
}
}
ans = ans + l;
}
// Return the secret
return ans.num;
}
// Function to encode and decode the
// given secret by using the above
// defined functions
void operation(int S, int N, int K)
{
// Vector to store the points
vector<pair<int, int> > points(N);
// Sharing of secret Code in N parts
secret_sharing(S, points, N, K);
cout << "Secret is divided to " << N
<< " Parts - " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cout << points[i].first << " "
<< points[i].second << endl;
}
cout << "We can generate Secret from any of "
<< K << " Parts" << endl;
// Input any M points from these
// to get back our secret code.
int M = 2;
// M can be greater than or equal to threshold but
// for this example we are taking for threshold
if (M < K) {
cout << "Points are less than threshold "
<< K << " Points Required" << endl;
}
int* x = new int[M];
int* y = new int[M];
// Input M points you will get the secret
// Let these points are first M points from
// the N points which we shared above
// We can take any M points
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
x[i] = points[i].first;
y[i] = points[i].second;
}
// Get back our result again.
cout << "Our Secret Code is : "
<< Generate_Secret(x, y, M) << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int S = 65;
int N = 4;
int K = 2;
operation(S, N, K);
return 0;
}
Secret is divided to 4 Parts - 1 602 2 1139 3 1676 4 2213 We can generate Secret from any of 2 Parts Our Secret Code is : 65
Referencia: Compartir el secreto de Shamir
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por shivamsinghal1012 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA