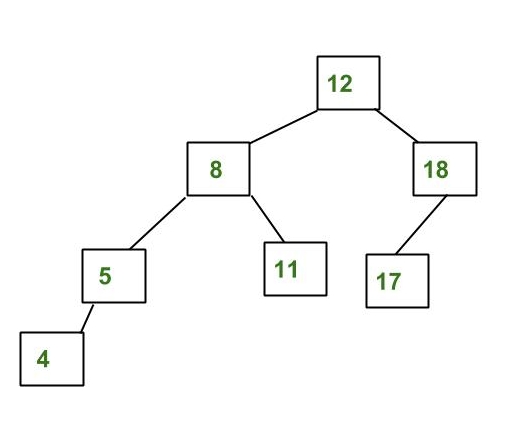
El árbol AVL es un árbol de búsqueda binaria (BST) autoequilibrado donde la diferencia entre las alturas de los subárboles izquierdo y derecho no puede ser más de uno para todos los Nodes.
Un árbol de ejemplo que es un árbol AVL
C++
// C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// An AVL tree node
class Node
{
public:
int key;
Node *left;
Node *right;
int height;
};
// A utility function to get maximum
// of two integers
int max(int a, int b);
// A utility function to get the
// height of the tree
int height(Node *N)
{
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return N->height;
}
// A utility function to get maximum
// of two integers
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b)? a : b;
}
/* Helper function that allocates a
new node with the given key and
NULL left and right pointers. */
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* node = new Node();
node->key = key;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
node->height = 1; // new node is initially
// added at leaf
return(node);
}
// A utility function to right
// rotate subtree rooted with y
// See the diagram given above.
Node *rightRotate(Node *y)
{
Node *x = y->left;
Node *T2 = x->right;
// Perform rotation
x->right = y;
y->left = T2;
// Update heights
y->height = max(height(y->left),
height(y->right)) + 1;
x->height = max(height(x->left),
height(x->right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return x;
}
// A utility function to left
// rotate subtree rooted with x
// See the diagram given above.
Node *leftRotate(Node *x)
{
Node *y = x->right;
Node *T2 = y->left;
// Perform rotation
y->left = x;
x->right = T2;
// Update heights
x->height = max(height(x->left),
height(x->right)) + 1;
y->height = max(height(y->left),
height(y->right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return y;
}
// Get Balance factor of node N
int getBalance(Node *N)
{
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return height(N->left) - height(N->right);
}
// Recursive function to insert a key
// in the subtree rooted with node and
// returns the new root of the subtree.
Node* insert(Node* node, int key)
{
/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */
if (node == NULL)
return(newNode(key));
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else if (key > node->key)
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
else // Equal keys are not allowed in BST
return node;
/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */
node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left),
height(node->right));
/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor
node to check whether this node became
unbalanced */
int balance = getBalance(node);
// If this node becomes unbalanced, then
// there are 4 cases
// Left Left Case
if (balance > 1 && key < node->left->key)
return rightRotate(node);
// Right Right Case
if (balance < -1 && key > node->right->key)
return leftRotate(node);
// Left Right Case
if (balance > 1 && key > node->left->key)
{
node->left = leftRotate(node->left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
// Right Left Case
if (balance < -1 && key < node->right->key)
{
node->right = rightRotate(node->right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// A utility function to print preorder
// traversal of the tree.
// The function also prints height
// of every node
void preOrder(Node *root)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
cout << root->key << " ";
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node *root = NULL;
/* Constructing tree given in
the above figure */
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 25);
/* The constructed AVL Tree would be
30
/ \
20 40
/ \ \
10 25 50
*/
cout << "Preorder traversal of the "
"constructed AVL tree is \n";
preOrder(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by
// rathbhupendra
C
// C program to insert a node in AVL tree
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// An AVL tree node
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node *left;
struct Node *right;
int height;
};
// A utility function to get maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b);
// A utility function to get the height of the tree
int height(struct Node *N)
{
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return 1+max(height(N->left), height(N->right));
}
// A utility function to get maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b)? a : b;
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and
NULL left and right pointers. */
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* node = (struct Node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->key = key;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
node->height = 0; // new node is initially added at leaf
return(node);
}
// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y
// See the diagram given above.
struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y)
{
struct Node *x = y->left;
struct Node *T2 = x->right;
// Perform rotation
x->right = y;
y->left = T2;
// Update heights
y->height = height(y);
x->height = height(x);
// Return new root
return x;
}
// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x
// See the diagram given above.
struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x)
{
struct Node *y = x->right;
struct Node *T2 = y->left;
// Perform rotation
y->left = x;
x->right = T2;
// Update heights
x->height = height(x);
y->height = height(y);
// Return new root
return y;
}
// Get Balance factor of node N
int getBalance(struct Node *N)
{
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return height(N->left) - height(N->right);
}
// Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted
// with node and returns the new root of the subtree.
struct Node* insert(struct Node* node, int key)
{
/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */
if (node == NULL)
return(newNode(key));
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else if (key > node->key)
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
else // Equal keys are not allowed in BST
return node;
/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */
node->height = height(node);
/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor
node to check whether this node became
unbalanced */
int balance = getBalance(node);
// If this node becomes unbalanced, then
// there are 4 cases
// Left Left Case
if (balance > 1 && key < node->left->key)
return rightRotate(node);
// Right Right Case
if (balance < -1 && key > node->right->key)
return leftRotate(node);
// Left Right Case
if (balance > 1 && key > node->left->key)
{
node->left = leftRotate(node->left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
// Right Left Case
if (balance < -1 && key < node->right->key)
{
node->right = rightRotate(node->right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// A utility function to print preorder traversal
// of the tree.
// The function also prints height of every node
void preOrder(struct Node *root)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", root->key);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
struct Node *root = NULL;
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 25);
/* The constructed AVL Tree would be
30
/ \
20 40
/ \ \
10 25 50
*/
printf("Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL"
" tree is \n");
preOrder(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for insertion in AVL Tree
class Node {
int key, height;
Node left, right;
Node(int d) {
key = d;
height = 1;
}
}
class AVLTree {
Node root;
// A utility function to get the height of the tree
int height(Node N) {
if (N == null)
return 0;
return N.height;
}
// A utility function to get maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b) {
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y
// See the diagram given above.
Node rightRotate(Node y) {
Node x = y.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
// Perform rotation
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
// Update heights
y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1;
x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return x;
}
// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x
// See the diagram given above.
Node leftRotate(Node x) {
Node y = x.right;
Node T2 = y.left;
// Perform rotation
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
// Update heights
x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1;
y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return y;
}
// Get Balance factor of node N
int getBalance(Node N) {
if (N == null)
return 0;
return height(N.left) - height(N.right);
}
Node insert(Node node, int key) {
/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */
if (node == null)
return (new Node(key));
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
else // Duplicate keys not allowed
return node;
/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */
node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left),
height(node.right));
/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor
node to check whether this node became
unbalanced */
int balance = getBalance(node);
// If this node becomes unbalanced, then there
// are 4 cases Left Left Case
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key)
return rightRotate(node);
// Right Right Case
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key)
return leftRotate(node);
// Left Right Case
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key) {
node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
// Right Left Case
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key) {
node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// A utility function to print preorder traversal
// of the tree.
// The function also prints height of every node
void preOrder(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25);
/* The constructed AVL Tree would be
30
/ \
20 40
/ \ \
10 25 50
*/
System.out.println("Preorder traversal" +
" of constructed tree is : ");
tree.preOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
Python3
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree
# Generic tree node class
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.height = 1
# AVL tree class which supports the
# Insert operation
class AVL_Tree(object):
# Recursive function to insert key in
# subtree rooted with node and returns
# new root of subtree.
def insert(self, root, key):
# Step 1 - Perform normal BST
if not root:
return TreeNode(key)
elif key < root.val:
root.left = self.insert(root.left, key)
else:
root.right = self.insert(root.right, key)
# Step 2 - Update the height of the
# ancestor node
root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left),
self.getHeight(root.right))
# Step 3 - Get the balance factor
balance = self.getBalance(root)
# Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced,
# then try out the 4 cases
# Case 1 - Left Left
if balance > 1 and key < root.left.val:
return self.rightRotate(root)
# Case 2 - Right Right
if balance < -1 and key > root.right.val:
return self.leftRotate(root)
# Case 3 - Left Right
if balance > 1 and key > root.left.val:
root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left)
return self.rightRotate(root)
# Case 4 - Right Left
if balance < -1 and key < root.right.val:
root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right)
return self.leftRotate(root)
return root
def leftRotate(self, z):
y = z.right
T2 = y.left
# Perform rotation
y.left = z
z.right = T2
# Update heights
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
# Return the new root
return y
def rightRotate(self, z):
y = z.left
T3 = y.right
# Perform rotation
y.right = z
z.left = T3
# Update heights
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
# Return the new root
return y
def getHeight(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return root.height
def getBalance(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right)
def preOrder(self, root):
if not root:
return
print("{0} ".format(root.val), end="")
self.preOrder(root.left)
self.preOrder(root.right)
# Driver program to test above function
myTree = AVL_Tree()
root = None
root = myTree.insert(root, 10)
root = myTree.insert(root, 20)
root = myTree.insert(root, 30)
root = myTree.insert(root, 40)
root = myTree.insert(root, 50)
root = myTree.insert(root, 25)
"""The constructed AVL Tree would be
30
/ \
20 40
/ \ \
10 25 50"""
# Preorder Traversal
print("Preorder traversal of the",
"constructed AVL tree is")
myTree.preOrder(root)
print()
# This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathak
C#
// C# program for insertion in AVL Tree
using System;
class Node
{
public int key, height;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int d)
{
key = d;
height = 1;
}
}
public class AVLTree
{
Node root;
// A utility function to get
// the height of the tree
int height(Node N)
{
if (N == null)
return 0;
return N.height;
}
// A utility function to get
// maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
// A utility function to right
// rotate subtree rooted with y
// See the diagram given above.
Node rightRotate(Node y)
{
Node x = y.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
// Perform rotation
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
// Update heights
y.height = max(height(y.left),
height(y.right)) + 1;
x.height = max(height(x.left),
height(x.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return x;
}
// A utility function to left
// rotate subtree rooted with x
// See the diagram given above.
Node leftRotate(Node x)
{
Node y = x.right;
Node T2 = y.left;
// Perform rotation
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
// Update heights
x.height = max(height(x.left),
height(x.right)) + 1;
y.height = max(height(y.left),
height(y.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return y;
}
// Get Balance factor of node N
int getBalance(Node N)
{
if (N == null)
return 0;
return height(N.left) - height(N.right);
}
Node insert(Node node, int key)
{
/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */
if (node == null)
return (new Node(key));
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
else // Duplicate keys not allowed
return node;
/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */
node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left),
height(node.right));
/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor
node to check whether this node became
unbalanced */
int balance = getBalance(node);
// If this node becomes unbalanced, then there
// are 4 cases Left Left Case
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key)
return rightRotate(node);
// Right Right Case
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key)
return leftRotate(node);
// Left Right Case
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key)
{
node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
// Right Left Case
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key)
{
node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// A utility function to print preorder traversal
// of the tree.
// The function also prints height of every node
void preOrder(Node node)
{
if (node != null)
{
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25);
/* The constructed AVL Tree would be
30
/ \
20 40
/ \ \
10 25 50
*/
Console.Write("Preorder traversal" +
" of constructed tree is : ");
tree.preOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed
// by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree
class Node {
constructor(d) {
this.key = d;
this.height = 1;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class AVLTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
// A utility function to get
// the height of the tree
height(N) {
if (N == null) return 0;
return N.height;
}
// A utility function to get
// maximum of two integers
max(a, b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
// A utility function to right
// rotate subtree rooted with y
// See the diagram given above.
rightRotate(y) {
var x = y.left;
var T2 = x.right;
// Perform rotation
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
// Update heights
y.height = this.max(this.height(y.left),
this.height(y.right)) + 1;
x.height = this.max(this.height(x.left),
this.height(x.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return x;
}
// A utility function to left
// rotate subtree rooted with x
// See the diagram given above.
leftRotate(x) {
var y = x.right;
var T2 = y.left;
// Perform rotation
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
// Update heights
x.height = this.max(this.height(x.left),
this.height(x.right)) + 1;
y.height = this.max(this.height(y.left),
this.height(y.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return y;
}
// Get Balance factor of node N
getBalance(N) {
if (N == null) return 0;
return this.height(N.left) - this.height(N.right);
}
insert(node, key) {
/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */
if (node == null) return new Node(key);
if (key < node.key)
node.left = this.insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = this.insert(node.right, key);
// Duplicate keys not allowed
else return node;
/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */
node.height =
1 + this.max(this.height(node.left),
this.height(node.right));
/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor
node to check whether this node became
unbalanced */
var balance = this.getBalance(node);
// If this node becomes unbalanced, then there
// are 4 cases Left Left Case
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key)
return this.rightRotate(node);
// Right Right Case
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key)
return this.leftRotate(node);
// Left Right Case
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key) {
node.left = this.leftRotate(node.left);
return this.rightRotate(node);
}
// Right Left Case
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key) {
node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right);
return this.leftRotate(node);
}
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// A utility function to print preorder traversal
// of the tree.
// The function also prints height of every node
preOrder(node) {
if (node != null) {
document.write(node.key + " ");
this.preOrder(node.left);
this.preOrder(node.right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
var tree = new AVLTree();
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25);
/* The constructed AVL Tree would be
30
/ \
20 40
/ \ \
10 25 50
*/
document.write(
"Preorder traversal of the " + "constructed AVL tree is <br>"
);
tree.preOrder(tree.root);
</script>
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA