En la publicación anterior , se realiza BFS solo con un vértice en particular, es decir, se supone que todos los vértices son accesibles desde el vértice inicial. Pero en el caso de un grafo desconectado o cualquier vértice inalcanzable desde todos los vértices, la implementación anterior no dará el resultado deseado, por lo que en esta publicación se realiza una modificación en BFS.
Todos los vértices son alcanzables. Entonces, para el gráfico anterior, BFS simple funcionará.
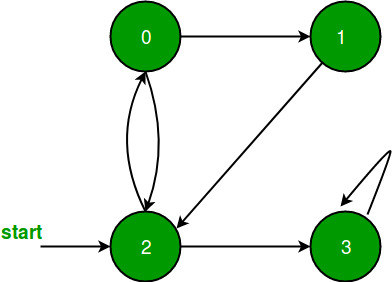
Como en el gráfico anterior, el vértice 1 es inalcanzable desde todos los vértices, por lo que BFS simple no funcionaría para él.
Just to modify BFS, perform simple BFS from each unvisited vertex of given graph.
El siguiente es el código cuando se usa la representación de array de adyacencia para el gráfico.
C++
// C++ implementation of modified BFS for adjacency matrix
// representation
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
void printBFS(int** edges, int V, int start, int* visited);
void BFSHelper(int** edges, int V);
void addEdge(int** edges, int f, int s);
void addEdge(int** edges, int f, int s) { edges[f][s] = 1; }
void printBFS(int** edges, int V, int start, int* visited)
{
if (V == 0)
return;
queue<int> BFS;
BFS.push(start);
visited[start] = 1;
while (!BFS.empty()) {
int data = BFS.front();
BFS.pop();
cout << data << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (edges[data][i] == 1) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
BFS.push(i);
visited[i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
void BFSHelper(int** edges, int V)
{
if (V == 0)
return;
int* visited = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
visited[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
printBFS(edges, V, i, visited);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int V = 5;
int E = 6;
if (E == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
cout << i << " ";
}
return 0;
}
int** edges = new int*[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
edges[i] = new int[V];
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
edges[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addEdge(edges, 0, 4);
addEdge(edges, 1, 2);
addEdge(edges, 1, 3);
addEdge(edges, 1, 4);
addEdge(edges, 2, 3);
addEdge(edges, 3, 4);
BFSHelper(edges, V);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of modified BFS for adjacency matrix
// representation
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void addEdge(int[][] edges, int f, int s)
{
edges[f][s] = 1;
}
static void printBFS(int[][] edges, int V, int start,
int[] visited)
{
if (V == 0)
return;
Queue<Integer> BFS = new LinkedList<Integer>();
BFS.add(start);
visited[start] = 1;
while (!BFS.isEmpty()) {
int data = BFS.poll();
System.out.print(data + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (edges[data][i] == 1) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
BFS.add(i);
visited[i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
static void bfsHelper(int[][] edges, int V)
{
if (V == 0)
return;
int[] visited = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
visited[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
printBFS(edges, V, i, visited);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int V = 5;
int E = 6;
if (E == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.exit(0);
}
int[][] edges = new int[V][V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
edges[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addEdge(edges, 0, 4);
addEdge(edges, 1, 2);
addEdge(edges, 1, 3);
addEdge(edges, 1, 4);
addEdge(edges, 2, 3);
addEdge(edges, 3, 4);
bfsHelper(edges, V);
}
}
// This code is contributed by cavi4762.
C#
// C# implementation of modified BFS for adjacency matrix
// representation
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Gfg {
static void AddEdge(int[, ] edges, int f, int s)
{
edges[f, s] = 1;
}
static void PrintBFS(int[, ] edges, int V, int start,
int[] visited)
{
if (V == 0)
return;
Queue<int> BFS = new Queue<int>();
BFS.Enqueue(start);
visited[start] = 1;
while (BFS.Count > 0) {
int data = BFS.Dequeue();
Console.Write(data + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (edges[data, i] == 1) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
BFS.Enqueue(i);
visited[i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
static void BFSHelper(int[, ] edges, int V)
{
if (V == 0)
return;
int[] visited = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
visited[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
PrintBFS(edges, V, i, visited);
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int V = 5;
int E = 6;
if (E == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Environment.Exit(0);
}
int[, ] edges = new int[V, V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
edges[i, j] = 0;
}
}
AddEdge(edges, 0, 4);
AddEdge(edges, 1, 2);
AddEdge(edges, 1, 3);
AddEdge(edges, 1, 4);
AddEdge(edges, 2, 3);
AddEdge(edges, 3, 4);
BFSHelper(edges, V);
}
}
// This code is contributed by cavi4762.
0 4 1 2 3
El siguiente es el código cuando se usa la representación de lista de adyacencia para el gráfico.
C++
// C++ implementation of modified BFS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A utility function to add an edge in an
// directed graph.
void addEdge(vector<int> adj[], int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
}
// A utility function to do BFS of graph
// from a given vertex u.
void BFSUtil(int u, vector<int> adj[],
vector<bool> &visited)
{
// Create a queue for BFS
list<int> q;
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
visited[u] = true;
q.push_back(u);
// 'i' will be used to get all adjacent vertices 4
// of a vertex list<int>::iterator i;
while(!q.empty())
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
u = q.front();
cout << u << " ";
q.pop_front();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex s. If an adjacent has not been visited,
// then mark it visited and enqueue it
for (int i = 0; i != adj[u].size(); ++i)
{
if (!visited[adj[u][i]])
{
visited[adj[u][i]] = true;
q.push_back(adj[u][i]);
}
}
}
}
// This function does BFSUtil() for all
// unvisited vertices.
void BFS(vector<int> adj[], int V)
{
vector<bool> visited(V, false);
for (int u=0; u<V; u++)
if (visited[u] == false)
BFSUtil(u, adj, visited);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int V = 5;
vector<int> adj[V];
addEdge(adj, 0, 4);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 4);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
BFS(adj, V);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of modified BFS
import java.util.*;
public class graph
{
//Implementing graph using HashMap
static HashMap<Integer,LinkedList<Integer>> graph=new HashMap<>();
//utility function to add edge in an undirected graph
public static void addEdge(int a,int b)
{
if(graph.containsKey(a))
{
LinkedList<Integer> l=graph.get(a);
l.add(b);
graph.put(a,l);
}
else
{
LinkedList<Integer> l=new LinkedList<>();
l.add(b);
graph.put(a,l);
}
}
//Helper function for BFS
public static void bfshelp(int s,ArrayList<Boolean> visited)
{
// Create a queue for BFS
LinkedList<Integer> q=new LinkedList<>();
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
q.add(s);
visited.set(s,true);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
int f=q.poll();
System.out.print(f+" ");
//Check whether the current node is
//connected to any other node or not
if(graph.containsKey(f))
{
Iterator<Integer> i=graph.get(f).listIterator();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex f. If an adjacent has not been visited,
// then mark it visited and enqueue it
while(i.hasNext())
{
int n=i.next();
if(!visited.get(n))
{
visited.set(n,true);
q.add(n);
}
}
}
}
}
//BFS function to check each node
public static void bfs(int vertex)
{
ArrayList<Boolean> visited=new ArrayList<Boolean>();
//Marking each node as unvisited
for(int i=0;i<vertex;i++)
{
visited.add(i,false);
}
for(int i=0;i<vertex;i++)
{
//Checking whether the node is visited or not
if(!visited.get(i))
{
bfshelp(i,visited);
}
}
}
//Driver Code-The main function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int v=5;
addEdge(0, 4);
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(3, 4);
bfs(v);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 implementation of modified BFS import queue # A utility function to add an edge # in an undirected graph. def addEdge(adj, u, v): adj[u].append(v) # A utility function to do BFS of # graph from a given vertex u. def BFSUtil(u, adj, visited): # Create a queue for BFS q = queue.Queue() # Mark the current node as visited # and enqueue it visited[u] = True q.put(u) # 'i' will be used to get all adjacent # vertices 4 of a vertex list<int>::iterator i while(not q.empty()): # Dequeue a vertex from queue # and print it u = q.queue[0] print(u, end = " ") q.get() # Get all adjacent vertices of the # dequeued vertex s. If an adjacent # has not been visited, then mark # it visited and enqueue it i = 0 while i != len(adj[u]): if (not visited[adj[u][i]]): visited[adj[u][i]] = True q.put(adj[u][i]) i += 1 # This function does BFSUtil() for all # unvisited vertices. def BFS(adj, V): visited = [False] * V for u in range(V): if (visited[u] == False): BFSUtil(u, adj, visited) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': V = 5 adj = [[] for i in range(V)] addEdge(adj, 0, 4) addEdge(adj, 1, 2) addEdge(adj, 1, 3) addEdge(adj, 1, 4) addEdge(adj, 2, 3) addEdge(adj, 3, 4) BFS(adj, V) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# implementation of modified BFS
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Graph
{
//Implementing graph using Dictionary
static Dictionary<int,List<int>> graph =
new Dictionary<int,List<int>>();
//utility function to add edge in an undirected graph
public static void addEdge(int a, int b)
{
if(graph.ContainsKey(a))
{
List<int> l = graph[a];
l.Add(b);
if(graph.ContainsKey(a))
graph[a] = l;
else
graph.Add(a,l);
}
else
{
List<int> l = new List<int>();
l.Add(b);
graph.Add(a, l);
}
}
// Helper function for BFS
public static void bfshelp(int s, List<Boolean> visited)
{
// Create a queue for BFS
List<int> q = new List<int>();
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
q.Add(s);
visited.RemoveAt(s);
visited.Insert(s,true);
while(q.Count != 0)
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
int f = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
Console.Write(f + " ");
//Check whether the current node is
//connected to any other node or not
if(graph.ContainsKey(f))
{
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex f. If an adjacent has not been visited,
// then mark it visited and enqueue it
foreach(int iN in graph[f])
{
int n = iN;
if(!visited[n])
{
visited.RemoveAt(n);
visited.Insert(n, true);
q.Add(n);
}
}
}
}
}
// BFS function to check each node
public static void bfs(int vertex)
{
List<Boolean> visited = new List<Boolean>();
// Marking each node as unvisited
for(int i = 0; i < vertex; i++)
{
visited.Insert(i, false);
}
for(int i = 0; i < vertex; i++)
{
// Checking whether the node is visited or not
if(!visited[i])
{
bfshelp(i, visited);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int v = 5;
addEdge(0, 4);
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(3, 4);
bfs(v);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
0 4 1 2 3
Este artículo es una contribución de Sahil Chhabra (akku) . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
