Recorrido de búsqueda primero en amplitud de un gráfico utilizando el algoritmo proporcionado en el libro CLRS .
BFS es una de las formas de recorrer un gráfico. Se llama así porque expande la frontera entre los vértices descubiertos y no descubiertos uniformemente a lo largo de la frontera. Lo que significa es que el algoritmo primero descubre todos los vértices conectados a «u» a una distancia de k antes de descubrir los vértices a una distancia de k+1 de u. El algoritmo proporcionado en CLRS utiliza el concepto de «color» para verificar si un vértice se descubre total o parcialmente o no se descubre. También mantiene un registro de la distancia entre un vértice u y la fuente s.
BFS(G,s)
1 for each vertex u in G.V - {s}
2 u.color = white
3 u.d = INF
4 u.p = NIL
5 s.color = green
6 s.d = 0
7 s.p = NIL
8 Q = NULL
9 ENQUEUE(Q,s)
10 while Q != NULL
11 u = DEQUEUE(Q)
12 for each v in G.Adj[u]
13 if v.color == white
14 v.color = green
15 v.d = u.d + 1
16 v.p = u
17 ENQUEUE(Q,v)
18 u.color = dark_green
Produce un «árbol primero en anchura» con raíz s que contiene todos los vértices alcanzables. Tomemos un gráfico dirigido simple y veamos cómo lo atraviesa BFS.
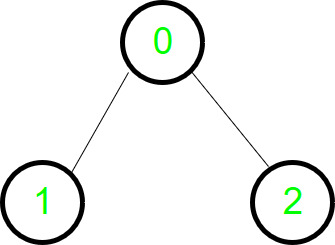
La gráfica
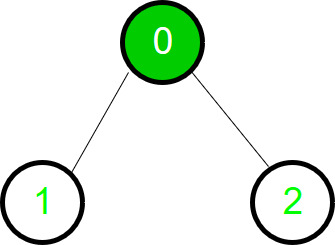
Comienzo del recorrido
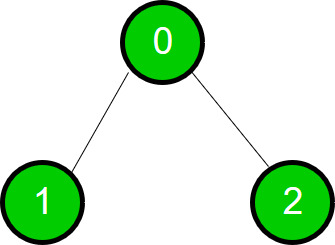
1er recorrido
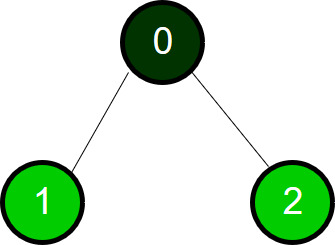
1er recorrido completo
C++
// CPP program to implement BFS as per CLRS
// algorithm.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Declaring the vectors to store color, distance
// and parent
vector<string> colour;
vector<int> d;
vector<int> p;
/* This function adds an edge to the graph.
It is an undirected graph. So edges are
added for both the nodes. */
void addEdge(vector <int> g[], int u, int v)
{
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
/* This function does the Breadth First Search*/
void BFSSingleSource(vector <int> g[], int s)
{
// The Queue used for the BFS operation
queue<int> q;
// Pushing the root node inside the queue
q.push(s);
/* Distance of root node is 0 & colour
is gray as it is visited partially now */
d[s] = 0;
colour[s] = "green";
/* Loop to traverse the graph. Traversal
will happen traverse until the queue is
not empty.*/
while (!q.empty())
{
/* Extracting the front element(node)
and popping it out of queue. */
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << u << " ";
/* This loop traverses all the child nodes of u */
for (auto i = g[u].begin(); i != g[u].end(); i++)
{
/* If the colour is white then the said node
is not traversed. */
if (colour[*i] == "white")
{
colour[*i] = "green";
d[*i] = d[u] + 1;
p[*i] = u;
/* Pushing the node inside queue
to traverse its children. */
q.push(*i);
}
}
/* Now the node u is completely traversed
and colour is changed to black. */
colour[u] = "dark_green";
}
}
void BFSFull(vector <int> g[], int n)
{
/* Initially all nodes are not traversed.
Therefore, the colour is white. */
colour.assign(n, "white");
d.assign(n, 0);
p.assign(n, -1);
// Calling BFSSingleSource() for all white
// vertices.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (colour[i] == "white")
BFSSingleSource(g, i);
}
// Driver Function
int main()
{
// Graph with 7 nodes and 6 edges.
int n = 7;
// The Graph vector
vector <int> g[n];
addEdge(g, 0, 1);
addEdge(g, 0, 2);
addEdge(g, 1, 3);
addEdge(g, 1, 4);
addEdge(g, 2, 5);
addEdge(g, 2, 6);
BFSFull(g, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to implement BFS as per CLRS
// algorithm.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Graph {
private int V;
private LinkedList<Integer>[] g;
// Declaring the arrays to store color, distance
// and parent
String[] colour;
int[] d, p;
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
g = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++)
g[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
}
// This function does the Breadth First Search
void BFSSingleSource(int s)
{
// The Queue used for the BFS operation
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Pushing the root node inside the queue
q.add(s);
/* Distance of root node is 0 & colour
is gray as it is visited partially now */
d[s] = 0;
colour[s] = "green";
/* Loop to traverse the graph. Traversal
will happen traverse until the queue is
not empty.*/
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
/* Extracting the front element(node)
and popping it out of queue. */
int u = q.poll();
System.out.print(u + " ");
/* This loop traverses all the child nodes of u
*/
for (int i : g[u]) {
/* If the colour is white then the said node
is not traversed. */
if (colour[i] == "white") {
colour[i] = "green";
d[i] = d[u] + 1;
p[i] = u;
/* Pushing the node inside queue
to traverse its children. */
q.add(i);
}
}
/* Now the node u is completely traversed
and colour is changed to black. */
colour[u] = "dark_green";
}
System.out.println();
}
void BFSFull(int n)
{
/* Initially all nodes are not traversed.
Therefore, the colour is white. */
colour = new String[n];
d = new int[n];
p = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(colour, "white");
Arrays.fill(d, 0);
Arrays.fill(p, -1);
// Calling BFSSingleSource() for all white
// vertices.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (colour[i] == "white")
BFSSingleSource(i);
}
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 7;
Graph g = new Graph(n);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 4);
g.addEdge(2, 5);
g.addEdge(2, 6);
g.BFSFull(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by cavi4762.
Python3
# Python3 program to implement BFS as # per CLRS algorithm. import queue # This function adds an edge to the graph. # It is an undirected graph. So edges # are added for both the nodes. def addEdge(g, u, v): g[u].append(v) g[v].append(u) # This function does the Breadth # First Search def BFSSingleSource(g, s): # The Queue used for the BFS operation q = queue.Queue() # Pushing the root node inside # the queue q.put(s) # Distance of root node is 0 & colour is # gray as it is visited partially now d[s] = 0 colour[s] = "green" # Loop to traverse the graph. Traversal # will happen traverse until the queue # is not empty. while (not q.empty()): # Extracting the front element(node) # and popping it out of queue. u = q.get() print(u, end = " ") # This loop traverses all the child # nodes of u i = 0 while i < len(g[u]): # If the colour is white then # the said node is not traversed. if (colour[g[u][i]] == "white"): colour[g[u][i]] = "green" d[g[u][i]] = d[u] + 1 p[g[u][i]] = u # Pushing the node inside queue # to traverse its children. q.put(g[u][i]) i += 1 # Now the node u is completely traversed # and colour is changed to black. colour[u] = "dark_green" def BFSFull(g, n): # Initially all nodes are not traversed. # Therefore, the colour is white. colour = ["white"] * n d = [0] * n p = [-1] * n # Calling BFSSingleSource() for all # white vertices for i in range(n): if (colour[i] == "white"): BFSSingleSource(g, i) # Driver Code # Graph with 7 nodes and 6 edges. n = 7 # Declaring the vectors to store color, # distance and parent colour = [None] * n d = [None] * n p = [None] * n # The Graph vector g = [[] for i in range(n)] addEdge(g, 0, 1) addEdge(g, 0, 2) addEdge(g, 1, 3) addEdge(g, 1, 4) addEdge(g, 2, 5) addEdge(g, 2, 6) BFSFull(g, n) # This code is contributed by Pranchalk
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to implement BFS as per CLRS
// algorithm.
// Declaring the vectors to store color, distance
// and parent
var colour = [];
var d = [];
var p = [];
/* This function adds an edge to the graph.
It is an undirected graph. So edges are
added for both the nodes. */
function addEdge(g, u, v)
{
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
/* This function does the Breadth First Search*/
function BFSSingleSource(g, s)
{
// The Queue used for the BFS operation
var q = [];
// Pushing the root node inside the queue
q.push(s);
/* Distance of root node is 0 & colour
is gray as it is visited partially now */
d[s] = 0;
colour[s] = "green";
/* Loop to traverse the graph. Traversal
will happen traverse until the queue is
not empty.*/
while (q.length!=0)
{
/* Extracting the front element(node)
and popping it out of queue. */
var u = q[0];
q.shift();
document.write( u + " ");
/* This loop traverses all the child nodes of u */
for(var i of g[u])
{
/* If the colour is white then the said node
is not traversed. */
if (colour[i] == "white")
{
colour[i] = "green";
d[i] = d[u] + 1;
p[i] = u;
/* Pushing the node inside queue
to traverse its children. */
q.push(i);
}
}
/* Now the node u is completely traversed
and colour is changed to black. */
colour[u] = "dark_green";
}
}
function BFSFull(g, n)
{
/* Initially all nodes are not traversed.
Therefore, the colour is white. */
colour = Array(n).fill("white");
d = Array(n).fill(0);
p = Array(n).fill(0);
// Calling BFSSingleSource() for all white
// vertices.
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (colour[i] == "white")
BFSSingleSource(g, i);
}
// Driver Function
// Graph with 7 nodes and 6 edges.
var n = 7;
// The Graph vector
var g = Array.from(Array(n), ()=>Array());
addEdge(g, 0, 1);
addEdge(g, 0, 2);
addEdge(g, 1, 3);
addEdge(g, 1, 4);
addEdge(g, 2, 5);
addEdge(g, 2, 6);
BFSFull(g, n);
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.
</script>
Producción:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por shubhamrath y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA