Dada una array arr[] de N elementos, la tarea es escribir una función para buscar un elemento dado x en arr[] .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {10, 20, 80, 30, 60, 50,110, 100, 130, 170}, x = 110;
Salida: 6
Explicación: El elemento x está presente en el índice 6Entrada: arr[] = {10, 20, 80, 30, 60, 50,110, 100, 130, 170}, x = 175;
Salida: -1
Explicación: El elemento x no está presente en arr[].
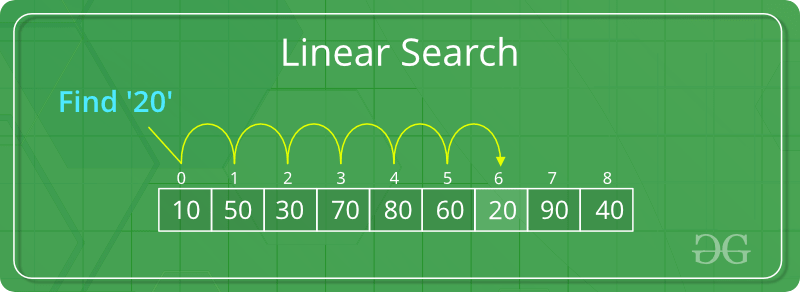
Acercarse:
Itere de 0 a N-1 y compare el valor de cada índice con la clave si coinciden con el índice de retorno, si el bucle termina, devuelva -1 .
Siga los pasos a continuación para implementar el enfoque anterior:
- Comience desde el elemento más a la izquierda de arr[] y compare x uno por uno con cada elemento de arr[]
- Si x coincide con un elemento, devuelve el índice.
- Si x no coincide con ninguno de los elementos, devuelve -1 .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ code to linearly search x in arr[]. If x
// is present then return its location, otherwise
// return -1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int search(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Driver code
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
int result = search(arr, n, x);
(result == -1)
? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
C
// C code to linearly search x in arr[]. If x
// is present then return its location, otherwise
// return -1
#include <stdio.h>
int search(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Driver code
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
int result = search(arr, n, x);
(result == -1)
? printf("Element is not present in array")
: printf("Element is present at index %d", result);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code for linearly searching x in arr[]. If x
// is present then return its location, otherwise
// return -1
class GFG
{
public static int search(int arr[], int x)
{
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
// Function call
int result = search(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.print(
"Element is not present in array");
else
System.out.print("Element is present at index "
+ result);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 code to linearly search x in arr[].
# If x is present then return its location,
# otherwise return -1
def search(arr, n, x):
for i in range(0, n):
if (arr[i] == x):
return i
return -1
# Driver Code
arr = [2, 3, 4, 10, 40]
x = 10
n = len(arr)
# Function call
result = search(arr, n, x)
if(result == -1):
print("Element is not present in array")
else:
print("Element is present at index", result)
C#
// C# code to linearly search x in arr[]. If x
// is present then return its location, otherwise
// return -1
using System;
class GFG {
public static int search(int[] arr, int x)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
// Function call
int result = search(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
Console.WriteLine(
"Element is not present in array");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element is present at index "
+ result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by DrRoot_
PHP
<?php
// PHP code for linearly search x in arr[].
// If x is present then return its location,
// otherwise return -1
function search($arr, $x)
{
$n = sizeof($arr);
for($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
{
if($arr[$i] == $x)
return $i;
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
$x = 10;
// Function call
$result = search($arr, $x);
if($result == -1)
echo "Element is not present in array";
else
echo "Element is present at index " ,
$result;
// This code is contributed
// by jit_t
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript code to linearly search x in arr[]. If x
// is present then return its location, otherwise
// return -1
function search(arr, n, x)
{
let i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ];
let x = 10;
let n = arr.length;
// Function call
let result = search(arr, n, x);
(result == -1)
? document.write("Element is not present in array")
: document.write("Element is present at index " + result);
// This code is contributed by Manoj
</script>
Element is present at index 3
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
La búsqueda lineal rara vez se usa en la práctica porque otros algoritmos de búsqueda, como el algoritmo de búsqueda binaria y las tablas hash, permiten una búsqueda significativamente más rápida en comparación con la búsqueda lineal.
Mejore la complejidad del peor de los casos de búsqueda lineal:
- Si el elemento encontrado en el último O (N) a O (1).
- Es lo mismo que el método anterior porque aquí estamos realizando operaciones ‘if’ de dos pasos en una iteración del ciclo y en el último método realizamos solo 1 operación ‘if’. Esto hace que ambas complejidades temporales sean iguales.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++14
// C++ program for linear search
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void search(vector<int> arr, int search_Element)
{
int left = 0;
int length = arr.size();
int position = -1;
int right = length - 1;
// Run loop from 0 to right
for(left = 0; left <= right;)
{
// If search_element is found with
// left variable
if (arr[left] == search_Element)
{
position = left;
cout << "Element found in Array at "
<< position + 1 << " Position with "
<< left + 1 << " Attempt";
break;
}
// If search_element is found with
// right variable
if (arr[right] == search_Element)
{
position = right;
cout << "Element found in Array at "
<< position + 1 << " Position with "
<< length - right << " Attempt";
break;
}
left++;
right--;
}
// If element not found
if (position == -1)
cout << "Not found in Array with "
<< left << " Attempt";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector<int> arr{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int search_element = 5;
// Function call
search(arr, search_element);
}
// This code is contributed by mayanktyagi1709
Java
// Java program for linear search
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
public static void search(int arr[], int search_Element)
{
int left = 0;
int length = arr.length;
int right = length - 1;
int position = -1;
// run loop from 0 to right
for (left = 0; left <= right;)
{
// if search_element is found with left variable
if (arr[left] == search_Element)
{
position = left;
System.out.println(
"Element found in Array at "
+ (position + 1) + " Position with "
+ (left + 1) + " Attempt");
break;
}
// if search_element is found with right variable
if (arr[right] == search_Element)
{
position = right;
System.out.println(
"Element found in Array at "
+ (position + 1) + " Position with "
+ (length - right) + " Attempt");
break;
}
left++;
right--;
}
// if element not found
if (position == -1)
System.out.println("Not found in Array with "
+ left + " Attempt");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int search_element = 5;
// Function call
search(arr,search_element);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program for linear search
def search(arr, search_Element):
left = 0
length = len(arr)
position = -1
right = length - 1
# Run loop from 0 to right
for left in range(0, right, 1):
# If search_element is found with
# left variable
if (arr[left] == search_Element):
position = left
print("Element found in Array at ", position +
1, " Position with ", left + 1, " Attempt")
break
# If search_element is found with
# right variable
if (arr[right] == search_Element):
position = right
print("Element found in Array at ", position + 1,
" Position with ", length - right, " Attempt")
break
left += 1
right -= 1
# If element not found
if (position == -1):
print("Not found in Array with ", left, " Attempt")
# Driver code
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
search_element = 5
# Function call
search(arr, search_element)
# This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.
C#
// C# program for linear search
using System;
class GFG
{
public static void search(int []arr,
int search_Element)
{
int left = 0;
int length = arr.Length;
int right = length - 1;
int position = -1;
// run loop from 0 to right
for (left = 0; left <= right;)
{
// if search_element is found with left variable
if (arr[left] == search_Element)
{
position = left;
Console.WriteLine(
"Element found in Array at "
+ (position + 1) + " Position with "
+ (left + 1) + " Attempt");
break;
}
// if search_element is found with right variable
if (arr[right] == search_Element)
{
position = right;
Console.WriteLine(
"Element found in Array at "
+ (position + 1) + " Position with "
+ (length - right) + " Attempt");
break;
}
left++;
right--;
}
// if element not found
if (position == -1)
Console.WriteLine("Not found in Array with "
+ left + " Attempt");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int search_element = 5;
// Function call
search(arr,search_element);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for linear search
function search(arr, search_Element)
{
let left = 0;
let length = arr.length;
let right = length - 1;
let position = -1;
// Run loop from 0 to right
for(left = 0; left <= right;)
{
// If search_element is found
// with left variable
if (arr[left] == search_Element)
{
position = left;
document.write(
"Element found in Array at " +
(position + 1) + " Position with " +
(left + 1) + " Attempt");
break;
}
// If search_element is found
// with right variable
if (arr[right] == search_Element)
{
position = right;
document.write(
"Element found in Array at " +
(position + 1) + " Position with " +
(length - right) + " Attempt");
break;
}
left++;
right--;
}
// If element not found
if (position == -1)
document.write("Not found in Array with " +
left + " Attempt");
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
let search_element = 5;
// Function call
search(arr, search_element);
// This code is contributed by code_hunt
</script>
Element found in Array at 5 Position with 1 Attempt
Complejidad temporal: O(n)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Otro método: enfoque recursivo para búsqueda lineal
Acercarse:
- Si el tamaño de la array es cero, devuelve -1 representación de que no se encuentra el elemento. Esto también se puede tratar como la condición base de una llamada recursiva).
- De lo contrario, compruebe si el elemento en el índice actual de la array es igual a la clave o no, es decir, arr[tamaño – 1] == clave.
- =Si es igual, devuelve el índice de la clave encontrada.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++14
// Recursive Code For Linear Search
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int linearsearch(int arr[], int size, int key)
{
if (size == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (arr[size - 1] == key) {
// Return the index of found key.
return size - 1;
}
else {
int ans = linearsearch(arr, size - 1, key);
return ans;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[5] = { 5, 15, 6, 9, 4 };
int key = 4;
int ans = linearsearch(arr, 5, key);
if (ans == -1) {
cout << "The element " << key << " is not found."
<< endl;
}
else {
cout << "The element " << key << " is found at "
<< ans << " index of the given array." << endl;
}
return 0;
}
// Code contributed by pragatikohli
Python3
"""Python Program to Implement Linear Search Recursively"""
def linear_search(arr, key, size):
# If the array is empty we will return -1
if size == 0:
return -1
# Otherwise if the array consists of only one element and that element is not the one
# we are searching for then it will also return -1
elif size == 1 and arr[0] != key:
return -1
# ELse , if the element at the size index is same as the element we are searching for
# Then return the size. This will return the index position is 0 index manner.
# i.e if the element is present at 6th position it will return 5.
# To get the exact position in human readble format (counting starts from 1 not 0)
# Then just return size + 1
elif arr[size] == key:
return size
# If none of the conditions are True then in else condition we will call the
# function recursively by decreasing the size by 1 each time.
else:
return linear_search(arr, key, size-1)
arr = [5, 15, 6, 9, 4]
key = 4
size = len(arr)-1
# Calling the Function
print("The element ", key, " is found at index: ",
linear_search(arr, key, size), " of given array")
# Code Contributed By - DwaipayanBandyopadhyay
The element 4 is found at 4 index of the given array.
Complejidad temporal: O(n)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Ver también – Búsqueda binaria
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA