Dado un archivo, ahora nuestra tarea es leer líneas desde el archivo hasta el final del archivo usando C#. Antes de leer las líneas de un archivo, debemos tener algunos datos, por lo que primero necesitamos un archivo vacío en nuestra ruta y luego insertamos líneas en nuestro archivo y luego leemos las líneas de un archivo. Entonces para hacer esta tarea usamos dos operaciones básicas que son leer y escribir. El archivo se convierte en un flujo cuando abrimos el archivo para escritura y lectura, aquí el flujo significa una secuencia de bytes que se utiliza para la comunicación. Así que para nuestra tarea, usamos:
Ruta: para leer un archivo de cualquier fuente, necesitamos la ubicación/ruta. Una ruta es una string que incluye una ruta de archivo en un sistema.
@"c:\folder\file_name.txt"
Verificaremos si el archivo existe en la ruta o no usando el método File.Exists (ruta)
StreamWriter: StreamWriter se utiliza para escribir un flujo de datos/líneas en un archivo.
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(myfilepath)
StreamReader: StreamReader se utiliza para leer un flujo de datos/líneas de un archivo.
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(myfilepath)
Peek: se utiliza para leer los datos/líneas del archivo hasta el final del archivo.
StreamReaderObject.Peek()
Entonces, todos se colocan en el bloque try() para detectar las excepciones que ocurren.
Ejemplo: considere que la ruta y el archivo son:
C#
// C# program to read lines from a file
// until the end of file is reached
using System;
using System.IO;
class GFG{
public static void Main()
{
// File name is data
// File path is the following path
string myfilepath = @"c:\sravan\data.txt";
try
{
// Check if file exists or not
if (File.Exists(path))
{
File.Delete(path);
}
// Write data into file using StreamWriter through the path
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(myfilepath))
{
sw.WriteLine("hello");
sw.WriteLine("geeks for geeks");
sw.WriteLine("welcome to c#");
}
// Read the file present in the path
using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(myfilepath))
{
// Iterating the file
while (sr.Peek() >= 0)
{
// Read the data in the file until the peak
Console.WriteLine(sr.ReadLine());
}
}
}
// Caught the exception
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("The process failed: {0}", e.ToString());
}
Console.Read();
}
Salida :
hello geeks for geeks welcome to c#
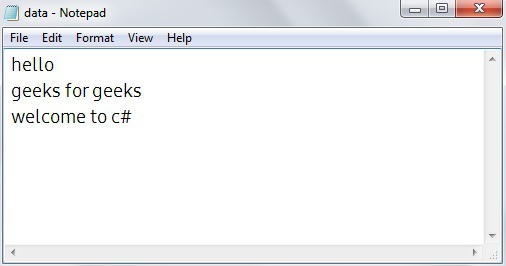
Ver los datos del archivo se inserta:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sravankumar8128 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA