Requisito previo: GUI de Python – tkinter
Tkinter es la biblioteca más utilizada para desarrollar GUI (interfaz gráfica de usuario) en Python. Es una interfaz estándar de Python para el kit de herramientas Tk GUI que se envía con Python. Como Tk y Tkinter están disponibles en la mayoría de las plataformas Unix, así como en el sistema Windows, el desarrollo de aplicaciones GUI con Tkinter se convierte en el más rápido y sencillo.
En este artículo, vamos a discutir cómo crear una calculadora de proporción utilizando el módulo Tkinter .
¿Qué es la Calculadora de Razones?
Es la calculadora que calcula la base del denominador en los valores de relación dados.
Explicación:
Input: a = 10 b = 20 c = 30 d = ? a : d = c : d Output: value of d is 60.0
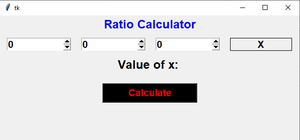
A continuación se muestra cómo se verá la calculadora:
Fórmula utilizada:
a/b = c/d
Aquí a y b se les da una relación y c es un valor ingresado para el cual tenemos que encontrar la relación, es decir, el denominador d .
Enfoque paso a paso:
- Crear ventana normal de Tkinter
Python3
# Import module
from tkinter import *
# Create object
root = Tk()
# Adjust size
root.geometry("400x400")
# Execute tkinter
root.mainloop()
Producción:
- Cree un marco usando el método Frame() y agregue tres cuadros de giro usando el método Spinbox() .
Sintaxis:
# Create Frame frame = Frame(Object Name) # Create Spin Box # Enter Range Spinbox(frame, from_= 0, to = 10,**attr)
- Cree otro marco, agregue Button, Label y cree una función llamada ratio_calculator , que calculará el valor de X .
Sintaxis:
# Create Frame frame1 = Frame(Object Name) # Create Label Label(frame1, text="Enter Text",**attr) # Create Button Button(root,text="Enter Text",**attr)
A continuación se muestra la implementación:
Python3
# Import Module
from tkinter import *
# Create Object
root = Tk()
# Set height and width
width = 600
height = 250
# Set Geometry and min, max size
root.geometry(f"{width}x{height}")
root.maxsize(width, height)
root.minsize(width, height)
# Create Label
Label(root, text="Ratio Calculator", font=(
"Helvetica", 18, "bold"), fg="blue").pack()
# Function will calculate the value of x
def ratio_calculator():
# Get the value of spinbox using get() method
s11 = int(s1.get())
s22 = int(s2.get())
s33 = int(s3.get())
# Formula Used
value = (s33*s22)/s11
# change the text of label using config method
value_of_x.config(text=value)
# Create Frame
frame = Frame(root)
frame.pack()
# Create Spin Boxes
s1 = Spinbox(frame, from_=0, to=10000000, width=10,
font=("Helvetica", 14, "bold"))
s1.pack(side=LEFT, padx=10, pady=10)
s2 = Spinbox(frame, from_=0, to=10000000, width=10,
font=("Helvetica", 14, "bold"))
s2.pack(side=LEFT, padx=10, pady=10)
s3 = Spinbox(frame, from_=0, to=10000000, width=10,
font=("Helvetica", 14, "bold"))
s3.pack(side=LEFT, padx=10, pady=10)
# Add Another Label
Label(frame, text="X", width=10, font=("Helvetica",
14, "bold"),
borderwidth=1, relief="solid").pack(side=LEFT,
padx=10,
pady=10)
# Add Another Frame
frame1 = Frame(root)
frame1.pack()
x_value = Label(frame1, text="Value of x:",
font=("Helvetica", 18, "bold"))
x_value.pack(side=LEFT)
value_of_x = Label(frame1, text="",
font=("Helvetica", 18, "bold"))
value_of_x.pack(side=LEFT)
# Create Button
Button(root, text="Calculate", borderwidth=2, width=15,
font=("Helvetica", 14, "bold"),
command=ratio_calculator, fg="red",
bg="black").pack(pady=20)
# Execute Tkinter
root.mainloop()
Producción: